【题解】2024 UESTC 暑假集训 第二轮
收录了二轮集训的部分题解。
先抛点链接,方便日后跳转。
7.31 https://codeforces.com/gym/537696(2024 HDU 多校 6)
8.1 https://codeforces.com/gym/539789(SEERC 2020)
8.2 https://codeforces.com/gym/540037(2023 江苏省赛/ CCPC Hunan)
8.3 https://codeforces.com/gym/540187(2020 CCPC Weihai)
8.4 https://codeforces.com/gym/105173(2024 东北四省赛 / CCPC Northeast)
8.5 https://codeforces.com/gym/540735(2023 Nanjing Regional / Ucup 2-11)
8.6 https://codeforces.com/gym/541036(UKIEPC 2023)
8.7 https://codeforces.com/gym/541235(NEERC 2019-2020)
8.8 https://codeforces.com/gym/541365(2024 上海市赛)
8.9 https://codeforces.com/gym/541786(2024 陕西省赛)
8.10 https://codeforces.com/gym/541891(2024 吉林省赛 / CCPC Changchun)
8.11 https://codeforces.com/gym/104976(2023 Hangzhou Regional / Ucup 2-22)
8.12 https://codeforces.com/gym/542320(毒瘤 psk / 998244353)
8.13 https://codeforces.com/gym/541594(SEERC 2022)
8.14 https://codeforces.com/gym/542837(ECNA 2022)
8.15 https://codeforces.com/gym/543029(2022 CCPC Weihai)
8.16 https://codeforces.com/gym/543323(NWERC 2019)
8.17 https://codeforces.com/gym/543433(2020 CCPC Changchun)
8.18 被赶出清水河
8.22 https://codeforces.com/gym/105231(2024 江西省赛)
8.23 https://codeforces.com/gym/102822(2020 CCPC Mianyang)
8.24 https://codeforces.com/gym/102769(2020 CCPC Qinhuangdao)
8.25 https://codeforces.com/gym/104252(2022-2023 Latin American Regional)
8.26 https://codeforces.com/gym/103081(SWERC 2020)
8.27 晓山瑞希生日
8.28 https://codeforces.com/gym/104064(NWERC 2021)
8.29 https://codeforces.com/gym/104787(2023 CCPC Qinhuangdao / Ucup 2-9)
8.30 https://codeforces.com/gym/104945(SWERC 2023)
2024 HDU 多校 第6场
B. 造花(困难版)【分类讨论】
给定一张无重边无自环不保证联通的无向图,若删去某个点后整个图被分为若干菊花图,则称这个点为混沌点。升序输出所有混沌点编号,或报告不存在。
\(1 \le n, m \le 2\cdot 10^6\)。
首先可以暴力 check(通过度数判断)这张图的每个连通分量是不是菊花图。若有两个及以上的连通分量不是菊花图,则无解;否则我们只考虑不是菊花图的那个连通分量。
分两种情况考虑:
- 这个连通分量是一棵树。通过以下步骤可以 \(O(n)\) check 每个点是不是混沌点:
- 对于每个点 \(x\),新建变量
sum = 0,遍历 \(x\) 的邻接点 \(y\)。若 \(y\) 的度数为 \(2\),则继续遍历 \(y\) 的邻接点 \(z\)(\(z \neq x\)),sum += deg[z] + 1;否则sum += deg[y]。若删去 \(x\) 该树被分为两个菊花图,那么此时度数统计完全,应有sum == n - 1。这里 \(n\) 是连通分量的大小。
- 对于每个点 \(x\),新建变量
- 这个联通分量不是树(有环)。此时有两个性质可以手玩出来:
- 若存在混沌点,该连通分量所有环的大小最多是四元环。
- 若有多个环,混沌点只能是所有环的交集。
由结论 \(2\),我们只需要随便从这个连通分量中找一个环,此时所有可能的混沌点都在这个环上。又由结论 \(1\),可以暴力 check 这些可能的混沌点,最多 check 不超过 \(4\) 次。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
vector<int> ori_rd(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
ori_rd[x]++;
ori_rd[y]++;
}
vector<int> cir(n + 1), fa(n + 1), vis(n + 1);
vector<int> need_to_check;
int cnt_circle = 0;
auto find_circle = [&] (auto self, int x, int fath) -> void {
cir[x] = true;
fa[x] = fath;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fath) {
continue;
}
if (cir[y]) {
fa[y] = x;
if (cnt_circle == 0) {
cnt_circle = 1;
need_to_check.push_back(y);
for (int i = fa[y]; i != y; i = fa[i]) {
cnt_circle++;
need_to_check.push_back(i);
}
}
}
if (vis[y]) {
continue;
}
vis[y] = true;
self(self, y, x);
}
cir[x] = false;
};
auto ok = [&] (int rt, int A = 0) {
vector<int> rd = ori_rd;
vector<int> vis(n + 1);
if (A == 0) {
for (auto x : adj[rt]) {
rd[x]--;
}
rd[rt] = 0;
vis[rt] = 1;
}
int rdn;
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x) -> void {
vis[x] = true;
rdn += rd[x] > 1;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (vis[y]) {
continue;
}
self(self, y);
}
};
bool flag = true;
for (auto x : adj[rt]) {
if (!vis[x]) {
rdn = 0;
dfs(dfs, x);
if (rdn > 1) {
flag = false;
break;
}
}
}
return flag;
};
int block = 0, block_id = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis[i]) {
if (!ok(i, 1)) {
block++;
block_id = i;
}
cnt_circle = 0;
find_circle(find_circle, i, 0);
if (cnt_circle > 4) {
cout << "-1\n";
return ;
}
}
}
if (block >= 2) {
cout << "-1\n";
return ;
}
vector<int> ans;
if (need_to_check.empty()) {
vector<int> vis(n + 1);
auto check_tree = [&] (int A) {
vector<int> b;
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int fath) -> void {
b.push_back(x);
vis[x] = true;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fath) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
}
};
dfs(dfs, A, 0);
for (auto x : b) {
int res = 0;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (ori_rd[y] == 2) {
for (auto o : adj[y]) {
if (o == x) {
continue;
}
res += ori_rd[o] + 1;
}
} else {
res += ori_rd[y];
}
}
if (res == b.size() - 1) {
ans.push_back(x);
}
}
};
if (block_id == -1) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis[i]) {
check_tree(i);
}
}
} else {
check_tree(block_id);
}
} else {
for (auto x : need_to_check) {
if (ok(x)) {
ans.push_back(x);
}
}
}
if (ans.empty()) {
cout << "-1\n";
return ;
}
sort(ans.begin(), ans.end());
for (auto x : ans) {
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}G. 树上 MEX 问题【dp】
定义一张图的 MEX 为:图中所有点的点权构成的集合中,最小的没有出现过的非负整数。
给定一棵 \(n\) 个点的树,点有点权 \(a_i\),保证点权互不相同。求这棵树的所有联通导出子图的 MEX 之和,对 998244353 取模。
\(1 \le n \le 10 ^6\),\(0 \le a_i < n\)。
设 \(T_i\) 为由点权为 \(0\sim i\) 的点构成的极小联通子图,\(cnt_i\) 为包含 \(T_i\) 的联通子图个数。
则有结论:\(ans = \sum_\limits{i = 0}^{n - 1}cnt_i\)。
- 证明:子图 \(T_i\) 的 mex 为 \(i + 1\),且 \(T_i\) 一定包含 \(T_0\sim T_{i - 1}\),故 mex 恰好为 \(i + 1\) 的联通子图个数为 \(cnt_i - cnt_{i + 1}\),有: \[ \large \begin{align} ans &=\sum_{i = 0}^{n - 1}(i + 1)(cnt_i-cnt_{i + 1})\\ &=(cnt_{0}-cnt_{1})+2(cnt_1 - cnt_2)+3(cnt_2-cnt_3)+\cdots \\ &=\sum_{i = 0}^{n - 1}cnt_i \end{align} \]
于是仅需求出 \(cnt_i\)。
接下来考虑如何对连通子图进行计数。
令 \(f_i\) 代表节点 \(i\) 可选可不选时以 \(i\) 为根的子树中以 \(i\) 为根的联通子图个数;
令 \(g_i\) 代表限定节点 \(i\) 必须选时以 \(i\) 为根的子树中以 \(i\) 为根的联通子图个数,则: \[ \large \begin{cases} g_x = \prod_{y\in son_x}f_y\\ f_x = g_x + 1 \end{cases} \] 显然 \(cnt_0=g_0\)。
再考虑如何从 \(cnt_{i - 1}\) 转移到 \(cnt_i\)。发现每次由 \(T_{i - 1}\) 变为 \(T_i\) 时,原来必选的点现在仍然必选,同时多出来了一些必选的点,称为目标点集。不难发现目标点集构成一条链,即点权为 \(0\sim {i}\) 的路径上 \(T_{i - 1}\) 中的非必选点。
我们用一个 vis 数组标记已经访问过的点,遍历到 \(i\) 时,若
!vis[i],就一直跳父亲(以点权为 \(0\) 的点为根),直到 vis 为
\(1\)。途径的点即目标点集。
每次新增一个必选点 \(x\) 时,有 \(cnt \leftarrow cnt \times \dfrac{g_x}{f_x}\),对目标点集中的每个点更新即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(n\log m)\),\(m\) 为模数。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
constexpr int modp = 998244353;
int qpow(int k, int n) {
int s = 1;
for ( ; n; n >>= 1, k = k * k % modp) {
if (n & 1) s = s * k % modp;
}
return s;
}
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1), id(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
id[a[i]] = i;
}
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
vector<int> dp(n + 1, 1), fa(n + 1);
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int fath) -> void {
fa[x] = fath;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fath) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
dp[x] *= (1 + dp[y]);
dp[x] %= modp;
}
};
int rt = id[0];
dfs(dfs, rt, 0);
vector<int> vis(n + 1);
vis[rt] = 1;
int ans = dp[rt], cur = ans;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int u = id[i];
if (!vis[u]) {
vector<int> b;
while (!vis[u]) {
b.push_back(u);
u = fa[u];
}
for (auto x : b) {
vis[x] = true;
cur *= dp[x] * qpow(1 + dp[x], modp - 2) % modp;
cur %= modp;
}
}
ans += cur;
ans %= modp;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}K. 天天爱跑步【基环树,单调队列,线段树】
给定一棵 \(n\) 个点的基环树。对 \(i\in[1, n]\) 求经过第 \(i\) 个点的最长简单路径长度。
\(1 \le n \le 5\cdot 10^5\)。
基环树的结构可概括为:一个环,然后环上的每个点向下延伸出子树。
以下是一些约定:
令 \(h_i\) 代表点 \(i\) 属于环上哪个点的子树。
令 \(dep_i\) 代表点 \(i\) 在子树内的深度。(\(h_i\) 深度为 \(1\))
令 \(a_i\) 代表环上的点 \(i\) 向下延伸出的最长链长度。
令 \(len_i\) 代表经过点 \(i\) 且仅在 \(h_i\) 子树内的最长链长度。
令 \(f_{i, 0/1}\) 代表点 \(i\) 向子树内延伸出的最长链/次长链长度。
令 \(g_{i, 0/1}\) 代表点 \(i\) 向子树内延伸出的最长链/次长链对应的子节点。
令 \(\text{ano}\text{side}_i\) 代表环上的点 \(i\) 向该点子树外延伸出的最长链长度。(包括环上的一段以及环上另一点向其子树延伸出的最长链)
根据点 \(i\) 在基环树中的位置可以分为两种情况:点 \(i\) 在环上和点 \(i\) 在子树中。
点 \(i\) 在环上时,我们要找的是 \(\max(a_i+\text{anoside}_i)=\max(a_i+a_j+i-j)\)。破环成链,则 \(i-j\) 代表环上的一段满足 \(i-j<m\) 的 \([j, i]\)。
首先,我们可以用单调队列求出这个最大值。具体地,按顺序遍历环,每次往双端队列中压入 \(i\),弹出队首不满足 \(i-j< m\) 的 \(j\),弹出队尾不满足 \(a_j-j\ge a_i-i\) 的 \(j\)。
求出最大值后,我们可以用线段树维护对应区间 \([j,i]\) 上的答案,每次用最大值与这个区间的值取 \(\max\)。
注意,对环上的两个方向都要分别跑单调队列,同样更新答案。
点 \(i\) 在子树中时,答案为: \[ \large \max(len_i,f_{i, 0}+dep_i-1+\text{anoside}_{h_i}) \] 前者为不经过环上的点的答案,后者为经过环上的点的答案。
对于一个子树,\(f_{i,0/1}\) 可以一次 dfs 求出,同时处理出 \(g_{i,0/1}\) 用于换根,求出 \(len_i\)。
具体地,换根时令 \(d_i\) 代表 \(i\) 所在的子树外不经过环的最长链,有: \[ \large d_x=\max\begin{cases} d_{fa}+1\\ f_{fa,0}+1 &,g_{fa,0}\neq x\\ f_{fa,1}+1 &,g_{fa,0}=x \end{cases} \] \[ \large len_x=f_{x,0}+\max(f_{x,1},d_x) \]
时间复杂度:\(O(n\log n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
struct Sgt{
int n;
vector<int> tr;
#define ls p << 1
#define rs p << 1 | 1
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
Sgt(int n) {
this->n = n;
tr.assign(4 * n + 5, 0);
}
void update(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, int x) {
if (ql <= l && qr >= r) {
tr[p] = max(tr[p], x);
return ;
}
if (ql <= mid) {
update(ls, l, mid, ql, qr, x);
}
if (qr > mid) {
update(rs, mid + 1, r, ql, qr, x);
}
}
void update(int l, int r, int x) {
l++; r++;
update(1, 1, n, l, r, x);
}
int query(int p, int l, int r, int pos) {
if (l == r) {
return tr[p];
}
if (pos <= mid) {
return max(tr[p], query(ls, l, mid, pos));
} else {
return max(tr[p], query(rs, mid + 1, r, pos));
}
}
int query(int pos) {
pos++;
return query(1, 1, n, pos);
}
};
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
vector<int> deg(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
deg[x]++;
deg[y]++;
}
auto find_cir = [&] () {
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (deg[i] == 1) {
q.push(i);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (--deg[y] == 1) {
q.push(y);
}
}
}
vector<int> o;
auto get_cir = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa, int rt) -> void {
o.push_back(x);
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa || y == rt || deg[y] <= 1) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x, rt);
return ;
}
};
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (deg[i] > 1) {
get_cir(get_cir, i, 0, i);
break;
}
}
return o;
};
vector cir = find_cir();
vector<int> h(n + 1), dep(n + 1);
vector<array<int, 2>> f(n + 1), g(n + 1);
auto dfs1 = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa, int rt) -> void {
h[x] = rt;
dep[x] = dep[fa] + 1;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa || deg[y] > 1) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x, rt);
if (f[y][0] + 1 > f[x][0]) {
f[x][0] = f[y][0] + 1;
g[x][0] = y;
}
}
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa || deg[y] > 1 || y == g[x][0]) {
continue;
}
if (f[y][0] + 1 > f[x][1]) {
f[x][1] = f[y][0] + 1;
g[x][1] = y;
}
}
};
vector<int> d(n + 1), len(n + 1);
auto dfs2 = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
if (fa) {
d[x] = d[fa] + 1;
if (g[fa][0] != x) {
d[x] = max(d[x], f[fa][0] + 1);
} else {
d[x] = max(d[x], f[fa][1] + 1);
}
}
len[x] = max(f[x][0] + f[x][1], f[x][0] + d[x]);
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa || deg[y] > 1) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
}
};
for (auto x : cir) {
dfs1(dfs1, x, 0, x);
dfs2(dfs2, x, 0);
}
int m = cir.size();
cir.insert(cir.end(), cir.begin(), cir.end());
vector<int> a(2 * m);
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * m; i++) {
a[i] = f[cir[i]][0];
}
Sgt seg(2 * m);
vector<int> ano_side(n + 1), ans(n + 1);
deque<int> q;
q.push_back(0);
for (int i = 1; i < 2 * m; i++) {
while (!q.empty() && i - q.front() + 1 > m) {
q.pop_front();
}
int j = q.front();
seg.update(j, i, a[i] + a[j] + i - j);
ano_side[cir[i]] = max(ano_side[cir[i]], a[j] + i - j);
while (!q.empty() && a[q.back()] - q.back() < a[i] - i) {
q.pop_back();
}
q.push_back(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * m; i++) {
ans[cir[i]] = max(ans[cir[i]], seg.query(i));
}
reverse(cir.begin(), cir.end());
reverse(a.begin(), a.end());
q.clear();
q.push_back(0);
for (int i = 1; i < 2 * m; i++) {
while (!q.empty() && i - q.front() + 1 > m) {
q.pop_front();
}
int j = q.front();
seg.update(2 * m - 1 - i, 2 * m - 1 - j, a[i] + a[j] + i - j);
ano_side[cir[i]] = max(ano_side[cir[i]], a[j] + i - j);
while (!q.empty() && a[q.back()] - q.back() < a[i] - i) {
q.pop_back();
}
q.push_back(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2 * m; i++) {
ans[cir[i]] = max(ans[cir[i]], seg.query(2 * m - 1 - i));
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ans[i] = max({ans[i], len[i], f[i][0] + dep[i] - 1 + ano_side[h[i]]});
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << ans[i] << " \n"[i == n];
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}SEERC 2020
B. Reverse Game【博弈,逆序对】
给定一个 \(01\) 串 \(s\),\(\text{Alice}\) 和 \(\text{Bob}\) 进行回合制博弈。轮到一个人时,该名玩家可以从 \(s\) 中任选一个恰为 \(10,110,100\) 或 \(1010\) 的子串,并将其翻转。无法进行操作的玩家输,问先手是否有必胜策略。
\(1 \le |s| \le 10^6\)。
很考验 Insight 的题。
注意到 \(s\) 的最后形态必然为 \(0\cdots01\cdots1\)(因为有 \(10\) 就可以翻转),特点是逆序对为 \(0\)。
而每次翻转操作可以将 \(s\) 的逆序对数减少 \(1\) 或 \(2\),并且手玩发现若 \(s\) 的逆序对数 \(\ge 2\),则子串中一定有 \(110,100,1010\) 中的一种。
根据必胜必败态定理,后手总存在策略使得一个轮次中 \(s\) 的逆序对数减少 \(3\)(即先手减 \(1\) 后手减 \(2\),先手减 \(2\) 后手减 \(1\))。
因此当 \(s\) 的逆序对数 \(\bmod 3 = 0\) 时,后手必胜;否则先手必胜。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
string s;
cin >> s;
int tot0 = 0, res = 0;
for (int i = s.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (s[i] == '0') {
tot0++;
} else {
res += tot0;
}
}
if (res % 3) {
cout << "Alice\n";
} else {
cout << "Bob\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}A. Archeologists【反悔贪心】
你在玩一个寻宝类游戏,一共有 \(n\) 个格子,编号为 \(1 \sim n\)。你每在第 \(i\) 号格子上下挖一层便会获得 \(a_i\) 的价值,你需要保证每个格子与其相邻格子的下挖深度不超过 \(1\)(注意此时 \(1\) 和 \(n\) 号点最多只能挖一层),求最大价值。
\(1 \le n \le 2.5\cdot 10^5\),\(-10^6 \le a_i \le 10^6\)。
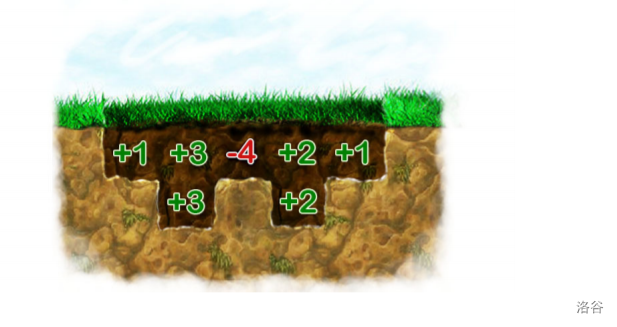
有一类用反悔贪心解决的经典问题:有一样物品,第 \(i\) 天价值为 \(v_i\),每一天你可以买入一件或卖出一件,问最大收益。
解决步骤是维护一个小根堆,然后遍历 \(v_i\),若 \(v_i\) 比堆顶 \(v_u\) 大,则收益加上 \(v_i - v_u\),弹出堆顶,并再向堆中塞入一个 \(v_i\)。这样下次再卖出时(假设为第 \(j\) 天),若定位到为第 \(i\) 天买入,就赚了 \(v_j - v_i\),加上之前赚的 \(v_i-v_u\),一共赚了 \(v_j-v_u\),等价于在第 \(u\) 天买入第 \(j\) 天卖出。以此涵盖了在任意天买入和卖出的情况。
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!q.empty() && q.top() < a[i]) {
ans += a[i] - q.top();
q.pop();
q.push(a[i]);
}
q.push(a[i]);
}
cout << ans << "\n";对于本题,令 \(b_i\) 为第 \(i\) 个格子的下挖深度,由于相邻项相差不超过 \(1\),因此其差分数组的每一项只可能是 \(-1, 0, 1\)。
将 \(1\) 看成一次买入,\(-1\) 看成一次卖出,就与经典题等价了。
将题给的 \(a_i\) 求前缀和作为物品的价值,跑反悔贪心即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(n \log n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1), sum(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + a[i];
}
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (!q.empty() && q.top() < sum[i]) {
ans += sum[i] - q.top();
q.pop();
q.push(sum[i]);
}
q.push(sum[i]);
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}H. AND = OR【线段树,位运算】
对于一个序列 \(\{b\}\),若可以将 \(\{b\}\) 划分为两个非空的子序列,满足其中一个子序列中所有元素的 \(\text{And}\) 与另一个子序列中所有元素的 \(\text{OR}\) 相等,则称 \(\{b\}\) 是 good 的。
给定一个长为 \(n\) 的数组 \(\{a\}\),以及 \(q\) 次询问。每次询问 \(\{a\}\) 的一个区间 \([l, r]\) 是否 good。
\(1 \le n,q \le 10^5\),\(0\le a_i < 2^{30}\)。
先考虑单个询问。设 \([l,r]\) 中的数被划分成 \(A,B\) 两个集合,\(A\) 集合的 \(\text{OR}\) 和 \(B\) 集合的 \(\text{And}\) 相等,均为 \(X\)。
那么宏观上有:\(A\) 中的所有数 \(\le X\),\(B\) 中的所有数 \(\ge X\)。因此把 \([l,r]\) 内的所有数升序排序,\(A\) 中的数一定是一段前缀,\(B\) 中的数一定是一段后缀,枚举分段点即可。
还能按位来看:设 \(p(x)=\text{popcount}(x)\),\(p(X)=k\),那么 \(\forall x\in A,p(x)\le k\),\(\forall x \in B,p(x)\ge k\)。
此时可以枚举分段点 \(g\),两种情况:
\[ \Large \begin{cases} \text{And}_{x\in[l, r],p(x)\le g} = \text{Or}_{x\in[l,r],p(x)>g} &, g\in [0,30)\\ \text{And}_{x\in[l, r],p(x)\le g}= \text{Or}_{x \in[l,r], p(x)\ge g} &, g \in[0,30] \end{cases} \]
对于第二种情况,可以证明若能划分,那么满足 \(p(x)=g\) 的所有 \(x\) 必须相等。\((\alpha)\)
- 证明:假设存在 \(a,b\) 满足 \(p(a)=g,p(b)=g\),且 \(a\) 被划分进 \(A\),\(b\) 被划分进 \(B\)。那么:
\[ \Large \begin{cases} a \text{ | }X=X \\ b \text{ \& } X = X \end{cases}\to a \text{ \& } b = b \xrightarrow{p(a)=p(b)} a= b \]
至此,我们可以用 \(30\) 个线段树或 \(30\) 个 st 表维护二进制下每一位 \(\{a\}\) 的区间按位或和区间按位与。对于一个询问 \([l,r]\),查询这个区间每一位的 \(\text{Or}\) 值(\(\text{Or}[g]\))和 \(\text{And}\) 值(\(\text{And}[g]\)),并对前者做前缀和,后者做后缀和(即 \(\text{SOr}[g]\) 代表区间内满足 \(p(x)\in[0,g]\) 的所有 \(x\) 的 \(\text{Or}\) 值,\(\text{SAnd}[g]\) 代表区间内满足 \(p(x)\in[g,30]\) 的所有 \(x\) 的 \(\text{And}\) 值),对上文两种情况分别 \(\text{check}\) 即可。
此外还要注意 \(\text{check}\) 两个集合必须非空,可以对每一位额外维护一个前缀和相同处理。
而 \((\alpha)\) 条件等价于判断 \(\text{Or}[g]=\text{And}[g]\),不用额外处理。
最开始写的 st 表没卡过,换了线段树过的。时间复杂度 \(O(30n+30q\log n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
struct SegmentTree {
int n;
vector<int> And, Or;
SegmentTree(int size) {
n = size;
And.resize(4 * n + 5, 0);
Or.resize(4 * n + 5, 0);
}
#define mid ((l + r) >> 1)
#define ls (p << 1)
#define rs (p << 1 | 1)
inline void pushup(int p) {
And[p] = And[ls] & And[rs];
Or[p] = Or[ls] | Or[rs];
}
void in_build(int p, int l, int r, vector<int> &nums, vector<int> &po, int k) {
if (l == r) {
if (po[l] == k) {
And[p] = Or[p] = nums[l];
} else {
And[p] = (1 << 30) - 1;
Or[p] = 0;
}
return ;
}
in_build(ls, l, mid, nums, po, k);
in_build(rs, mid + 1, r, nums, po, k);
pushup(p);
}
int range_query_And(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr) {
if (ql <= l && qr >= r) {
return And[p];
}
int res = (1 << 30) - 1;
if (ql <= mid) {
res &= range_query_And(ls, l, mid, ql, qr);
}
if (qr > mid) {
res &= range_query_And(rs, mid + 1, r, ql, qr);
}
return res;
}
int range_query_Or(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr) {
if (ql <= l && qr >= r) {
return Or[p];
}
int res = 0;
if (ql <= mid) {
res |= range_query_Or(ls, l, mid, ql, qr);
}
if (qr > mid) {
res |= range_query_Or(rs, mid + 1, r, ql, qr);
}
return res;
}
void build(vector<int> &nums, vector<int> &po, int k) {
in_build(1, 1, n, nums, po, k);
}
int query_And(int ql, int qr) {
return range_query_And(1, 1, n, ql, qr);
}
int query_Or(int ql, int qr) {
return range_query_Or(1, 1, n, ql, qr);
}
};
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, q;
cin >> n >> q;
vector<int> a(n + 1), p(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
p[i] = __builtin_popcount(a[i]);
}
vector st_Sum(31, vector<int>(n + 1));
for (int k = 0; k <= 30; k++) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
st_Sum[k][i] = st_Sum[k][i - 1] + (p[i] == k ? 1 : 0);
}
}
vector<SegmentTree> seg(31, SegmentTree(n));
for (int i = 0; i <= 30; i++) {
seg[i].build(a, p, i);
}
vector<int> Sum(31), And(31), Or(31);
vector<int> preSum(32), preOr(32), sufAnd(32);
while (q--) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
for (int i = 0; i <= 30; i++) {
Sum[i] = st_Sum[i][r] - st_Sum[i][l - 1];
And[i] = seg[i].query_And(l, r);
Or[i] = seg[i].query_Or(l, r);
}
preSum[0] = Sum[0];
preOr[0] = Or[0];
sufAnd[31] = (1 << 30) - 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++) {
preSum[i] = preSum[i - 1] + Sum[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++) {
preOr[i] = preOr[i - 1] | Or[i];
}
for (int i = 30; i >= 0; i--) {
sufAnd[i] = sufAnd[i + 1] & And[i];
}
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
if (preOr[i] == sufAnd[i + 1] && preSum[i] && preSum[i] < preSum[30]) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if (!flag) {
for (int i = 0; i <= 30; i++) {
if (preOr[i] == sufAnd[i] && Or[i] == And[i] && Sum[i] > 1) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
cout << (flag ? "YES\n" : "NO\n");
}
}
int main() {
freopen("test.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("test.out", "w", stdout);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
solve();
return 0;
}2023 江苏省赛/ CCPC Hunan
B. Honkai in TAIKULA【拆点,缩点,全源最短路】
给定一张 \(n\) 个节点 \(m\) 条边的有向带权图,对每个节点,报告是否存在经过该点的奇权圈(可经过重复顶点、重复边、若经过重复边,边权计多次)。若存在,输出最小奇权圈的权值(或报告为负无穷)。
\(1\le n \le 1000\),\(1 \le m \le 10^4\),\(0\le x_i,y_i < n\),\(|w_i| \le 10^7\)。
处理带权图的边权奇偶性问题常用缩点:把一个点 \(x\) 拆成一个奇点 \(\text{Odd}_x\)、一个偶点 \(\text{Even}_x\)。
- 若存在 \(x\xrightarrow{w} y\),\(w\) 为奇数。则连 \(\text{Odd}_x \to \text{Even}_y\),\(\text{Even}_x \to \text{Odd}_y\)。
- 若存在 \(x \xrightarrow{w} y\),\(w\) 为偶数。则连 \(\text{Odd}_x\to \text{Odd}_y\),\(\text{Even}_x\to \text{Even}_y\)。
若存在一个经过点 \(x\) 的奇权圈,等价于存在一条 \(\text{Odd}_x \to \text{Even}_x\) 的路径。(或 \(\text{Even}_x \to \text{Odd}_x\),钦定一种即可)
接着,由于环只存在于单个强连通分量内,所以考虑缩点得到一张有向无环图 \(G\)。
注意到只要存在一条路径从 \(x\) 出发,经过负环,再回到 \(x\)。那么最小奇权圈的权值就是负无穷,因为可以再负环上无限绕再返回 \(x\)。所以对 \(G\) 中每个点代表的子图都跑 SPFA 算法判断负环。
设 \(\text{Odd}_x\) 和 \(\text{Even}_x\) 所在的 SCC 编号分别为 \(A\) 和 \(B\)。利用 dfs 判断 \(G\) 中是否存在 \(A\to B\) 的路径,路径上又是否有标记为负环的点即可完成无解和负无穷解的判断。
接下来是有解的情况。在未缩点的原图上跑 Johnson 全源最短路即可,注意避开 “位于被标记负环的 SCC 中” 的所有点。
时间复杂度 \(O(nm\log m)\)。
Funfact:有人拓扑图上 dfs 不用标记数组标记走过的点,狂 T 两小时QAQ。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
#define _node vector<vector<array<int, 2>>>
struct Johnson {
int n;
_node adj;
vector<int> h, dis, A;
Johnson(_node Adj, vector<int> &B) {
adj = Adj;
A = B;
this->n = Adj.size() - 1;
init();
}
void init() {
h.resize(n + 1);
dis.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
adj[0].push_back({i, 0});
}
}
bool spfa(int s) {
vector<int> vis(n + 1), circle(n + 1);
h.assign(n + 1, inf);
queue<int> q;
vis[s] = true;
h[s] = 0;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
vis[x] = false;
for(auto [y, w] : adj[x]) {
if (!A[y]) {
continue;
}
if(h[y] > h[x] + w) {
h[y] = h[x] + w;
if(!vis[y]) {
if(++circle[y] >= n + 1) {
return false;
}
vis[y] = true;
q.push(y);
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
void dijkstra(int s) {
priority_queue<array<int, 2>> q;
dis.assign(n + 1, inf);
vector<int> vis(n + 1);
dis[s] = 0;
q.push({0, s});
while(!q.empty()) {
int x = q.top()[1];
q.pop();
if(vis[x]) {
continue;
}
vis[x] = true;
for(auto [y, w] : adj[x]) {
if (!A[y]) {
continue;
}
if(dis[y] > dis[x] + w) {
dis[y] = dis[x] + w;
q.push({-dis[y], y});
}
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> work() {
vector ans(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, -inf));
if (!spfa(0)) {
return ans;
}
for (int x = 1; x <= n; x++) {
for (auto &[y, w] : adj[x]) {
w += h[x] - h[y];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
dijkstra(i);
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (dis[j] == inf) {
ans[i][j] = inf;
} else {
ans[i][j] = dis[j] + (h[j] - h[i]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<array<int, 2>>> adj(2 * n + 1);
vector<array<int, 3>> E;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x, y, w;
cin >> x >> y >> w;
x++; y++;
if (w % 2) {
adj[x].push_back({y + n, w});
adj[x + n].push_back({y, w});
E.push_back({x, y + n, w});
E.push_back({x + n, y, w});
} else {
adj[x].push_back({y, w});
adj[x + n].push_back({y + n, w});
E.push_back({x, y, w});
E.push_back({x + n, y + n, w});
}
}
vector<int> dfn(2 * n + 1), low(2 * n + 1), stack_(2 * n + 1), c(2 * n + 1);
vector<bool> VIS(2 * n + 1);
vector<vector<int>> scc(2 * n + 1);
int tim = 0, top = 0, cnt = 0;
function<void(int)> tarjan = [&](int x) {
dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim;
VIS[x] = true;
stack_[++top] = x;
for (auto [y, _] : adj[x]) {
if (!dfn[y]) {
tarjan(y);
low[x] = min(low[x], low[y]);
} else if (VIS[y]) {
low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[y]);
}
}
if (dfn[x] == low[x]) {
int now; ++cnt;
do {
now = stack_[top--];
VIS[now] = false;
c[now] = cnt;
scc[cnt].push_back(now);
} while(x != now);
}
};
vector<vector<int>> Adj(2 * n + 1);
auto shrinkPoint = [&]() {
for (int x = 1; x <= 2 * n; x++) {
for (auto [y, _] : adj[x]) {
if (c[x] == c[y]) continue;
Adj[c[x]].push_back(c[y]);
}
}
};
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++)
if (!dfn[i]) tarjan(i);
shrinkPoint();
vector<vector<array<int, 2>>> G(2 * n + 1);
vector<int> dis(2 * n + 2), num(2 * n + 2);
vector<bool> vis(2 * n + 2);
auto spfa = [&](int s) {
dis.assign(2 * n + 2, inf);
vis.assign(2 * n + 2, 0);
num.assign(2 * n + 2, 0);
dis[s] = 0;
vis[s] = true;
priority_queue<int> q;
q.push(s);
num[s]++;
int flag = 0;
while(!q.empty()) {
int x = q.top();
q.pop();
vis[x] = false;
for (auto [y, z] : G[x]) {
if(dis[y] > dis[x] + z) {
dis[y] = dis[x] + z;
if (!vis[y]) {
vis[y] = true;
q.push(y);
if (++num[y] > scc[c[s]].size()) {
return false;
}
}
}
}
}
return true;
};
vector<int> ans(2 * n + 1), have_circle(cnt + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
vector<int> exist(2 * n + 1);
for (auto rt : scc[i]) {
exist[rt] = 1;
}
G.clear();
for (auto [x, y, w] : E) {
if (exist[x] && exist[y]) {
G[x].push_back({y, w});
}
}
if (!spfa(scc[i][0])) {
have_circle[i] = true;
}
}
int T, success;
vector<int> vis2(cnt + 1);
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int flag) -> bool {
if (have_circle[x]) {
flag = 1;
}
if (x == T) {
if(flag) {
success = true;
}
return true;
}
for (auto y : Adj[x]) {
if (vis2[y]) {
continue;
}
vis2[y] = true;
if (self(self, y, flag)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
T = c[i + n];
success = 0;
int res = dfs(dfs, c[i], 0);
if (!res) {
ans[i] = -1;
} else if (success) {
ans[i] = inf;
}
}
vector<int> A(2 * n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
if (!have_circle[i]) {
for (auto x : scc[i]) {
A[x] = true;
}
}
}
Johnson H(adj, A);
vector diss = H.work();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (ans[i] == -1) {
cout << "Battle with the crazy Honkai\n";
} else if (ans[i] == inf) {
cout << "Haha, stupid Honkai\n";
} else {
cout << diss[i][i + n] << "\n";
}
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}L. Architect【思维,扫描线】
给定 \(n\) 个长方体,询问其是否能拼接成一个 \(W\times H\times L\) 的立方体,没有重叠和空隙,所有长方体都要用到。
\(1\le n \le 10^5\),\(1\le W, H, L \le 10^9\)。
一种绝世聪明的想法是 “只需判断 \(n\) 个立方体的体积和是否 \(=\) \(W\times H\times L\),且八个角的出现次数是否是偶数次即可”。
体积一样限定了这 \(n\) 个立方体不能有重叠。
八个角出现了偶数次限定了这 \(n\) 个立方体与大立方体间没有空隙。
注意 \(10^9\cdot 10^9\cdot
10^9=10^{27}\),需要开 __int128。
时间复杂度 \(O(8n\log n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int __int128
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
istream &operator>>(istream &is, __int128 &n) {
string s;
is >> s;
n = 0;
for (char c : s) {
n = n * 10 + (c - '0');
}
return is;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, __int128 n) {
if (n == 0) {
return os << 0;
}
string s;
while (n > 0) {
s += char('0' + n % 10);
n /= 10;
}
reverse(s.begin(), s.end());
return os << s;
}
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int W, H, L, n;
cin >> W >> H >> L >> n;
int All = W * H * L, all = 0;
map<array<int, 3>, int> mp;
auto ins = [&] (int x0, int y0, int z0, int x1, int y1, int z1) {
mp[{x0, y0, z0}]++;
mp[{x0, y0, z1}]++;
mp[{x0, y1, z0}]++;
mp[{x0, y1, z1}]++;
mp[{x1, y0, z0}]++;
mp[{x1, y0, z1}]++;
mp[{x1, y1, z0}]++;
mp[{x1, y1, z1}]++;
};
ins(0, 0, 0, W, H, L);
while (n--) {
int x0, y0, z0, x1, y1, z1;
cin >> x0 >> y0 >> z0 >> x1 >> y1 >> z1;
all += (x1 - x0) * (y1 - y0) * (z1 - z0);
ins(x0, y0, z0, x1, y1, z1);
}
for (auto [_, x] : mp) {
if (x & 1) {
cout << "No\n";
return ;
}
}
cout << (all == All ? "Yes\n" : "No\n");
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}另一种朴素但也颇具技巧性的方法是扫描线。
先将 \(n\) 个小立方体的底面看作 \(1\),顶面看作 \(-1\);大立方体的底面看作 \(-1\),顶面看作 \(1\)。
如果每个表面紧紧贴合,那么代数和为 \(0\)。
接着不断降维,同样的思想能判断线是否紧密贴合,点是否紧密贴合。
时间复杂度 \(O(n\log^2 n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
bool check2(vector<array<int, 3>> a) {
map<int, int> mp;
for (auto [x1, x2, flag] : a) {
mp[x1] += flag;
mp[x2] += -flag;
}
for (auto [_, v] : mp) {
if (v) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool check(vector<array<int, 5>> a) {
map<int, vector<array<int, 3>>> mp;
for (auto [x1, y1, x2, y2, flag] : a) {
mp[y1].push_back({x1, x2, flag});
mp[y2].push_back({x1, x2, -flag});
}
for (auto [_, v] : mp) {
if (!check2(v)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void solve() {
int W, H, L;
cin >> W >> H >> L;
map<int, vector<array<int, 5>>> mp;
mp[0].push_back({0, 0, W, H, -1});
mp[L].push_back({0, 0, W, H, 1});
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x1, y1, z1, x2, y2, z2;
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> z1 >> x2 >> y2 >> z2;
mp[z1].push_back({x1, y1, x2, y2, 1});
mp[z2].push_back({x1, y1, x2, y2, -1});
}
for (auto [_, v] : mp) {
if (!check(v)) {
cout << "No\n";
return ;
}
}
cout << "Yes\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}2020 CCPC Weihai
B. Labyrinth【bfs】
给定一个 \(n\times m\) 的网格图,有 \(k\) 个格子有障碍不能通行。\(q\) 次询问,每次询问两点间的最短路长度。
\(1\le n,m\le2\cdot 10^5\),\(1\le n\cdot m\le 2\cdot 10^5\),\(0\le k \le 42\),\(1\le q\le 10^5\)。
对于一组询问,假设询问的两个点是 \((x_1,y_1)\) 和 \((x_2, y_2)\)。
那么当 \((x_1,y_1)\) 和 \((x_2,y_2)\) 作为对角线的两个端点围成的矩形中没有一个障碍时,答案就是这两点间的曼哈顿距离;否则可以想象到最短路一定经过某个障碍周围四格中的某一格。
把所有障碍的四联通预处理出来并去重,以每个点为起点跑 bfs 求出其到所有格子的最短路。
询问时枚举一下这 \(O(4k)\) 个点作为中转点的最短路,取 \(\min\) 即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(knm)-O(k)\)。
#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast")
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define double long double
#define inf 0x7fffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, m, k, Q;
cin >> n >> m >> k >> Q;
vector bomb(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1));
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
bomb[x][y] = 1;
}
vector sum = bomb;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
sum[i][j] += sum[i - 1][j] + sum[i][j - 1] - sum[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
auto query = [&] (int sx, int sy, int fx, int fy) {
return sum[fx][fy] - sum[sx - 1][fy] - sum[fx][sy - 1] + sum[sx - 1][sy - 1];
};
int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int dy[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
vector<array<int, 2>> waiting;
vector VIS(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
if (bomb[i][j]) {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = i + dx[k];
int y = j + dy[k];
if (x < 1 || y < 1 || x > n || y > m || bomb[x][y] || VIS[x][y]) {
continue;
}
VIS[x][y] = true;
waiting.push_back({x, y});
}
}
}
}
int all = waiting.size();
vector dis(all, vector(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1, inf)));
for (int id = 0; id < all; id++) {
auto [sx, sy] = waiting[id];
queue<array<int, 3>> q;
q.push({sx, sy, 0});
vector vis(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1));
vis[sx][sy] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [x, y, lst_dis] = q.front();
dis[id][x][y] = lst_dis;
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int xx = x + dx[i];
int yy = y + dy[i];
if (xx < 1 || yy < 1 || xx > n || yy > m || bomb[xx][yy] || vis[xx][yy]) {
continue;
}
vis[xx][yy] = true;
int cur_dis = lst_dis + 1;
q.push({xx, yy, cur_dis});
}
}
}
auto check = [&] (int sx, int sy, int fx, int fy) {
};
while (Q--) {
int sx, sy, fx, fy;
cin >> sx >> sy >> fx >> fy;
if (bomb[sx][sy] || bomb[fx][fy]) {
cout << "-1\n";
continue;
}
if (sx == fx && sy == fy) {
cout << "0\n";
continue;
}
int lx = min(sx, fx);
int ly = min(sy, fy);
int rx = max(sx, fx);
int ry = max(sy, fy);
if (!query(lx, ly, rx, ry)) {
cout << abs(sx - fx) + abs(sy - fy) << "\n";
continue;
}
long long ans = inf;
for (int i = 0; i < all; i++) {
if (dis[i][sx][sy] == inf || dis[i][fx][fy] == inf) {
continue;
}
long long res = dis[i][sx][sy] + dis[i][fx][fy];
ans = min(ans, res);
}
if (ans == inf) {
ans = -1;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}C. Rencontre【结论,期望】
给定一棵 \(n\) 个点的树,边有边权 \(w_i\)。给定三个点集,从三个点集中分别随机选出 \(u_1,u_2,u_3\),问以下式子的期望: \[ f(u_1,u_2,u_3)=\min_{i\in[1,n]}(dis(u_1,i)+dis(u_2,i)+dis(u_3,i)) \] 其中 \(dis(x,y)\) 代表点 \(x,y\) 间的树上距离。
\(1\le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5\),\(1\le w \le 1000\)。
结论题。所给式子等价于: \[ f(u_1,u_2,u_3)=\frac{1}{2}(dis(u_1,u_2)+dis(u_2,u_3)+dis(u_1,u_3)) \] 根据期望的线性性,只需分别求出这三项每一项的期望再相加。
以 \(dis(u_1,u_2)\) 举例,考虑拆贡献:对于一条边 \(x\xleftrightarrow{w}y\),设 \(x\) 一侧有 \(A_x\) 个点属于点集一,\(B_x\) 个点属于点集二;\(y\) 一侧有 \(A_y\) 个点属于点集一,\(B_y\) 个点属于点集二。
那么该条边的贡献为 \(w\cdot \dfrac{A_x B_y+A_yB_x}{|A||B|}\),\(|A|\) 和 \(|B|\) 分别为点集一和点集二的大小。最终贡献就是所有边的贡献之和。
dfs 简单处理,时间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<vector<array<int, 2>>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x, y, w;
cin >> x >> y >> w;
adj[x].push_back({y, w});
adj[y].push_back({x, w});
}
vector<int> A, B, C;
int An, Bn, Cn;
cin >> An;
while (An--) {
int x;
cin >> x;
A.push_back(x);
}
cin >> Bn;
while (Bn--) {
int x;
cin >> x;
B.push_back(x);
}
cin >> Cn;
while (Cn--) {
int x;
cin >> x;
C.push_back(x);
}
auto calc = [&] (vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b) {
vector<int> isa(n + 1), isb(n + 1);
int asz = 0, bsz = 0;
for (auto x : a) {
isa[x] = true;
asz++;
}
for (auto x : b) {
isb[x] = true;
bsz++;
}
vector f = isa, g = isb;
auto dfs1 = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
for (auto [y, w] : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
f[x] += f[y];
g[x] += g[y];
}
};
dfs1(dfs1, 1, 0);
double res = 0;
auto dfs2 = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
for (auto [y, w] : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa) {
continue;
}
double t = 1.0 * f[y] * (bsz - g[y]);
t += 1.0 * g[y] * (asz - f[y]);
res += 1.0 * w * t;
self(self, y, x);
}
};
dfs2(dfs2, 1, 0);
res /= (asz * bsz);
return res;
};
double ans = 0;
ans += calc(A, B);
ans += calc(B, C);
ans += calc(A, C);
ans /= 2;
cout << fixed << setprecision(8) << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}G. Caesar Cipher【线段树维护哈希值】
维护一个序列 \(\{a\}\),支持两种操作:
1 l r:\(\forall i\in[l, r]\),\(a_i=(a_i+1)\bmod 65536\).2 x y L:询问区间 \([x,x+L-1]\) 和区间 \([y,y+L-1]\) 是否完全相同。
\(1\le n,q\le 5\cdot10^5\)。
经典题,线段树维护哈希值。
预处理出 pow[i] 代表 \(\text{base}^i\),pre[i] 代表
\(\sum_{j=0}^{i}\text{base}^j\)。
区间合并时,左区间的哈希值需要乘 pow[r - mid]
再加上右区间的哈希值。
区间修改时,相当于区间加 pre[r - l]。
区间查询时,合并答案需要左区间答案乘
pow[max(0, min(r, qr) - mid)] 再加上右区间答案。
这道题的创新点是操作一需要模一个数。
注意到值溢出(即 \(\ge 65536\))的次数不超过 \(\frac{nq}{65536}\approx 4\cdot10^6\) 次,可以维护区间最大值,每次定位到那个溢出的点然后单点修改。
时间复杂度 \(O(\frac{nq\log n}{65536}+q\log n)\)。时限给了 10s,实际上 1s 多一点就跑完了。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
constexpr int base = 65536;
constexpr int mod = 1145141;
struct Sgt{
int n;
vector<int> h, mx, Add;
vector<int> pow, pre;
Sgt(int n) : n(n), h(4 * n + 5), mx(4 * n + 5),
Add(4 * n + 5), pow(n + 1), pre(n + 1) {
pow[0] = pre[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
pow[i] = pow[i - 1] * base % mod;
pre[i] = (pre[i - 1] + pow[i]) % mod;
}
}
#define ls p << 1
#define rs p << 1 | 1
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
void pushup(int p, int l, int r) {
h[p] = (h[ls] * pow[r - mid] % mod + h[rs]) % mod;
mx[p] = max(mx[ls], mx[rs]);
}
void pushdown(int p, int l, int r) {
if (Add[p]) {
h[ls] = (h[ls] + Add[p] * pre[mid - l] % mod) % mod;
h[rs] = (h[rs] + Add[p] * pre[r - mid - 1] % mod) % mod;
mx[ls] += Add[p];
mx[rs] += Add[p];
Add[ls] += Add[p];
Add[rs] += Add[p];
Add[p] = 0;
}
}
void build(int p, int l, int r, vector<int> &a) {
if (l == r) {
h[p] = a[l];
mx[p] = a[l];
return ;
}
build(ls, l, mid, a);
build(rs, mid + 1, r, a);
pushup(p, l, r);
}
void build(vector<int> &a) {
build(1, 1, n, a);
}
void update(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr) {
if (ql <= l && qr >= r) {
h[p] = (h[p] + pre[r - l]) % mod;
Add[p]++;
mx[p]++;
return ;
}
pushdown(p, l, r);
if (ql <= mid) {
update(ls, l, mid, ql, qr);
}
if (qr > mid) {
update(rs, mid + 1, r, ql, qr);
}
pushup(p, l, r);
}
void update(int ql, int qr) {
update(1, 1, n, ql, qr);
}
void update_mod(int p, int l, int r) {
if (mx[p] < base) {
return ;
}
if (l == r) {
h[p] -= base;
mx[p] -= base;
return ;
}
pushdown(p, l, r);
if (mx[ls] >= base) {
update_mod(ls, l, mid);
}
if (mx[rs] >= base) {
update_mod(rs, mid + 1, r);
}
pushup(p, l, r);
}
void update_mod() {
update_mod(1, 1, n);
}
int query(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr) {
if (ql <= l && qr >= r) {
return h[p];
}
pushdown(p, l, r);
int res = 0;
if (ql <= mid) {
int len = max(0ll, min(r, qr) - mid);
res = (res + query(ls, l, mid, ql, qr) * pow[len] % mod) % mod;
}
if (qr > mid) {
res = (res + query(rs, mid + 1, r, ql, qr)) % mod;
}
return res;
}
int query(int ql, int qr) {
return query(1, 1, n, ql, qr);
}
};
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, q;
cin >> n >> q;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
Sgt seg(n);
seg.build(a);
while (q--) {
int opt;
cin >> opt;
if (opt == 1) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
seg.update(l, r);
seg.update_mod();
} else {
int x, y, L;
cin >> x >> y >> L;
int h1 = seg.query(x, x + L - 1);
int h2 = seg.query(y, y + L - 1);
cout << (h1 == h2 ? "yes\n" : "no\n");
}
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}J. Steins;Game【博弈,SG函数,线性基】
现定义一种博弈游戏:有 \(n\) 堆石子,每堆石子被涂成了黑色或白色。双方轮流从以下两种取石子方式中选择一种并操作:
- 从石子数最少的黑色堆中取任意个石子。这里“最少”是与其它黑色堆比较。
- 从任意白色堆中取任意个石子。
轮到某一方时无石子可取则败。
现在这 \(n\) 堆石子每一堆的数量 \(a_i\) 固定,但并未上色。
求有多少种上色方案,使得先手必败。方案数对 \(10^9+7\) 取模。
\(1\le n \le 10^5\),\(1 \le a_i \le 10^{18}\)。
将白色堆和黑色堆分开来看,称为白色游戏和黑色游戏。
当白色游戏的 SG 值和黑色游戏的 SG 值异或为 \(0\) 时,先手必败。
白色游戏即 nim 游戏——当所有白色堆石子数目的异或和为 \(0\) 时,先手必败。
接着尝试求出黑色游戏的 SG 值,可以打表找规律。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
#define node priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>>
void solve() {
int n = 7, mx = 8;
map<vector<int>, int> mp;
auto sg = [&] (auto self, node q) -> int {
if (q.empty()) {
return 0;
}
vector<int> A;
node o_q = q;
while (!o_q.empty()) {
A.push_back(o_q.top());
o_q.pop();
}
if (mp.count(A)) {
return mp[A];
}
vector<bool> vis(10);
int x = q.top();
q.pop();
vis[self(self, q)] = true;
for (int i = 1; i < x; i++) {
auto tmp = q;
tmp.push(i);
vis[self(self, tmp)] = true;
}
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
if (!vis[i]) {
return mp[A] = i;
}
}
};
vector<int> a;
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int dep, int lst) -> void {
if (dep == n) {
node q;
for (auto x : a) {
q.push(x);
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << " sg = " << sg(sg, q) << "\n";
return ;
}
for (int i = lst; i <= mx; i++) {
if (i > 0) {
a.push_back(i);
}
self(self, dep + 1, i);
if (i > 0) {
a.pop_back();
}
}
};
dfs(dfs, 0, 0);
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}结论是: \[ \text{SG}_{黑色游戏}=\text{最小堆石子数量}-(有多少堆石子数最少+[所有堆石子数相同])\bmod2 \] 然后是计数。将 \(a_i\) 排序,预处理出前缀异或和 \(\text{pre}_i\),后缀异或和 \(\text{suf}_i\),有 \(\text{tot}_i\) 堆石子数为 \(i\),以及第 \(i\sim n\) 堆中有 \(\text{same}_i\) 堆石子数为 \(a_i\)。在以下过程中,相同石子数的堆可以先被当成无标号来做,最后再乘上组合数转为有标号。
从后向前扫 \(\{a\}\),设当前扫到第 \(i\) 堆,钦定第 \(i\) 堆为黑色且在黑色堆中石子数量最少。此时第 \(1\sim (i-1)\) 堆只能是黑色,异或和为 \(X=\text{pre}_{i-1}\)。然后分 “所有黑色堆石子数是否相同” 来讨论第 \((i + 1) \sim n\) 堆。
若选出的黑色堆要满足石子数相同,则第 \(i\sim (i+\text{same}_i-1)\) 堆为黑色(因为是从后往前扫,所以涵盖了该连续段所有后缀为黑色堆的情况),第 \((i+\text{same}_i)\sim n\) 堆为白色。它们的 SG 值可以用上述公式以及后缀异或和快速求。
若选出的黑色堆不需要满足石子数相同,那么黑色游戏的 SG 为 \(Y=a_{i}-\text{same}_i \bmod 2\)。此时需要从后面的堆中选出若干白色堆使得它们的异或和是 \(X\oplus Y\),方案数可以用线性基求出。
具体地,设线性基 \(S\) 的大小为 \(|S|\),此前插入了 \(x\) 个数。若 \(X\oplus Y\) 能被线性基表示出来,则方案数为 \(2^{x-|S|}\)。
最后,别忘了乘组合数 \(\dbinom{\text{tot}_i}{\text{same}_i}\) 再累加到答案中。
时间复杂度 \(O(n\log w)\),\(w\) 为值域。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
constexpr int modp = 1e9 + 7;
int qpow(int k, int n) {
int s = 1;
for ( ; n; n >>= 1, k = k * k % modp) {
if (n & 1) s = s * k % modp;
}
return s;
}
struct Node {
int n, tot, all;
vector<int> p;
Node(int _n) : n(_n), tot(0), all(0), p(_n + 1) {}
void insert(int x) {
all++;
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
if (!(x >> i)) {
continue;
}
if (!p[i]) {
p[i] = x;
tot++;
break;
}
x ^= p[i];
}
}
int getans() {
int res = 0;
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
if ((res ^ p[i]) > res) {
res ^= p[i];
}
}
return res;
}
int count(int x) {
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
if (x >> i & 1) {
x ^= p[i];
}
}
return x == 0;
}
int getways(int x) {
if (!count(x)) {
return 0;
}
return qpow(2, all - tot);
}
};
vector<int> frac, inv;
void init(int n) {
frac.resize(n + 1);
inv.resize(n + 1);
frac[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
frac[i] = frac[i - 1] * i % modp;
}
inv[n] = qpow(frac[n], modp - 2);
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
inv[i - 1] = inv[i] * i % modp;
}
}
int C(int n, int m) {
if (n < m || m < 0) return 0LL;
return frac[n] * inv[m] % modp * inv[n - m] % modp;
}
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
// SG = 最小堆的石子数 - (最小堆数量 + [所有堆石子数相同]) % 2
int n;
cin >> n;
init(n + 1);
vector<int> a(n + 1);
map<int, int> mp;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
mp[a[i]]++;
}
sort(a.begin() + 1, a.end());
vector<int> pre(n + 1), suf(2 * n + 1), same(n + 2);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
pre[i] = pre[i - 1] ^ a[i];
}
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
suf[i] = suf[i + 1] ^ a[i];
same[i] = (a[i] == a[i + 1] ? same[i + 1] + 1 : 1);
}
Node t(60);
int ans = (pre[n] == 0) ? 1 : 0;
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
int res = 0;
int X = pre[i - 1];
int Y = a[i] - (same[i] + 1) % 2;
int Z = suf[i + same[i]];
if ((X ^ Y ^ Z) == 0) {
res++;
res %= modp;
}
Y = a[i] - same[i] % 2;
int need = X ^ Y;
res += t.getways(need);
if ((need ^ Z) == 0) {
res = (res - 1 + modp) % modp;
}
if (same[i - 1] <= 1) {
for (int j = 0; j < same[i]; j++) {
t.insert(a[i]);
}
}
res *= C(mp[a[i]], same[i]);
res %= modp;
ans += res;
ans %= modp;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}2024 东北四省赛 / CCPC Northeast
H. Meet【树上差分,分类讨论】
给定一棵 \(n\) 个点的树,以及 \(m\) 组点对构成的集合 \(S\)。你需要选定一个点作为根节点,使得 \(\max_\limits{(x, y)\in S} \max(\text{dis}(x, \text{lca}_{x, y}), \text{dis}(y, \text{lca}_{x, y}))\) 最小,输出这个最小值。
\(1 \le n, m \le 10^5\)。
二分答案,设二分出的答案为 \(d\)。
对于每一组点对 \((x, y)\),可以确定一个点集(一个树上连通块),使得以该点集中的点为根时,答案 \(\le d\)。接着只需要用树上差分判断这 \(m\) 个点集是否有交即可。
需要纸上分几种情况讨论,红温了挺久。
时间复杂度 \(O(n\log^2 n)\)。
#pragma GCC optmize("Ofast")
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
struct RMQ_LCA {
int n, tim;
vector<int> dfn, lg, twdep;
vector<int> dep, st;
vector<vector<int>> adj, fa, A, B;
RMQ_LCA(vector<vector<int>> &Adj) {
this->n = Adj.size() - 1;
adj = Adj;
init();
}
void init() {
dfn.resize(2 * n + 1);
lg.resize(2 * n + 1);
twdep.resize(2 * n + 1);
dep.resize(n + 1);
st.resize(n + 1);
tim = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= 2 * n; i++) {
lg[i] = lg[i >> 1] + 1;
}
}
void dfs(int x, int fath, int d) {
st[x] = ++tim;
dfn[tim] = x;
twdep[tim] = d;
dep[x] = dep[fath] + 1;
fa[x][0] = fath;
for (int i = 1; i <= lg[dep[x]] + 1; i++) {
fa[x][i] = fa[fa[x][i - 1]][i - 1];
}
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (!st[y]) {
dfs(y, x, d + 1);
dfn[++tim] = x;
twdep[tim] = d;
}
}
}
void work(int rt) {
fa.resize(n + 1, vector<int>(25));
dfs(rt, 0, 1);
A.resize(25, vector<int>(tim + 1));
B.resize(25, vector<int>(tim + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= tim; i++) {
A[0][i] = twdep[i];
B[0][i] = dfn[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= lg[tim]; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j + (1LL << i) - 1 <= tim; j++) {
if (A[i - 1][j] < A[i - 1][j + (1LL << i - 1)]) {
A[i][j] = A[i - 1][j];
B[i][j] = B[i - 1][j];
} else {
A[i][j] = A[i - 1][j + (1LL << i - 1)];
B[i][j] = B[i - 1][j + (1LL << i - 1)];
}
}
}
}
int LCA(int x, int y) {
int l = min(st[x], st[y]);
int r = max(st[x], st[y]);
int k = lg[r - l + 1];
if (A[k][l] < A[k][r + 1 - (1LL << k)]) {
return B[k][l];
} else {
return B[k][r + 1 - (1LL << k)];
}
}
int dist(int x, int y) {
return dep[x] + dep[y] - 2 * dep[LCA(x, y)];
}
int jump(int x, int len) {
for (int i = 24; i >= 0; i--) {
if (len >> i & 1) {
x = fa[x][i];
}
}
return x;
}
};
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
RMQ_LCA G(adj);
G.work(1);
vector<array<int, 2>> people(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
people[i] = {x, y};
}
auto check = [&] (int goal) {
for (auto [x, y] : people) {
if (2 * goal < G.dist(x, y)) {
return false;
}
}
vector<int> del(n + 1);
int A = 0;
for (auto [x, y] : people) {
if (G.dist(x, y) <= goal) {
A++;
continue;
}
int lca = G.LCA(x, y);
int tx, ty;
if (G.dist(lca, x) >= goal) {
tx = G.jump(x, goal);
} else {
int res = goal - G.dist(lca, x);
tx = G.jump(y, G.dist(lca, y) - res);
}
if (G.dist(lca, y) >= goal) {
ty = G.jump(y, goal);
} else {
int res = goal - G.dist(lca, y);
ty = G.jump(x, G.dist(lca, x) - res);
}
int lca_t = G.LCA(tx, ty);
if (lca == x || lca == y) {
del[lca_t]++;
int son;
if (lca == x) {
son = G.jump(y, G.dist(y, lca_t == tx ? ty : tx) - 1);
} else {
son = G.jump(x, G.dist(x, lca_t == tx ? ty : tx) - 1);
}
del[son]--;
} else {
if (lca == lca_t) {
del[1]++;
int son_x, son_y;
if (G.dist(x, tx) <= G.dist(x, ty)) {
son_x = G.jump(x, G.dist(x, tx) - 1);
son_y = G.jump(y, G.dist(y, ty) - 1);
} else {
son_x = G.jump(x, G.dist(x, ty) - 1);
son_y = G.jump(y, G.dist(y, tx) - 1);
}
del[son_x]--;
del[son_y]--;
} else {
int son;
if (G.dist(x, tx) <= G.dist(x, lca)) {
if (G.dep[tx] < G.dep[ty]) {
del[tx]++;
son = G.jump(x, G.dist(x, ty) - 1);
} else {
del[ty]++;
son = G.jump(x, G.dist(x, tx) - 1);
}
} else {
if (G.dep[tx] < G.dep[ty]) {
del[tx]++;
son = G.jump(y, G.dist(y, ty) - 1);
} else {
del[ty]++;
son = G.jump(y, G.dist(y, tx) - 1);
}
}
del[son]--;
}
}
}
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
del[x] += del[fa];
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
}
};
dfs(dfs, 1, 0);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (del[i] == m - A) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
int l = 0, r = n - 1, ans = -1;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (check(mid)) {
ans = mid;
r = mid - 1;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}K. Tasks【贪心】
有 \(n\) 个区间,定义一个区间的烦躁度等于所有包含它的区间的最大烦躁值 \(+1\)(如果没有包含它的区间,则烦躁值为 \(0\))。
现在你知道这 \(n\) 个区间的左端点 \(l_i\) 和烦躁值 \(b_i\),你需要构造对应的右端点以满足条件,或报告 \(-1\)。
特别规定给出的构造需要满足没有两个完全相同的区间且没有一个右端点 \(> 10^6\)。
\(1\le n \le 10^5\),\(1 \le l_i \le 10^6\)。
把 \(b_i\) 相同的区间看作一层,从 \(b_i=0\) 开始从低层向高层构造。
对于同一层,若存在两个区间左端点相同,那么无解;否则必要条件是每个区间都要被一个上一层的区间包含。
那么有如下贪心的构造:从右向左考虑当前层的左端点,设当前左端点为
\(l\),那肯定是选上一层中左端点 \(<l\) 且离 \(l\)
最近的区间来被包含。若有多个左端点满足,则选右端点最靠右的,这样能给下一层留够最多的空间。这个过程可以通过
std::lower_bound 简单实现。
如遇区间完全相同,右端点向左缩一位即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(n\log n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<vector<array<int, 2>>> a(n + 2);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int l, b;
cin >> l >> b;
a[b + 1].push_back({l, i});
}
a[0].push_back({0, 0});
vector<int> r(n + 1);
r[0] = 1e6;
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
sort(a[i].begin(), a[i].end(), greater());
for (int j = 0; j + 1 < a[i].size(); j++) {
if (a[i][j][0] == a[i][j + 1][0]) {
cout << "-1\n";
return ;
}
}
int R = 1e6;
for (auto [l, id] : a[i]) {
auto it = lower_bound(a[i - 1].begin(), a[i - 1].end(), array<int, 2>{l + 1, 0});
if (it == a[i - 1].begin()) {
cout << "-1\n";
return ;
}
it = prev(it);
auto [lstL, lstid] = *it;
R = min(R, r[lstid]);
if (l == lstL && R == r[lstid]) {
R--;
}
if (R < l) {
cout << "-1\n";
return ;
}
r[id] = R;
R--;
}
sort(a[i].begin(), a[i].end());
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << r[i] << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}B. Charging Station【最大权闭合子图】
有 \(3n\) 个能源站,分为三级,每级 \(n\) 个,从高级向低级编号为 \(1\sim n\),\(n\sim 2n\),\(2n\sim 3n\)。
每个能源站有三种状态:不工作、供能、吸能。供能有供能功率 \(a_i\),吸能有吸能功率 \(b_i\)。
有 \(m\) 个限制关系,每一条形如 “能源站 \(x\) 要处于供能状态当且仅当低一级的能源站 \(y\) 在吸能状态”。
问最大总供能功率。
\(1\le n, m\le 10^5\),\(1\le a_i,b_i\le 10^9\)。
假设只有两级,并且低级能源站都处于吸能状态,那么就是经典的最大权闭合子图问题。
具体地,将供能站视作左部点,吸能站视作右部点。
源点 \(S\) 向左部点连收益大小的边,左部点向右部点连正无穷的边,右部点向汇点 \(T\) 连代价大小的边,最大供能功率就是 左部点权值之和 \(-\) 最小割。
现在考虑这个三级模型。最高级的能源站只能处在供能或不工作状态,最低级的能源站只能处在供能或吸能状态(不工作还不如供能),中级能源站的状态则取决于上下两级。
假设这么一个初始状态:中级能源站供能,高级能源站不工作,低级能源站吸能。
当低级能源站由吸能 \(\to\) 供能时,中级能源站只能供能 \(\to\) 不工作;当高级能源站由不工作 \(\to\) 供能时,中级能源站只能不工作 \(\to\) 吸能。
于是我们把中级能源站拆成两个点,分别为 “供能 \(\to\) 不工作” 和 “不工作 \(\to\) 吸能”,对应的代价恰好为 \(a_i\) 和 \(b_i\)。建图如下:
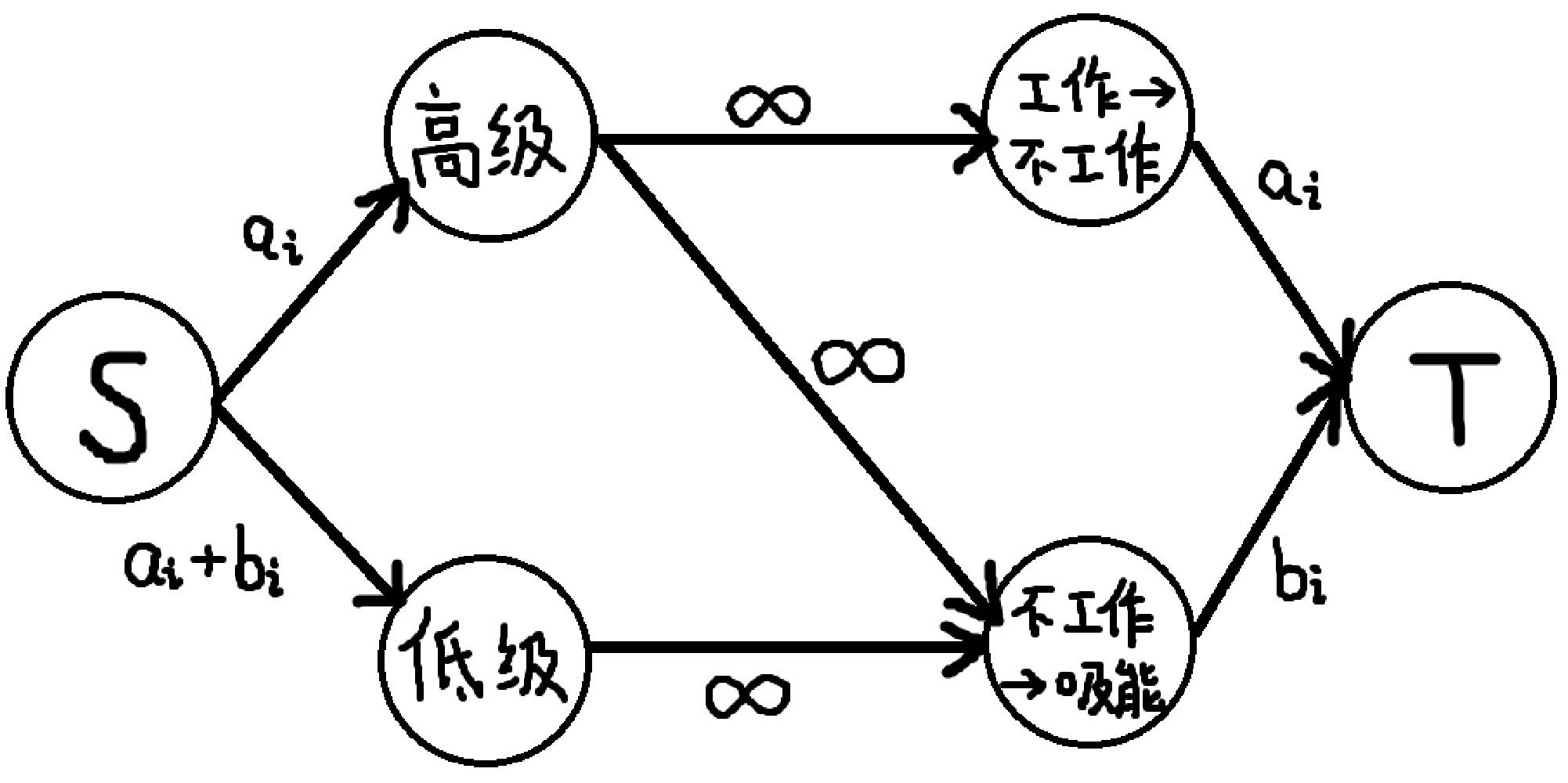
其中,\(S\) 向低级能源站连 \(a_i+b_i\) 的边是因为只考虑从吸能状态转换为供能状态带来的总收益。
时间复杂度 \(O(m\sqrt{n})\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
struct Dinic {
struct Edge {
int x, cap;
Edge(int x, int cap) : x(x), cap(cap) {}
};
int n;
vector<Edge> e;
vector<vector<int>> adj;
vector<int> dep, cur;
Dinic(int size) {
this->n = size;
adj.resize(n + 1);
}
void add(int x, int y, int cap) {
adj[x].push_back(e.size());
e.push_back({y, cap});
adj[y].push_back(e.size());
e.push_back({x, 0});
}
int bfs(int S, int T) {
dep.assign(n + 1, -1);
queue<int> q;
q.push(S);
dep[S] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for (auto i : adj[x]) {
auto [y, cap] = e[i];
if (cap > 0 && dep[y] == -1) {
dep[y] = dep[x] + 1;
if (y == T) {
return true;
}
q.push(y);
}
}
}
return false;
}
int dfs(int x, int T, int limit) {
if (x == T) {
return limit;
}
int r = limit;
for (int &i = cur[x]; i < adj[x].size(); i++) {
const int j = adj[x][i];
auto [y, cap] = e[j];
if (cap > 0 && dep[y] == dep[x] + 1) {
int t = dfs(y, T, min(r, cap));
e[j].cap -= t;
e[j ^ 1].cap += t;
r -= t;
if (r == 0) {
return limit;
}
}
}
return limit - r;
}
int dinic(int S, int T) {
int flow = 0;
while (bfs(S, T)) {
cur.assign(n + 1, 0);
flow += dfs(S, T, inf);
}
return flow;
}
};
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(3 * n + 1), b(3 * n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= 3 * n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 3 * n; i++) {
cin >> b[i];
}
// 1 ~ n:一级 3n ~ 4n:三级
// n ~ 2n:二级供能 -> 不工作
// 2n ~ 3n:二级不工作 -> 吸能
int S = 4 * n + 1;
int T = 4 * n + 2;
Dinic G(T);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
G.add(S, i, a[i]);
G.add(S, i + 3 * n, a[i + 2 * n] + b[i + 2 * n]);
G.add(i + n, T, a[i + n]);
G.add(i + 2 * n, T, b[i + n]);
}
int m;
cin >> m;
while (m--) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if (x <= n) {
G.add(x, y, inf);
G.add(x, y + n, inf);
} else {
G.add(y + n, x, inf);
}
}
int ans = accumulate(a.begin(), a.end(), 0ll);
ans -= G.dinic(S, T);
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}G. Diamond【根号分治】
给定一个长为 \(n\) 的序列 \(\{a\}\)。有 \(m\) 次询问,每次指定 \(l, r, p, q\) 四个参数,问若只保留下标在 \([l, r]\) 内且值为 \(p\) 或者 \(q\) 的数,其它数全部删除,此时剩下序列的逆序对数量。询问间相互独立。
\(2\le n \le 10^5\),\(1 \le m \le 10^5\),\(1\le a_i \le n\)。
较为明显的根号分治。把每个数的出现位置存到 std::vector
中,记为 pos。
若 \(p,q\) 的出现次数都 \(\le\sqrt{n}\),直接在 pos
上暴跳计算贡献,\(O(\sqrt{n})\)。
否则 \(p, q\) 中至少有一个出现次数
\(>\sqrt{n}\)。由于这样的数(设为
\(X\))不超过 \(\dfrac{n}{\sqrt{n}}=\sqrt{n}\)
个,我们可以对 \(1\sim n\) 的每一个位置
\(i\) 处理出 count[i][j]
代表 \(1\sim i\) 中值 \(j\in X\) 出现了多少次。
那么对于一个区间 \([l, r]\),不妨设
\(p<q\),答案就是: \[
\left(\sum_{i\in[l,r],a[i]=p}\text{count}[i][q]\right)-\text{occ}[l-1][q]\times\left(\text{occ}[r][p]-\text{occ}[l-1][p]\right)
\] 其中 occ[i][j] 代表 \(1\sim i\) 中 \(j\in[1,n]\)
的出现次数,这里只是为方便说明,实际存不下,可修改为 occ[i]
代表 \(1\sim i\) 中 \(a[i]\) 的出现次数,然后二分查询。
至于第一项,可以预处理出 count[i][j]
的前缀和,然后二分出 \(j\) 在 \([l, r]\) 中第一次出现和最后一次出现的位置
\(O(1)\) 回答。
那如果 \(p>q\) 且 \(q\) 的出现次数 \(\le \sqrt{n}\) 呢?我们没处理出这样的
count[i][q],但可以把 \(p,q\) swap
一下求出顺序对的数量,然后容斥。
时间复杂度 \(O((n+q)\sqrt{n})\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
constexpr int Block = 320;
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<int> a(n + 1), cnt(n + 1);
vector<vector<int>> pos(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
cnt[a[i]]++;
pos[a[i]].push_back(i);
}
vector<int> id(n + 1);
int tim = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (cnt[i] > Block) {
id[i] = ++tim;
}
}
vector count(n + 1, vector<int>(tim + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
count[i] = count[i - 1];
if (cnt[a[i]] > Block) {
count[i][id[a[i]]]++;
}
}
vector<int> pre(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (pos[i].size() < 2) {
continue;
}
for (int j = 1; j < pos[i].size(); j++) {
pre[pos[i][j]] = pos[i][j - 1];
}
}
vector<int> occ(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
occ[i] = occ[pre[i]] + 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= tim; j++) {
count[i][j] += count[pre[i]][j];
}
}
auto calc_1 = [&] (int l, int r, int p, int q) {
auto it1 = lower_bound(pos[p].begin(), pos[p].end(), l);
auto it2 = lower_bound(pos[q].begin(), pos[q].end(), l);
if (it1 == pos[p].end() || it2 == pos[q].end()) {
return 0LL;
}
int A = it1 - pos[p].begin();
int B = it2 - pos[q].begin();
if (pos[p][A] > r || pos[q][B] > r) {
return 0LL;
}
int big = 0, res = 0;
while (true) {
int posA = (A >= pos[p].size() ? r + 1 : pos[p][A]);
int posB = (B >= pos[q].size() ? r + 1 : pos[q][B]);
if (min(posA, posB) > r) {
break;
}
if (posA < posB) {
res += big;
A++;
} else {
big++;
B++;
}
}
return res;
};
auto calc_2 = [&] (int l, int r, int p, int q) {
auto it1 = lower_bound(pos[p].begin(), pos[p].end(), l);
auto it2 = upper_bound(pos[p].begin(), pos[p].end(), r);
auto it3 = lower_bound(pos[q].begin(), pos[q].end(), l);
auto it4 = upper_bound(pos[q].begin(), pos[q].end(), r);
if (it1 == pos[p].end() || it3 == pos[q].end()) {
return 0LL;
}
int A = it1 - pos[p].begin();
int B = it2 - pos[p].begin() - 1;
int C = it3 - pos[q].begin();
int D = it4 - pos[q].begin() - 1;
if (pos[p][A] > r || pos[q][C] > r) {
return 0LL;
}
int res = 0;
if (cnt[q] > Block) {
res += count[pos[p][B]][id[q]] - (A > 0 ? count[pos[p][A - 1]][id[q]] : 0);
if (C > 0) {
res -= (occ[pos[p][B]] - (A > 0 ? occ[pos[p][A - 1]] : 0)) * occ[pos[q][C - 1]];
}
} else {
res += count[pos[q][D]][id[p]] - (C > 0 ? count[pos[q][C - 1]][id[p]] : 0);
if (A > 0) {
res -= (occ[pos[q][D]] - (C > 0 ? occ[pos[q][C - 1]] : 0)) * occ[pos[p][A - 1]];
}
int all = B - A + 1 + D - C + 1;
all = all * (all - 1) / 2;
all -= (B - A + 1) * (B - A) / 2;
all -= (D - C + 1) * (D - C) / 2;
res = all - res;
}
return res;
};
while (m--) {
int l, r, p, q;
cin >> l >> r >> p >> q;
if (cnt[p] <= Block && cnt[q] <= Block) {
cout << calc_1(l, r, p, q) << "\n";
} else {
cout << calc_2(l, r, p, q) << "\n";
}
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}2023 Nanjing Regional / Ucup 2-11
M. Trapping Rain Water【吉司机线段树】
给定长为 \(n\) 的序列 \(\{a\}\),有 \(q\) 次修改,每次将 \(a_{x_i}\) 加上 \(v_i\)。令 \(f_i=\max(a_1,a_2,\cdots,a_i)\),\(g_i=\max(a_i,a_{i + 1},\cdots,a_n)\),你需要在每次修改后回答: \[ \sum_{i=1}^{n}(\min(f_i,g_i)-a_i) \] \(1\le n, q \le 10^6\),\(1\le a_i \le 10^6\),\(1\le v_i \le 10^6\)。
这题最关键的观察是 \(\max(f_i,g_i)=\max a_i\),即 \(\min(f_i,g_i)=f_i+g_i-\max a_i\)。
于是式子化为 \(\sum f_i+\sum g_i -n\cdot\max a_i-\sum a_i\).
后两项在修改时很容易维护,主要考虑前两项,这里以 \(\sum f_i\) 为例。
根据 \(f_i\) 的定义,设当前将 \(a_i\) 增加至 \(x\),则相当于给 \(f_{i\sim n}\) 中的每一项与 \(x\) 取 \(\max\)。
吉司机线段树处理即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(n\log^2 n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
struct Node {
vector<int> sum, mx, mn;
vector<int> tc, ta, L, R;
#define N 4 * n + 5
Node(int n) : sum(N), mx(N), mn(N), tc(N), ta(N), L(N), R(N) {}
#define ls (p << 1)
#define rs (p << 1 | 1)
#define mid (L[p] + R[p] >> 1)
void pushup(int p) {
sum[p] = sum[ls] + sum[rs];
mx[p] = max(mx[ls], mx[rs]);
mn[p] = min(mn[ls], mn[rs]);
}
void Cover(int p, int w) {
sum[p] = (R[p] - L[p] + 1) * w;
mx[p] = mn[p] = tc[p] = w;
ta[p] = 0;
}
void Add(int p, int w) {
sum[p] += (R[p] - L[p] + 1) * w;
mx[p] += w;
mn[p] += w;
ta[p] += w;
}
void pushdown(int p) {
if (tc[p] != inf) {
Cover(ls, tc[p]);
Cover(rs, tc[p]);
tc[p] = inf;
}
if (ta[p]) {
Add(ls, ta[p]);
Add(rs, ta[p]);
ta[p] = 0;
}
}
void build(int p, int l, int r, vector<int> &a) {
L[p] = l;
R[p] = r;
tc[p] = inf;
if (l == r) {
sum[p] = mx[p] = mn[p] = a[l];
return ;
}
build(ls, l, mid, a);
build(rs, mid + 1, r, a);
pushup(p);
}
int get_sum(int p, int l, int r) {
if (l <= L[p] && r >= R[p]) {
return sum[p];
}
pushdown(p);
int res = 0;
if (l <= mid) {
res += get_sum(ls, l, r);
}
if (r > mid) {
res += get_sum(rs, l, r);
}
return res;
}
void modify_max(int p, int l, int r, int w) {
if (mn[p] >= w) {
return ;
}
if (l <= L[p] && r >= R[p] && mx[p] <= w) {
return Cover(p, w);
}
pushdown(p);
if (l <= mid) {
modify_max(ls, l, r, w);
}
if (r > mid) {
modify_max(rs, l, r, w);
}
pushup(p);
}
};
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
int q;
cin >> q;
vector<array<int, 2>> qry(q);
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int pos, x;
cin >> pos >> x;
qry[i] = {pos, x};
}
vector<int> f(n + 1), g(n + 2);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
f[i] = max(f[i - 1], a[i]);
}
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
g[i] = max(g[i + 1], a[i]);
}
vector<int> ansf(q), ansg(q), ans_mx(q), ans_sum(q);
int Sum = accumulate(a.begin(), a.end(), 0LL);
int Mx = *max_element(a.begin(), a.end());
vector b = a;
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
auto [pos, x] = qry[i];
a[pos] += x;
Sum += x;
ans_sum[i] = Sum;
Mx = max(Mx, a[pos]);
ans_mx[i] = Mx;
}
a = b;
Node t(n);
t.build(1, 1, n, f);
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
auto [pos, x] = qry[i];
a[pos] += x;
t.modify_max(1, pos, n, a[pos]);
ansf[i] = t.get_sum(1, 1, n);
}
a = b;
t = Node(n);
t.build(1, 1, n, g);
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
auto [pos, x] = qry[i];
a[pos] += x;
t.modify_max(1, 1, pos, a[pos]);
ansg[i] = t.get_sum(1, 1, n);
}
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int res = ansf[i] + ansg[i] - n * ans_mx[i] - ans_sum[i];
cout << res << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}D. Red Black Tree【dp,凸序列】
现存网上的任何一篇题解都看得不是很明白,占坑。
E. Extending Distance【网络流,对偶图】
有一个 \(n\) 行 \(m\) 列的网格图,相邻格点之间有边,边有边权。
你可以进行任意次操作,每次操作可以使某条边的边权增加 \(1\)。
求一种操作次数最少的方案使得从第一列任意一个点出发到最后一列任意一个点的最短路恰好增加 \(K\),输出方案。
\(1 \le n\cdot m \le 5000\),\(1 \le K\le 100\)。
网格图是一种特殊的平面图。所谓平面图,是指能画在平面上,满足任何两条边没有交叉。
将平面图 \(G\) 的每个面看作一个点,\(G\) 中每条边两侧的两个面(可以是同一个面)进行连边,就得到了一个对偶图。
一个经典的题目是 “P4001 狼抓兔子”,它展示了一种平面图最小割转对偶图最短路的思想,不再赘述。
同样地,对本题中的网格图进行对偶,那么原图的最短路等价于对偶图的最小割。
建图,将原图中的边费用设为 \(0\),流量设为边权;再对每条边建费用为 \(1\),流量为 \(+\infin\) 的额外边。
此时题目等价于找一条流量为 \(D+K\) 的费用最小的流,其中 \(D\) 为原图的最短路。
分两步处理:
- 先只连费用为 \(0\) 的边,不连额外边。跑从源点 \(S\) 流向汇点 \(T\) 的最大流。
- 对每条边连额外边,再连一条从 super 源点 \(P\) 向源点 \(S\) 费用为 \(0\) 流量为 \(K\) 的边。跑从 super 源点 \(P\) 流向汇点 \(T\) 的最大流。此时跑出来的费用即为最小操作次数。
至于方案,可以遍历残量网络上费用为 \(1\) 的边,检查剩余流量。这条边的操作次数就是原始流量和剩余流量的差。
时间复杂度 \(O(n^2m^2k)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
struct Dinic {
struct Edge {
int x, cap, cost, all;
Edge(int x, int cap, int cost) : x(x), cap(cap), cost(cost), all(cap) {}
};
int n;
vector<Edge> e;
vector<vector<int>> adj;
vector<int> dis, pre, vis;
vector<int> h;
Dinic(int size) {
this->n = size;
adj.resize(n + 1);
}
void add(int x, int y, int w, int f) {
adj[x].push_back(e.size());
e.push_back({y, w, f});
adj[y].push_back(e.size());
e.push_back({x, 0, -f});
}
bool dijkstra(int S, int T) {
dis.assign(n + 1, inf);
vis.assign(n + 1, false);
pre.assign(n + 1, -1);
#define Pair pair<int, int>
priority_queue<Pair, vector<Pair>, greater<Pair>> q;
dis[S] = 0;
q.push({0, S});
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.top().second;
q.pop();
if (vis[x]) {
continue;
}
vis[x] = true;
for (auto i : adj[x]) {
auto [y, cap, cost, _] = e[i];
if (cap > 0 && dis[y] > dis[x] + h[x] - h[y] + cost) {
dis[y] = dis[x] + h[x] - h[y] + cost;
pre[y] = i;
q.push({dis[y], y});
}
}
}
return (dis[T] != inf);
}
array<int, 2> dinic(int S, int T) {
int flow = 0, cost = 0;
h.assign(n + 1, 0);
while (dijkstra(S, T)) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
h[i] += dis[i];
}
int res = inf;
for (int i = T; i != S; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1].x) {
res = min(res, e[pre[i]].cap);
}
for (int i = T; i != S; i = e[pre[i] ^ 1].x) {
e[pre[i]].cap -= res;
e[pre[i] ^ 1].cap += res;
}
flow += res;
cost += res * h[T];
}
return {flow, cost};
}
};
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, m, k;
cin >> n >> m >> k;
int S = (n - 1) * (m - 1) + 1;
int T = S + 1;
auto id = [&] (int x, int y) {
if (x == 0) {
return S;
}
if (x == n) {
return T;
}
return (x - 1) * (m - 1) + y;
};
vector A(n + 1, vector<int>(m));
vector B(n, vector<int>(m + 1));
Dinic G(T);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++) {
int w;
cin >> w;
A[i][j] = w;
int x = id(i - 1, j);
int y = id(i, j);
G.add(x, y, w, 0);
G.add(y, x, w, 0);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
int w;
cin >> w;
B[i][j] = w;
if (j == 1 || j == m) {
continue;
}
int x = id(i, j - 1);
int y = id(i, j);
G.add(x, y, w, 0);
G.add(y, x, w, 0);
}
}
auto res1 = G.dinic(S, T);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++) {
int x = id(i - 1, j);
int y = id(i, j);
G.add(x, y, inf, 1);
G.add(y, x, inf, 1);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
if (j == 1 || j == m) {
continue;
}
int x = id(i, j - 1);
int y = id(i, j);
G.add(x, y, inf, 1);
G.add(y, x, inf, 1);
}
}
G.add(0, S, k, 0);
auto res2 = G.dinic(0, T);
cout << res2[1] << "\n";
vector flow(T + 1, vector<int>(T + 1));
for (int x = 0; x <= T; x++) {
for (auto id : G.adj[x]) {
auto [y, cap, cost, all] = G.e[id];
cap = all - cap;
if (cost == 1 && cap) {
flow[x][y] += cap;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++) {
int x = id(i - 1, j);
int y = id(i, j);
A[i][j] += flow[x][y] + flow[y][x];
cout << A[i][j] << " \n"[j == m - 1];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
if (j == 1 || j == m) {
} else {
int x = id(i, j - 1);
int y = id(i, j);
B[i][j] += flow[x][y] + flow[y][x];
}
cout << B[i][j] << " \n"[j == m];
}
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}一种较为简洁的网格图转对偶图建图方法:
auto id = [&] (int x, int y) {
if (x == 0) {
return S;
}
if (x == n) {
return T;
}
return (x - 1) * (m - 1) + y;
};
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < m; j++) {
int x = id(i - 1, j);
int y = id(i, j);
// x -> y
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
if (j == 1 || j == m) {
continue;
}
int x = id(i, j - 1);
int y = id(i, j);
// x -> y
}
}UKIEPC 2023
G. Glacier Travel【计算几何】
给定平面上 \(n\) 个点 \((x_i,y_i)\),按顺序依次连成折线段。两个人一前一后沿着折线移动,它们的路程差固定为 \(s\),问移动过程中两人的最短距离。
\(2\le n\le 10^6\),\(-10^6\le x_i,y_i\le 10^6\),\(1\le s \le 1000\)。
可以从折线段的起点开始维护一对双指针,每次从状态 \(\{(x_A,y_A),(x_B,y_B)\}\) 转移到状态 \(\{(x_A',y_A'),(x_B',y_B')\}\) 当且仅当 \((x_A',y_A')\) 或 \((x_B',y_B')\) 为某条线段的一个端点。
至于计算距离,有一个能使码量简单许多的转化:相对速度。
首先,两个人在同一条线段上移动肯定不优。否则假定 \(A\) 不动,根据速度的合成法则,此时 \(B\) 的运动轨迹是一条线段,于是可以三分或直接运用点到线段的距离公式计算。
具体地,答案是点 \((0,0)\) 到线段 \((x_B-x_A,y_B-y_A)\sim(x_B'-x_A',y_B'-y_A')\) 的距离。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
template<class T>
struct Point {
T x, y;
Point(T x_ = 0, T y_ = 0) : x(x_), y(y_) {}
template<class U>
operator Point<U>() {
return Point<U>(U(x), U(y));
}
Point &operator+=(Point p) & {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
return *this;
}
Point &operator-=(Point p) & {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
return *this;
}
Point &operator*=(T v) & {
x *= v;
y *= v;
return *this;
}
Point operator-() const {
return Point(-x, -y);
}
friend Point operator+(Point a, Point b) {
return a += b;
}
friend Point operator-(Point a, Point b) {
return a -= b;
}
friend Point operator*(Point a, T b) {
return a *= b;
}
friend Point operator*(T a, Point b) {
return b *= a;
}
friend bool operator==(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y;
}
friend istream &operator>>(istream &is, Point &p) {
return is >> p.x >> p.y;
}
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, Point p) {
return os << "(" << p.x << ", " << p.y << ")";
}
};
template<class T>
T dot(Point<T> a, Point<T> b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
template<class T>
T cross(Point<T> a, Point<T> b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
template<class T>
double dist(Point<T> p1, Point<T> p2) {
return sqrtl(1.0 * (p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x) + 1.0 * (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y));
}
template<class T>
struct Line {
Point<T> a, b;
Line(Point<T> a_ = Point<T>(), Point<T> b_ = Point<T>()) : a(a_), b(b_) {}
};
template<class T>
double distToLine(Point<T> p, Line<T> l) {
return abs(cross(p - l.a, l.b - l.a)) / dist(l.a, l.b);
}
template<class T>
double distToSegment(Point<T> p, Line<T> l) {
if (l.a == l.b) {
return dist(l.a, p);
}
if (dot(p - l.a, l.b - l.a) <= 0) {
return dist(l.a, p);
}
if (dot(p - l.b, l.b - l.a) >= 0) {
return dist(l.b, p);
}
return distToLine(p, l);
}
using P = Point<double>;
using L = Line<double>;
void solve() {
double s;
cin >> s;
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<P> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
P X = a[0], Y = a[0];
int ptr_x = 1, ptr_y = 1;
while (s > 0) {
double d = dist(a[ptr_y], Y);
if (d < s) {
s -= d;
Y = a[ptr_y++];
} else {
Y += (a[ptr_y] - Y) * s * (1.0 / dist(a[ptr_y], Y));
break;
}
}
double ans = dist(X, Y);
while (ptr_y < n) {
double d1 = dist(a[ptr_x], X);
double d2 = dist(a[ptr_y], Y);
P nxt_X, nxt_Y;
if (d1 < d2) {
nxt_X = a[ptr_x++];
nxt_Y = Y + (a[ptr_y] - Y) * d1 * (1.0 / d2);
ans = min(ans, distToSegment(P{0, 0}, L{Y - X, nxt_Y - nxt_X}));
} else {
nxt_X = X + (a[ptr_x] - X) * d2 * (1.0 / d1);
nxt_Y = a[ptr_y++];
ans = min(ans, distToSegment(P{0, 0}, L{Y - X, nxt_Y - nxt_X}));
}
X = nxt_X;
Y = nxt_Y;
}
cout << fixed << setprecision(7) << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}H. History in Numbers【线段树】
维护长为 \(n\) 的序列 \(\{a\}\),并有 \(m\) 次操作,每次可能是以下两种之一。
update l r d:\(\forall i\in
[l, r]\),\(a_i := a_i+d\)。
check l r:查询 \([l,
r]\) 中的局部最小值是否严格递增。
区间 \([l,r]\) 的局部最小值序列被定义为将 \([l, r]\) 中相邻且相同的元素只保留一个后,数值上小于两侧元素的数构成的集合。
\(1 \le n,m \le 3\cdot 10^5\),\(-10^8\le a_i,d\le 10^8\)。
线段树板题,就是维护起来细节比较多。
线段树维护七个值:
l1:区间左起第一个数。l2:区间左起和l1不同的第二个数。r1:区间右起第一个数。r2:区间右起和r1不同的第二个数。f1:区间左起第一个局部最小值的值。f2:区间右起第一个局部最小值的值。ok:该区间的局部最小值序列是否递增。
然后就是分类讨论了,代码里我分区间去重后只有一个值,只有两个值,超过两个值讨论了一下。
注意区间左右两侧的边界情况需要特判。
时间复杂度 \(O((n+m)\log n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
template<class Info, class Tag>
struct LazySegmentTree {
int n;
vector<Info> tr;
vector<Tag> tag;
LazySegmentTree(vector<Info> &a) {
n = a.size() - 1;
const int N = (4 << __lg(n + 1)) + 5;
tr.assign(N, Info());
tag.assign(N, Tag());
build(1, 1, n, a);
}
#define ls (p << 1)
#define rs (p << 1 | 1)
void build(int p, int l, int r, vector<Info> &a) {
if (l == r) {
tr[p] = a[l];
return ;
}
int m = l + r >> 1;
build(ls, l, m, a);
build(rs, m + 1, r, a);
pushup(p);
}
void pushup(int p) {
tr[p] = tr[ls] + tr[rs];
}
void apply(int p, const Tag &x) {
tr[p].apply(x);
tag[p].apply(x);
}
void pushdown(int p) {
apply(ls, tag[p]);
apply(rs, tag[p]);
tag[p] = Tag();
}
void modify(int p, int l, int r, int pos, const Info &x) {
if (l == r) {
tr[p] = x;
return;
}
int m = l + r >> 1;
pushdown(p);
if (pos <= m) {
modify(ls, l, m, pos, x);
} else {
modify(rs, m + 1, r, pos, x);
}
pushup(p);
}
void modify(int pos, const Info &x) {
modify(1, 1, n, pos, x);
}
Info query(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr) {
if (ql <= l && qr >= r) {
return tr[p];
}
pushdown(p);
int m = l + r >> 1;
if (qr <= m) {
return query(ls, l, m, ql, qr);
} else if (ql >= m + 1) {
return query(rs, m + 1, r, ql, qr);
} else {
return query(ls, l, m, ql, qr) + query(rs, m + 1, r, ql, qr);
}
}
Info query(int ql, int qr) {
return query(1, 1, n, ql, qr);
}
void modify(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, const Tag &x) {
if (l > qr || r < ql) {
return ;
}
if (ql <= l && qr >= r) {
apply(p, x);
return ;
}
pushdown(p);
int m = l + r >> 1;
modify(ls, l, m, ql, qr, x);
modify(rs, m + 1, r, ql, qr, x);
pushup(p);
}
void modify(int ql, int qr, const Tag &x) {
return modify(1, 1, n, ql, qr, x);
}
template<class F>
int findFirst(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, F &&pred) {
if (l > qr || r < ql) {
return -1;
}
if (ql <= l && qr >= r && !pred(tr[p])) {
return -1;
}
if (l == r) {
return l;
}
pushdown(p);
int m = l + r >> 1;
int res = findFirst(ls, l, m, ql, qr, pred);
if (res == -1) {
res = findFirst(rs, m + 1, r, ql, qr, pred);
}
return res;
}
template<class F>
int findFirst(int ql, int qr, F &&pred) {
return findFirst(1, 1, n, ql, qr, pred);
}
template<class F>
int findLast(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, F &&pred) {
if (l > qr || r < ql) {
return -1;
}
if (ql <= l && qr >= r && !pred(tr[p])) {
return -1;
}
if (l == r) {
return l;
}
pushdown(p);
int m = l + r >> 1;
int res = findLast(rs, m + 1, r, ql, qr, pred);
if (res == -1) {
res = findLast(ls, l, m, ql, qr, pred);
}
return res;
}
template<class F>
int findLast(int ql, int qr, F &&pred) {
return findLast(1, 1, n, ql, qr, pred);
}
};
struct Tag {
int add = 0;
Tag() {}
Tag(int A) {
add = A;
}
void apply(const Tag &t) & {
add += t.add;
}
};
struct Info {
int l = 0;
int r = 0;
int l1 = inf;
int l2 = inf;
int r1 = inf;
int r2 = inf;
int f1 = inf;
int f2 = inf;
bool ok = true;
Info() {}
Info(int A, int B) {
l1 = r1 = A;
l = r = B;
}
void apply(const Tag &t) & {
l1 += t.add;
r1 += t.add;
if (l2 != inf) {
l2 += t.add;
}
if (r2 != inf) {
r2 += t.add;
}
if (f1 != inf) {
f1 += t.add;
}
if (f2 != inf) {
f2 += t.add;
}
}
};
pair<array<int, 2>, bool> check(int a1, int a2, int d, int b1, int b2) {
if (d == inf) {
if (a1 == inf) {
return {{b1, b2}, true};
} else if (b1 == inf) {
return {{a1, a2}, true};
} else {
return {{a1, b2}, a2 < b1};
}
} else {
if (a1 == inf && b1 == inf) {
return {{d, d}, true};
} else if (a1 == inf) {
return {{d, b2}, d < b1};
} else if (b1 == inf) {
return {{a1, d}, a2 < d};
} else {
return {{a1, b2}, a2 < d && d < b1};
}
}
}
Info operator+(const Info &a, const Info &b) {
Info c;
if (a.l2 == inf && b.l2 == inf) {
if (a.l1 == b.l1) {
c = a;
} else {
c.l1 = a.l1;
c.l2 = b.l1;
c.r1 = b.r1;
c.r2 = a.r1;
}
} else if (a.l2 == inf) {
c = b;
if (a.r1 != b.l1) {
c.l1 = a.r1;
c.l2 = b.l1;
if (a.r1 > b.l1 && b.l1 < b.l2) {
auto [res, t] = check(a.f1, a.f2, b.l1, b.f1, b.f2);
c.f1 = res[0];
c.f2 = res[1];
c.ok &= t;
}
}
} else if (b.l2 == inf) {
c = a;
if (a.r1 != b.l1) {
c.r1 = b.l1;
c.r2 = a.r1;
if (a.r2 > a.r1 && a.r1 < b.l1) {
auto [res, t] = check(a.f1, a.f2, a.r1, b.f1, b.f2);
c.f1 = res[0];
c.f2 = res[1];
c.ok &= t;
}
}
} else {
c.l1 = a.l1;
c.l2 = a.l2;
c.r1 = b.r1;
c.r2 = b.r2;
c.ok = (a.ok && b.ok);
int d = inf;
if (a.r1 == b.l1) {
if (a.r2 > a.r1 && b.l1 < b.l2) {
d = a.r1;
}
} else {
if (a.r2 > a.r1 && a.r1 < b.l1) {
d = a.r1;
}
if (a.r1 > b.l1 && b.l1 < b.l2) {
d = b.l1;
}
}
auto [res, t] = check(a.f1, a.f2, d, b.f1, b.f2);
c.f1 = res[0];
c.f2 = res[1];
c.ok &= t;
}
c.l = min(a.l, b.l);
c.r = max(a.r, b.r);
return c;
}
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<Info> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
a[i] = Info(x, i);
}
LazySegmentTree<Info, Tag> seg(a);
int q;
cin >> q;
while (q--) {
string s;
int l, r;
cin >> s >> l >> r;
if (s == "update") {
int x;
cin >> x;
seg.modify(l, r, Tag{x});
} else {
auto cur = seg.query(l, r);
if (cur.l1 < cur.l2) {
auto [res, t] = check(inf, inf, cur.l1, cur.f1, cur.f2);
cur.f1 = res[0];
cur.f2 = res[1];
cur.ok &= t;
}
if (cur.r1 < cur.r2) {
auto [res, t] = check(cur.f1, cur.f2, cur.r1, inf, inf);
cur.f1 = res[0];
cur.f2 = res[1];
cur.ok &= t;
}
cur.ok |= cur.l2 == inf;
cout << (cur.ok ? "YES" : "NO") << "\n";
}
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}NEERC 2019-2020
L. Lengths and Periods【后缀自动机】
SAM 真是人类智慧的结晶啊!占坑。
2024 上海市赛
F. 羁绊大师【bitset 优化背包】
有 \(n\) 个英雄,每个英雄有 \(a_i,b_i\) 两种羁绊,且不存在 \(i,j\in[1,n]\) 使得 \(a_i=a_j\and b_i=b_j\)。
共有 \(m\) 种羁绊,每种羁绊至多只有两个英雄拥有。当上阵英雄中有两个英雄拥有此羁绊时,该羁绊为激活状态。
对 \(k\in[1,n]\) 分别回答当有 \(k\) 个英雄上阵时,激活羁绊的最大数量。
\(1\le n \le 10^5\),\(n \le m \le 2n\),\(1\le a_i < b_i \le m\)。
将英雄看成点,羁绊看成边,拥有相同羁绊的两个英雄连边,问题转化为对 \(k\in [1,n]\) 分别回答选中 \(k\) 个点时导出子图的最大边数。
这个图具有特殊性质——每个点的度数至多是 \(2\),因此图中只包含环或链。
对于同样数目的点,选环比选链更具性价比,而对于两条链,优先选更长的链肯定也不劣。于是推断出以下策略:
- 选择一些环使得这些环的总点数 \(x\le k\) 且 \(x\) 尽可能大。
- 按链的长度降序选择直到剩下的 \(k-x\) 个点用完。
第一步可以做 \(01\) 背包 \(O(n^2)\)
地解决。又因为这是存在性背包,于是可以用 std::bitset 优化到
\(O(\frac{n^2}{w})\)。
第二步用一个指针维护当前选择的边数即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(\frac{n^2}{w})\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
constexpr int N = 1e5 + 5;
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> bel(m + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
bel[x].push_back(i);
bel[y].push_back(i);
}
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
if (bel[i].size() == 2) {
int x = bel[i][0];
int y = bel[i][1];
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
}
vector<int> vis(n + 1);
vector<int> cir, line;
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int len) -> void {
bool end = true;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (vis[y]) {
continue;
}
vis[y] = true;
end = false;
self(self, y, len + 1);
}
if (end) {
if (adj[x].size() == 1) {
line.push_back(len - 1);
} else {
cir.push_back(len);
}
}
};
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis[i] && adj[i].size() == 1) {
vis[i] = true;
dfs(dfs, i, 1);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis[i] && adj[i].size() > 0) {
vis[i] = true;
dfs(dfs, i, 1);
}
}
bitset<N> dp;
dp[0] = 1;
for (auto x : cir) {
dp |= dp << x;
}
sort(line.begin(), line.end(), greater());
int sum = accumulate(cir.begin(), cir.end(), 0LL);
int ptr = 0, ex = 0, res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (dp[i]) {
cout << i << " ";
ex = 0;
res = i;
continue;
}
ex++;
if (i <= sum) {
cout << (ex >= 2 ? i - 1 : res) << " ";
continue;
}
if (ptr >= line.size()) {
cout << res << " ";
continue;
}
if (ex > line[ptr]) {
res += line[ptr];
ptr++;
ex = 0;
}
cout << res + (ex >= 2 ? ex - 1 : 0) << " ";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}D. 咸鱼跑酷【线段树】
长为 \(n\)
的操作序列,每个位置有两种操作,形如 +x 或
*x。
给定 \(q\) 组询问,每次给定
u l r,问以初值 \(u\),执行 \(l\to
r\)
的操作序列,每个位置可以选择两种给定操作中的一种,最后能得到的最大数值。答案对
998244353 取模。
\(1\le n,q \le 10^5\),\(1\le x,u \le 10^9\)。
对于一个位置,如果都是 + 或都是
*,那么一定选数字大的那个;否则一加一乘,且只有乘的数 \(>1\)
时才有选择的可能,我们称这样的位置为关键位置。
注意到 \(1\le x \le 10^9\),故当当前 \(u>10^9\) 时,选乘一定比选加更优。
又因为每次经过一个关键位置,数字大小至少\(\times 2\),故经过 \(O(\log W)\) 个关键位置之后当前数字就会超过临界值。
于是我们预处理出下一个关键位置的坐标,暴力跳 \(O(\log W)\) 个段。由于段间都为
+ 操作,故维护一个前缀和即可。
当跳到数值 \(>10^9\),之后的选择就固定了。用线段树维护一段区间累计乘了多少,累计加了多少,就能快速计算。
pushup 的方式:
Mul[p] = Mul[p << 1] * Mul[p << 1 | 1]
Add[p] = Add[p << 1] * Mul[p << 1 | 1] + Add[p << 1 | 1]时间复杂度 \(O(n\log n+q\log(nW))\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
constexpr int modp = 998244353;
struct SegmentTree {
int n;
vector<int> Add, Mul;
SegmentTree(int size) {
n = size;
Add.resize(4 * n + 5, 0);
Mul.resize(4 * n + 5, 1);
}
#define ls p << 1
#define rs p << 1 | 1
#define mid (l + r >> 1)
void pushup(int p) {
Mul[p] = Mul[ls] * Mul[rs] % modp;
Add[p] = (Add[ls] * Mul[rs] + Add[rs]) % modp;
}
void modify(int p, int l, int r, int pos, array<int, 2> &val) {
if (l == r) {
Mul[p] = val[0];
Add[p] = val[1];
return ;
}
if (pos <= mid) {
modify(ls, l, mid, pos, val);
} else {
modify(rs, mid + 1, r, pos, val);
}
pushup(p);
}
array<int, 2> query(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr) {
if(ql <= l && qr >= r) {
return {Mul[p], Add[p]};
}
array<int, 2> res = {1, 0};
if(ql <= mid) {
auto o = query(ls, l, mid, ql, qr);
res[0] = res[0] * o[0] % modp;
res[1] = (res[1] * o[0] + o[1]) % modp;
}
if(qr > mid) {
auto o = query(rs, mid + 1, r, ql, qr);
res[0] = res[0] * o[0] % modp;
res[1] = (res[1] * o[0] + o[1]) % modp;
}
return res;
}
void modify(int pos, array<int, 2> val) {
modify(1, 1, n, pos, val);
}
array<int, 2> query(int ql, int qr) {
return query(1, 1, n, ql, qr);
}
};
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> add(n + 1), mul(n + 1, 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
string s;
cin >> s;
if (s[0] == '+') {
add[i] = max(add[i], stoll(s.substr(1)));
} else {
mul[i] = max(mul[i], stoll(s.substr(1)));
}
}
}
SegmentTree seg(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (mul[i] == 1) {
seg.modify(i, {1, add[i]});
} else {
seg.modify(i, {mul[i], 0});
}
}
vector<int> pre(n + 1), nxt(n + 2, n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
pre[i] = pre[i - 1] + add[i];
}
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
nxt[i] = mul[i] > 1 ? i : nxt[i + 1];
}
int q;
cin >> q;
while (q--) {
int u, l, r;
cin >> u >> l >> r;
int pl = l;
while (pl <= r && u < 1e9) {
int pr = min(r, nxt[pl] - 1);
u += pre[pr] - pre[pl - 1];
pl = pr + 1;
if (u >= 1e9 || pl > r) {
break;
}
u = max(u + add[pl], u * mul[pl]);
pl++;
}
auto [Mul, Add] = seg.query(pl, r);
int ans = (u % modp * Mul % modp + Add) % modp;
cout << ans << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}SEERC 2022
I. Inadequate Operation【贪心、单调栈】
给定长为 \(n\) 的非负序列 \(\{a\}\),每次操作你可以选择一个 \(i\in[1,n)\),满足 \(\max(a_i,a_{i+1}) >0\),然后用 \(\max(a_i,a_{i + 1})-1\) 替换 \(a_i\) 和 \(a_{i+1}\)。问使得序列所有元素变为 \(0\) 的最小操作次数。
\(2 \le n \le 2\cdot 10^5\),\(0\le a_i\le 10^9\)。
略微诈骗。因为这个操作每次最多让两个位置 \(-1\)(即 \(a_i=a_{i+1}\) 时),就算你让一个位置 \(-1\),另一个位置被拉高,你继续操作这个下标操作次数也不会更劣。于是策略就是贪心地从大到小删。
对于一个相同高度长为 \(L\) 的连续段,删掉它需要 \(\lceil \frac{L}{2}\rceil\) 次操作。形式化地,答案是: \[ \sum_{i=1}^{mx}\left( \left\lceil\frac{L_{i1}}{2}\right\rceil + \left\lceil\frac{L_{i2}}{2}\right\rceil +\cdots \right) \] 其中 \(L_i\) 是指考虑所有 \(\ge i\) 的元素,它们形成的若干连续段长度。
进一步地,记 \(l_i\) 为 \(i\) 左侧第一个 \(<a_i\) 的位置,\(r_i\) 为 \(i\) 右侧第一个 \(<a_i\) 的位置。式子可以化成: \[ \sum_{i=1}^{n} \left\lceil\frac{r_i-l_i-1}{2}\right\rceil (a_i-\max(a_{l_i},a_{r_i})) \] 实现的时候,可以维护一个内部递增的单调栈,扫一遍就能求出 \(l_i\) 和 \(r_i\)。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
struct DSU {
vector<int> f, siz;
DSU() {}
DSU(int n) { init(n);}
void init(int n) {
f.resize(n + 2);
siz.resize(n + 2);
for(int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) {
f[i] = i;
siz[i] = 1;
}
}
int find(int x) {
if (x == f[x]) return x;
return f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
bool same(int x, int y) {
return find(x) == find(y);
}
bool merge(int x, int y) {
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x == y) return false;
if (siz[x] < siz[y]) {
swap(x, y);
}
siz[x] += siz[y];
f[y] = x;
return true;
}
int size(int x) {
return siz[find(x)];
}
};
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<array<int, 2>> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i][0];
a[i][1] = i;
}
sort(a.begin() + 1, a.end());
int ans = 0;
DSU dsu(n);
vector<int> vis(n + 2);
for (int i = n, lst = 0; i >= 1; i--) {
int j = i;
while (j > 0 && a[j][0] == a[i][0]) {
j--;
}
int len = lst;
int del = a[i][0] - (j == 0 ? 0 : a[j][0]);
for (int k = j + 1; k <= i; k++) {
int pos = a[k][1];
vis[pos] = true;
if (vis[pos - 1]) {
len -= (dsu.size(pos - 1) + 1) / 2;
dsu.merge(pos, pos - 1);
}
if (vis[pos + 1]) {
len -= (dsu.size(pos + 1) + 1) / 2;
dsu.merge(pos, pos + 1);
}
len += (dsu.size(pos) + 1) / 2;
}
ans += len * del;
lst = len;
i = j + 1;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 2);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
vector<int> stk(n + 1), l(n + 1), r(n + 1, n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
while (!stk.empty() && a[stk.back()] >= a[i]) {
r[stk.back()] = i;
stk.pop_back();
}
if (!stk.empty()) {
l[i] = stk.back();
}
stk.push_back(i);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ans += (r[i] - l[i]) / 2 * (a[i] - max(a[l[i]], a[r[i]]));
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}K. Knowledge Testing Problem【整体二分】
给定一个 \(n\) 个点 \(m\) 条边的无向图,边有边权 \(w_i\)。其中任意一条边 \(x_i\to y_i\) 都满足 \(|x_i-y_i|\le 10\)。给定 \(q\) 组询问,每次询问两个点问最短路。
\(1 \le n \le 10^5\),\(1\le m \le 2\cdot 10^5\),\(1\le q \le 2.5\cdot 10^4\),\(1 \le w_i \le 10^9\)。
考虑整体二分。
对于当前区间 \([l, r]\),设中点为 \(m\),取中点周围 \([m-4,m+5]\) 共 \(10\) 个点,并以这些点为起点跑单源最短路(经过的点必须在 \([l,r]\) 内,即只连两个端点都在 \([l, r]\) 内的边),然后再以这些点为中转点分治下去。
对于一个询问 \(x,y\),若 \(\max(x,y)<m-4\),就把它放到 \([l,m-4)\) 里继续更新;若 \(\min(x,y)>m+5\),就把它放到 \((m+5,r]\) 里继续更新;否则此次更新完后不用继续更新,因为必然以 \(x,y\) 中的至少一个点为起点跑了单源最短路。
保证正确性的根据是:对于一个询问 \(x,y\)(不妨设 \(x<y<m-4\)),如果最短路需要经过 \(m+5\) 右侧的点,就必然经过 \([m-4,m+5]\) 中的某一个(因为任意一条边两侧的点编号相差 \(\le 10\)),故以这 \(10\) 个点为中转点更新出的最短路能覆盖所有的情况。
假设 \(n,m\) 同级,时间复杂度 \(O(nd\log^2n)\),\(d=10\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, m, q;
cin >> n >> m >> q;
vector<array<int, 3>> E, Q;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x, y, w;
cin >> x >> y >> w;
E.push_back({x, y, w});
}
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
Q.push_back({x, y, i});
}
vector<int> ans(q, inf);
vector<vector<array<int, 2>>> adj(n + 1);
vector<int> dis(n + 1, inf), vis(n + 1);
auto dijkstra = [&] (int S, int l, int r) {
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
dis[i] = inf;
vis[i] = false;
}
#define P pair<int, int>
priority_queue<P, vector<P>, greater<P>> pq;
pq.push({0, S});
dis[S] = 0;
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto [dist, x] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if (vis[x]) {
continue;
}
vis[x] = true;
for (auto [y, w] : adj[x]) {
if (dis[y] > dist + w) {
dis[y] = dist + w;
pq.push({dis[y], y});
}
}
}
};
auto calc = [&] (auto self, int l, int r,
vector<array<int, 3>> &vE, vector<array<int, 3>> &vQ) -> void {
if (l > r) {
return ;
}
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
adj[i].clear();
}
for (auto [x, y, w] : vE) {
adj[x].push_back({y, w});
adj[y].push_back({x, w});
}
int mid = l + r >> 1;
for (int i = max(l, mid - 4); i <= min(r, mid + 5); i++) {
dijkstra(i, l, r);
for (auto [x, y, id] : vQ) {
ans[id] = min(ans[id], dis[x] + dis[y]);
}
}
vector<array<int, 3>> lE, rE, lQ, rQ;
for (auto [x, y, w] : vE) {
if (max(x, y) <= mid - 5) {
lE.push_back({x, y, w});
} else if (min(x, y) >= mid + 6) {
rE.push_back({x, y, w});
}
}
for (auto [x, y, id] : vQ) {
if (max(x, y) <= mid - 5) {
lQ.push_back({x, y, id});
} else if (min(x ,y) >= mid + 6) {
rQ.push_back({x, y, id});
}
}
self(self, l, mid - 5, lE, lQ);
self(self, mid + 6, r, rE, rQ);
};
calc(calc, 1, n, E, Q);
for (auto x : ans) {
cout << (x == inf ? -1 : x) << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}NWERC2021
H. Heating Up【双向链表】
有 \(n\) 个辣椒,第 \(i\) 个辣度为 \(a_i\),排成环形(即 \(1\) 和 \(n\) 看作相邻)。你要吃光这些辣椒,你可以任意选择一个辣椒开始,并在之后每一步选择”已选择辣椒”中的一个相邻辣椒吃下。你初始有忍耐度 \(f\),你吃下一个辣度为 \(k\) 的辣椒当且仅当 \(f\ge k\),并且当你吃掉它后你的忍耐值会增加 \(k\) 个单位。问吃光所有辣椒所需的最小初始忍耐值。\(3\le n \le 5\cdot 10^5\),\(0\le a_i \le 10^{13}\)。
二分答案,设二分出的答案为 \(s\),问题转化为判定初始忍耐值为 \(s\) 时是否能吃完所有辣椒。
拆环成链,用一个双向链表操作以下过程:
遍历 \(i\in[1,2n]\),若 \(a_i>s\),跳过;否则以点 \(i\) 为中心向两侧尝试扩张。
对每一个连续段维护这个段 \(a_i\) 的最小值 \(b\),当忍耐值不小于这个值时,就可以吞并这个段,新的 \(b\) 即两段取 \(\min\)。
这个被合并的段有贡献 \(\sum a_i\),合并时可以另开一个数组 \(c\) 维护。
判定成功当且仅当链表合并到最后只剩一个元素,即删除了 \(2n-1\) 个元素。
时间复杂度 \(O(n\log w)\),\(w\) 为二分值域。具体实现见代码。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(2 * n + 2);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
a[i + n] = a[i];
}
a[0] = a[2 * n + 1] = inf;
auto check = [&] (int st) {
vector<int> L(2 * n + 2), R(2 * n + 2);
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++) {
L[i] = i - 1;
R[i] = i + 1;
}
int cnt = 2 * n;
auto del = [&] (auto pos) {
L[R[pos]] = L[pos];
R[L[pos]] = R[pos];
cnt--;
};
vector b = a, c = a;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i = R[i]) {
if (b[i] > st) {
continue;
}
int cur = st + b[i];
while (true) {
if ((L[i] < 1 || b[L[i]] > cur) && (R[i] > 2 * n || b[R[i]] > cur)) {
break;
}
if (L[i] >= 1 && b[L[i]] <= cur) {
cur += c[L[i]];
c[i] += c[L[i]];
b[i] = min(b[i], b[L[i]]);
del(L[i]);
}
if (R[i] <= 2 * n && b[R[i]] <= cur) {
cur += c[R[i]];
c[i] += c[R[i]];
b[i] = min(b[i], b[R[i]]);
del(R[i]);
}
}
}
return cnt == 1;
};
int l = 0, r = 1e13, ans = -1;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (check(mid)) {
ans = mid;
r = mid - 1;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}SWERC 2023
G. Favourite Dish【凸包】
有 \(n\) 道菜,第 \(i\) 道菜有属性 \(a_i\) 和 \(b_i\)。有 \(m\) 个客人,第 \(i\) 个人有属性 \(c_{i}\) 和 \(d_i\)。
第 \(i\) 个人对第 \(j\) 道菜的喜爱度为 \(\dfrac{c_ia_j+d_ib_j}{c_i+d_i}\),即加权平均值。你需要对每个人求出他最喜欢的菜品编号(若对两道菜的喜爱度相同,取编号较小者)。保证有序对 \((a_i,b_i)\) 两两不同,\((c_i,d_i)\) 两两不同。
\(1\le n,m\le 5\cdot 10^5\),\(0\le a_i,b_i,c_i,d_i\le 10^6\)。
把每个人看作一个询问。对于单个询问,\(c+d\) 固定,衡量指标是 \(ac+bd\)。
问题转化为给定 \(n\) 个点 \((a, b)\),每次询问一个 \((c, d)\),问 \(ac+bd\) 取到最大值时对应点的编号。
这是一个经典问题。令 \(w=ac+bd\),两边除以 \(d\): \[ \frac{w}{d}=\frac{ac}{d}+b\longrightarrow b=(-\frac{c}{d})a+\frac{w}{d} \]
这是一个 \(y=kx+b\) 形式的直线方程,让 \(w\) 最大,即让这条直线的截距 \(\left(\dfrac{w}{d}\right)\) 最大。
由于 \(a,b,c,d\) 均为非负整数,我们可以求出这 \(n\) 个点 \((a, b)\) 在第一象限的上凸壳,将询问按斜率 \(\left(-\dfrac{c}{d}\right)\) 排序,用一对双指针即可维护。(一个在凸壳上顺时针扫,一个按直线斜率从大到小扫) 时间复杂度 \(O(n\log n+m\log m)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<array<int, 3>> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
a[i] = {x, y, i};
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end(), [&] (array<int, 3> i, array<int, 3> j) {
return i[0] == j[0] ? i[1] > j[1] : i[0] < j[0];
});
auto getk = [&] (int i, int j) {
return (double)(a[j][1] - a[i][1]) / (a[j][0] - a[i][0]);
};
vector<int> h{0};
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
while (h.size() > 1 && getk(h[h.size() - 2], h.back()) < getk(h[h.size() - 2], i)) {
h.pop_back();
}
h.push_back(i);
}
vector<pair<double, int>> l;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int c, d;
cin >> c >> d;
l.push_back({-1.0L * c / d, i});
}
sort(l.begin(), l.end(), greater());
vector<int> ans(m);
for (int i = 0, j = 0, res = inf; i < m; i++) {
auto [k, id] = l[i];
if (i > 0 && k == l[i - 1].first) {
ans[id] = res;
continue;
}
while (j + 1 < h.size() && k < getk(h[j], h[j + 1])) {
j++;
}
res = a[h[j]][2];
while (j + 1 < h.size() && k == getk(h[j], h[j + 1])) {
j++;
res = min(res, a[h[j]][2]);
}
ans[id] = res;
}
for (auto x : ans) {
cout << x + 1 << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}\(1.0\cdot \text{int}=\text{double}\)
\(1.0L\cdot \text{int}=\text{long double}\)
望周知 (QwQ)。