【游记】2024 CCPC 网络预选赛
UESTC_EndlessEmbrace 第一场正式的比赛。
快到九点才起床,本来昨晚和同样晕车的 kkaaxxrrdxing4c 商量好了一起做地铁去,但起床一刷消息发现被鸽了,只好重新买上了九点半的车票,赶忙跑去东门把模板印了。
很困,昨晚临时补了一些板子,两点才睡。车上很颠,没睡着,意料之中。
12点整,PTA 准时开崩。以前只是有所耳闻,这下身临其境了。
队友和我上去打了点板子,期间刷新出了一道签 L,马上秒了(伏笔),继续敲板子。
大概 44min 终于能交题了,交,WA,字符串读的 0-index 写的 1-index,气晕了,47minL2A。
接着签 B,WA。wbc 签 K,63minK1A,随后发现我少了个特判,加上过了,64minB2A。
队友开 D,我开其它的,两个队友都是 dp 糕手,讨论出了一个区间 dp,115minD1A。
PTA 发了延时通知,延了 1h,很难评价。
看榜 UESTC_PenaltyAutomaton 过了不到 10 个队过的 C,大为震撼。
于是看了 C,跟 wp 说了一个贪心,不知道对不对就上去写了,WA,换了一个贪心策略又 WA 了两发,耻辱换题。按榜看了 J,写了两发线性基,还是 WA,红了。
这期间队友一直在攻 E,两个多小时终于找对了方向,283minE2A。
冷静了一下,改了一下线性基的逻辑,终于 287minJ3A。
时间不多了,一起看 I,wp 很快就会 dp 了,就让他上去写,我在研究 C。
跟队友简单说了一下我的做法,觉得很对啊,就打印了一下肉眼查错,后来发现假完了。
最后半小时 I 题狂 T,一起帮着 wp 卡常,可惜的是直到比赛结束也没卡过。
6 题 Rank360/9 收尾,有点沮丧。赛后发现 C,G,I 都不应该丢,但马后炮也意义不大,只能希望下周 ICPC 打得好一点。
FunFact:赛后把 I 题 clone 下来开大了时限把赛时代码交了上去,1952msAccepted,赛时时限是 1s。
A. 军训 I
可以预见的是合法的状态数很少。
实际上可以证明 \(k > 13\) 时无解:把所有人移到一个角,这些人在这个角最多只有 \(2\) 种方案,移到一个角之后向另外三个角移动一共 \(2\cdot 4=8\) 种。四个方向单移动一次共 \(4\) 种,再加上原状态 \(1\) 种共 \(13\) 种。
对 \(k\in [1,13]\) 打表发现 \(k=8,10,12\) 时无解,同时还能很快打出 \(\min(n,m)<3\) 的情况进行特判。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int k = 1; k <= 20; k++) {
vector a(n, vector<int>(m));
auto do_L = [&] () {
vector b = a;
b.assign(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cnt += a[i][j];
}
for (int j = 0; j < cnt; j++) {
b[i][j] = 1;
}
}
a = b;
};
auto do_R = [&] () {
vector b = a;
b.assign(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cnt += a[i][j];
}
for (int j = m - 1; j >= m - cnt; j--) {
b[i][j] = 1;
}
}
a = b;
};
auto do_U = [&] () {
vector b = a;
b.assign(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cnt += a[i][j];
}
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
b[i][j] = 1;
}
}
a = b;
};
auto do_D = [&] () {
vector b = a;
b.assign(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cnt += a[i][j];
}
for (int i = n - 1; i >= n - cnt; i--) {
b[i][j] = 1;
}
}
a = b;
};
for (int i = 1; i < (1 << (n * m)); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int l = 0; l < m; l++) {
int o = j * m + l;
if (i >> o & 1) {
a[j][l] = 1;
} else {
a[j][l] = 0;
}
}
}
map<vector<vector<int>>, int> mp;
int res = 0;
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int step) -> void {
if (res > k) {
return ;
}
if (!mp[a]) {
mp[a] = 1;
res++;
} else {
return ;
}
if (step > 100) {
return ;
}
vector b = a;
do_U();
self(self, step + 1);
a = b;
do_D();
self(self, step + 1);
a = b;
do_L();
self(self, step + 1);
a = b;
do_R();
self(self, step + 1);
};
dfs(dfs, 0);
if (res == k) {
cout << "k = " << k << " is ok" << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int l = 0; l < m; l++) {
int o = j * m + l;
if (i >> o & 1) {
cout << "1";
} else {
cout << "0";
}
}
cout << "\n";
}
break;
}
}
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}当 \(n,m \ge 3\) 时,分出以下情况,打表找规律(听着难,实际上打出字典序最小的一个就能看出来):
\(k=1\),把所有格子填满。
\(k=2\),把第一行填满。
\(k=3\),把第二行填满。
\(k=4\),填 \((1,1)\)。
\(k=5\),此时合法的局面需要满足移动一次后向任意方向移动都没意义。当 \(n=m\) 时填满任意一条对角线是好想的。\(n \neq m\) 时考虑把 \(n\times m\) 分成若干个 \(x\times x\) 的子矩阵,每个子矩阵填满一条对角线。此时可取 \(x = \gcd(n, m)\)。
\(k=6\), 填 \((1, 2)\)。
\(k=7\),填 \((2, 1)\land (1,x),x\in[2, m]\)。
\(k=9\),填 \((1, 2)\land (2, 1)\)。
\(k=11\),填 \((1, 3)\land (2, 1)\)。
\(k=13\),填 \((1, 3)\land (3, 1)\)。
代码写的比较 shit,如果把 \(n=2\) 和 \(m=2\) 单独列出来会直观很多,但我懒得改 shit 了。
时间复杂度 \(O(nm)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
#define NO (void)(cout << "No\n")
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, m, k;
cin >> n >> m >> k;
if (k == 1) {
cout << "Yes\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++, cout << "\n") {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cout << '*';
}
}
return ;
}
auto print = [&] (vector<array<int, 2>> a) -> void {
cout << "Yes\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++, cout << "\n") {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
bool ok = false;
for (auto [x, y] : a) {
if (x == i + 1 && y == j + 1) {
ok = true;
break;
}
}
cout << (ok ? '*' : '-');
}
}
};
auto printl = [&] (int x, int y) -> void {
cout << "Yes\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++, cout << "\n") {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if ((x && x == i + 1) || (y && y == j + 1)) {
cout << "*";
} else {
cout << "-";
}
}
}
};
if (n == 1 && m == 1) {
NO;
} else if (min(n, m) == 1 && max(n, m) == 2) {
k == 2 ? print({{1, 1}}) : NO;
} else if (min(n, m) == 1) {
if (k == 2) {
print({{1, 1}});
} else if (k == 3) {
n == 1 ? print({{1, 2}}) : print({{2, 1}});
} else {
NO;
}
} else if (k == 4) {
print({{1, 1}});
} else if (n == 2 && m == 2) {
if (k == 2) {
print({{1, 1}, {1, 2}});
} else if (k == 5) {
print({{1, 1}, {2, 2}});
} else {
NO;
}
} else if (n == 2 && m == 3) {
if (k == 2) {
printl(0, 1);
} else if (k == 3) {
printl(0, 2);
} else if (k == 6) {
print({{1, 2}});
} else if (k == 7) {
print({{1, 2}, {2, 1}});
} else if (k == 9) {
print({{1, 3}, {2, 1}});
} else {
NO;
}
} else if (n == 3 && m == 2) {
if (k == 2) {
printl(1, 0);
} else if (k == 3) {
printl(2, 0);
} else if (k == 6) {
print({{2, 1}});
} else if (k == 7) {
print({{1, 2}, {2, 1}});
} else if (k == 9) {
print({{1, 2}, {3, 1}});
} else {
NO;
}
} else {
if (k == 2) {
printl(1, 0);
} else if (k == 3) {
n > m ? printl(2, 0) : printl(0, 2);
} else if (k == 5) {
if (__gcd(n, m) == 1) {
NO;
} else {
cout << "Yes\n";
int g = __gcd(n, m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++, cout << "\n") {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int x = i % g;
int y = j % g;
if (x == y) {
cout << "*";
} else {
cout << "-";
}
}
}
}
} else if (k == 6) {
n < m ? print({{1, 2}}) : print({{2, 1}});
} else if (k == 7) {
cout << "Yes\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++, cout << "\n") {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if ((i == 1 && j == 0) || (i == 0 && j > 0)) {
cout << "*";
} else {
cout << "-";
}
}
}
} else if (k == 9) {
if (n == 2) {
print({{1, 3}, {2, 1}});
} else if (m == 2) {
print({{3, 1}, {1, 2}});
} else {
print({{1, 2}, {2, 1}});
}
} else if (k == 11) {
if (n == 2) {
print({{1, 2}, {2, 1}, {1, 4}});
} else if (m == 2) {
print({{1, 2}, {2, 1}, {4, 1}});
} else {
print({{1, 3}, {2, 1}});
}
} else if (k == 13) {
if (n == 2 || m == 2) {
NO;
} else {
print({{1, 3}, {3, 1}});
}
} else {
NO;
}
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}B. 军训 II
感性地,排序后不整齐度最小。
\(ans1\) 可以单 \(\log\) 求,但允许 \(O(n^2)\) 就没必要自讨苦吃。
接着设每个连续段长 \(cnt_i\),那么 \(ans2=2\prod cnt_i\)。系数来自升序排序和降序排序两种。
特判:所有数都相同时,升序和降序看作一种,\(ans2=\prod cnt_i\)。
时间复杂度 \(O(n^2)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
constexpr int modp = 998244353;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> fac(n + 1);
fac[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
fac[i] = fac[i - 1] * i % modp;
}
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
int ans1 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int mx = a[i], mn = a[i];
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
mx = max(mx, a[j]);
mn = min(mn, a[j]);
ans1 += mx - mn;
}
}
int cnt = 1, ans2 = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] != a[i - 1]) {
ans2 *= fac[cnt];
ans2 %= modp;
cnt = 1;
} else {
cnt++;
}
}
ans2 *= fac[cnt];
ans2 %= modp;
vector b = a;
reverse(b.begin(), b.end());
if (a != b) {
ans2 *= 2;
ans2 %= modp;
}
cout << ans1 << " " << ans2 << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}C. 种树
将已经种了树的点称为黑点,否则白点。
两种错误的贪心举例:
两个黑点间夹 \(k\) 个白点,\(k\) 为偶数时用 \(\dfrac{k}{2}\) 次操作填满。
以两个或以上相连的黑点为界,每个连通块贡献为 \(\left\lceil \dfrac{白点个数}{2}\right\rceil\)。
反例对应如下。
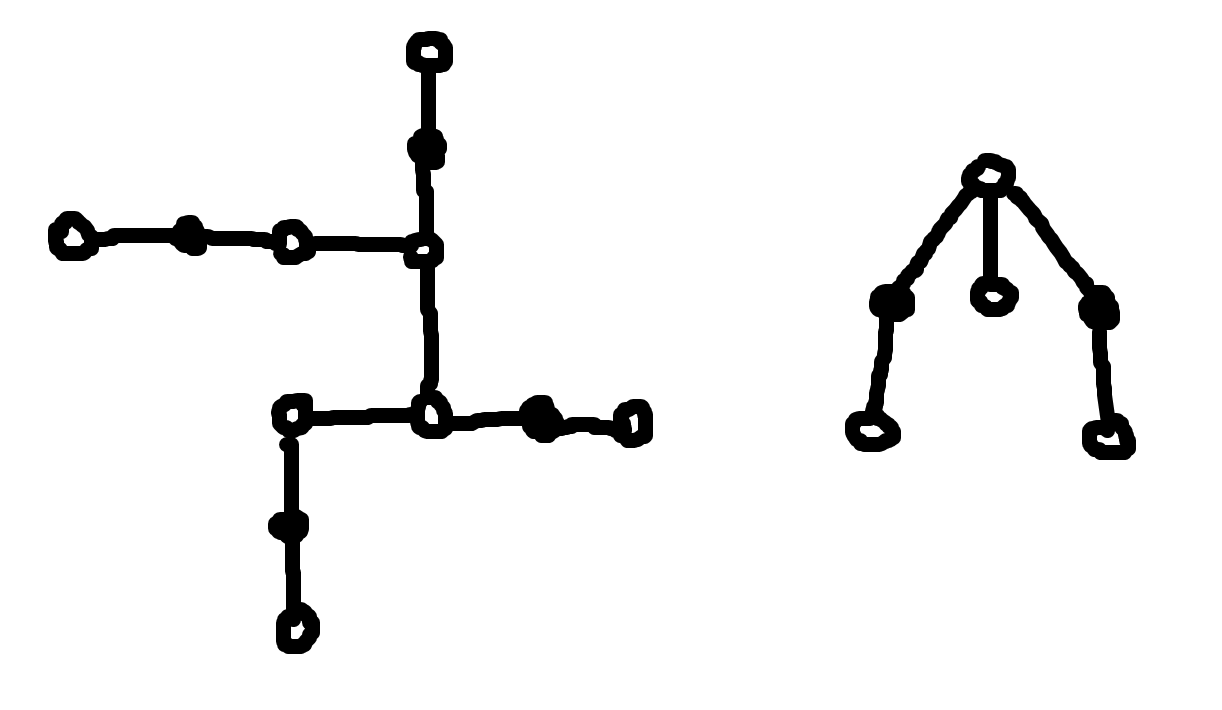
正确的贪心:任选一黑点为根 dfs,自下而上贪心,每次填两个。对于一个黑点:
若当前子树中白点数为偶数,填满。
否则考虑是否能把多余的一个涂色操作摊给当前黑点的父亲。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
int rt = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
a[x] = true;
rt = x;
}
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
int ans = 0;
vector<int> sz(n + 1);
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int fath) -> void {
sz[x] = a[x] == 0;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fath) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
sz[x] += sz[y];
}
if (a[x]) {
ans += sz[x] / 2;
if (sz[x] % 2) {
ans++;
if (fath && a[fath] == 0) {
a[fath] = 1;
sz[fath]--;
}
}
sz[x] = 0;
}
};
dfs(dfs, rt, 0);
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}G. 疯狂星期六
yyq 需要尽可能花多的钱,而他花的最多的钱数是可以处理出来的,即 \(X=\min(\sum \text{能摊到 yyq 上的菜钱}+T_1,a_1)\)。
令 \(mx_i\) 为第 \(i\) 个人能花在菜上的最多钱数,首先 \(mx_1=X-T_1\),那么 \(mx_i=\min(a_i,mx_1-1)\)。
接着只需 check 是否存在一种满足上述条件的方案。
转化为网络流问题:
源点向每个菜连容量为菜钱的边。
每个菜向付它钱的两个人连容量为菜钱的边。
每个人向汇点连容量为 \(mx_i\) 的边。
check 成功当且仅当最大流 \(=\) 总菜钱。
时间复杂度 \(O(n\sqrt{m})\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
struct Dinic {
struct Edge {
int x, cap;
Edge(int x, int cap) : x(x), cap(cap) {}
};
int n;
vector<Edge> e;
vector<vector<int>> adj;
vector<int> dep, cur;
Dinic(int size) {
this->n = size;
adj.resize(n + 1);
}
void add(int x, int y, int cap) {
adj[x].push_back(e.size());
e.push_back({y, cap});
adj[y].push_back(e.size());
e.push_back({x, 0});
}
int bfs(int S, int T) {
dep.assign(n + 1, -1);
queue<int> q;
q.push(S);
dep[S] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for (auto i : adj[x]) {
auto [y, cap] = e[i];
if (cap > 0 && dep[y] == -1) {
dep[y] = dep[x] + 1;
if (y == T) {
return true;
}
q.push(y);
}
}
}
return false;
}
int dfs(int x, int T, int limit) {
if (x == T) {
return limit;
}
int r = limit;
for (int &i = cur[x]; i < adj[x].size(); i++) {
const int j = adj[x][i];
auto [y, cap] = e[j];
if (cap > 0 && dep[y] == dep[x] + 1) {
int t = dfs(y, T, min(r, cap));
e[j].cap -= t;
e[j ^ 1].cap += t;
r -= t;
if (r == 0) {
return limit;
}
}
}
return limit - r;
}
int dinic(int S, int T) {
int flow = 0;
while (bfs(S, T)) {
cur.assign(n + 1, 0);
flow += dfs(S, T, inf);
}
return flow;
}
};
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<int> a(n + 1), Taxi(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i] >> Taxi[i];
}
vector<array<int, 3>> dish(m + 1);
vector<int> mxcost(n + 1);
int all = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int x, y, w;
cin >> x >> y >> w;
dish[i] = {x, y, w};
all += w;
if (x == 1 || y == 1) {
mxcost[1] += w;
}
}
mxcost[1] = min(a[1], mxcost[1] + Taxi[1]);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
mxcost[i] = min(a[i], mxcost[1] - 1) - Taxi[i];
if (mxcost[i] < 0) {
cout << "NO\n";
return ;
}
}
mxcost[1] -= Taxi[1];
int S = m + n + 1;
int T = m + n + 2;
Dinic G(T);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
auto [x, y, w] = dish[i];
G.add(S, i, w);
G.add(i, m + x, w);
G.add(i, m + y, w);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
G.add(m + i, T, mxcost[i]);
}
if (G.dinic(S, T) == all) {
cout << "YES\n";
} else {
cout << "NO\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}J. 找最小
令 \(c_i=a_i\oplus b_i\),\(A=\oplus_{i=1}^{n} a_i\),\(B=\oplus_{i=1}^{n} b_i\)。
根据异或运算的自反性,题目转化为需要选一些 \(c_i\)(设选出的 \(c_i\) 的异或和为 \(C\))使得 \(\max(A\oplus C,B\oplus C)\) 最小。
联想到线性基,其能解决这样一类问题:从一堆数中选出若干个数,它们的异或和最大/最小。
插入操作不用修改,查询时不妨将 \(\max(A,B)\) 作为初值,代表已经选出这么多。
随后从高位向低位贪心,判断到某位异或之后 \(\max\) 变小就更新即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(n\log w)\),\(w\) 为值域。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
struct Node {
int n;
vector<int> p;
Node(int _n) : n(_n), p(_n + 1) {}
void insert(int x) {
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
if (!(x >> i)) {
continue;
}
if (!p[i]) {
p[i] = x;
break;
}
x ^= p[i];
}
}
int getans(int st1, int st2) {
int res = max(st1, st2);
int X = st1, Y = st2;
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
if (max(X ^ p[i], Y ^ p[i]) < res) {
X ^= p[i];
Y ^= p[i];
res = max(X, Y);
}
}
return res;
}
};
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1), b(n + 1);
int val1 = 0, val2 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
val1 ^= a[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> b[i];
val2 ^= b[i];
}
Node t(31);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
t.insert(a[i] ^ b[i]);
}
cout << t.getans(val1, val2) << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}K. 取沙子游戏
当 \(n\) 为奇数时,先手拿 \(1\),之后后手和先手都只能轮流拿 \(1\),先手必胜。
否则,先手只能拿偶数,一种策略是每次拿 \(\text{lowbit(n)}\),之后后手无论拿什么,先手跟着拿就行。
故当 \(\text{lowbit(n)}\le k\) 时,先手必胜。否则无论拿 \(1\sim k\) 中的多少,\(\text{lowbit(n)}\) 都会落到 \(k\) 以内,让后手取得胜利。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
if ((n & -n) <= k) {
cout << "Alice\n";
} else {
cout << "Bob\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}