【游记】2024 UESTC 暑假集训 第一轮
半年没写过游记了,因为懒。
感觉还是要写点什么才行。
【7.5】 Day -2
我暑假呢?
【7.6】 Day -1
我暑假呢?我暑假呢?
【7.7】 Day 0
我暑假呢?我暑假呢?我暑假呢?
【7.8】 Day 1
前一晚因为不可抗力没睡着。
本来预定的是早上 7 点 10 分的校车,结果开窗一看下了很大的雨,倒霉!
干脆取消了改成 8 点的校车,好在雨停了,但我有衣服还没干,唉先上车再说。
到清水河了,脑浆都要颠出来了,体验最差的一次班车,还贼堵。
到宿舍了,6 楼,累晕了,光是上楼就满身汗。
早上 10 点,有 yp 讲话。到了立人楼发现里面又挤又热,直接把凳子搬出来坐门边了。
刚坐出来,怎么专题开了鸭,看了一眼感觉都好难鸭qwq。
听 yp 讲零基础逆袭故事,有点自卑。
继续听,更自卑了。
下午的开盒环节提前了,要说自己有没有高中信息学基础。思索了一下,挺可笑的,参加了几次 csp 和 noip 结果只是稍微会写签到题,甚至不会写签到题的水平,这能叫有基础么。
于是说了零基础,但大家好像不是很理解我。
听 yp 讲暑假集训有多残酷,感觉要拿到 div.1 的资格我还差得远。
不知不觉真的讲了一个半小时,期间 lyc 还率先开卷。我把所有题都阅览了一遍,感觉都入手不能,遂放弃。
后面合照不知道为什么不拍了,商量了一下去朝阳吃午饭。
朝阳二楼吃的 ¥17 原汤五谷牛肉,淡而无味。而且这粉我吃不惯,不知道是不是地域原因,这种细而溜的像粉丝一样的东西能有啥味?不理解。
当时阿姨本来想多给一块牛肉,结果夹了三次夹不上她直接放弃了,可惜!
如果能打 1~5 星的话这玩意最多 2 星。
回宿舍吹空调,但只吹了 15 分钟,又要赶 1 点的车回沙河搬东西。
不过好在这一来一回比上午那班车体验好多了,补了一点觉,但又感觉没补。
6 点,终于把行李搬上 6 楼了,虽然我带的行李应该是最少的,但这也太为难大胖子了。
床板质量令人堪忧,感觉一踩上去就会裂成几大块,不过铺上凉席之后感觉还行鸭。
7 点收到了波波王的果茶!好喝捏,幸福捏。
然后不知道干什么了,不知道是专题启动还是 tr 启动。
室友是不是都在学阿!打成共识,开泰!
怎么群号被群主复读了,这下似摸Q了。
【7.9】 Day 2
8 点 05 准时起床,看了眼专题过题情况,大家都好努力。但不计一血,我也不急。
早餐没吃,感觉以后也没什么必要。
xcy 讲课,感觉 ppt 做的好认真鸭,出乎意料的除了势能分析都听懂了,虽然讲的是最基础的 kmp。
接着 lxy 讲课,我爆了,z 函数听不懂一点,上面板书也小小的看不清。讲到后面写的更小了,这我听集贸啊,就不听了。
翻了下 oiwiki,写的一般鸭,更加认真地看了看,还是放弃了,去翻洛谷题解了。
稍微会了点,果然有点图示会好很多。
提前下课!好也不好,外卖点了个 ¥20 的猪脚饭。时间还早,冒雨去便利店买了点物资,这便利店完爆沙河。
外卖被偷了。骑手找了半天,说一分钟前刚放。我不知道该说什么,到了清水河这边干啥都不顺,心态感觉不出几天就垮完了。
中午补了一下课件上提到的四题。
【CF1200E Compress Words】
题意:给定 \(n\) 个单词,需要依次合并他们,使得最终单词尽可能短。
\(\sum|S|\le 10^6\)。
需要尽可能短,那对于合并后的母串 \(S\) 和待并入的子串 \(T\),要找到 \(S\) 的最长后缀使之和 \(T\) 相应长度的前缀等同。
不难发现所求即为 \(T + S\) 的 border。
对于每一个串都要对 \(T+S\) 做一次 KMP 是不能接受的,因为 \(S\) 会随着合并越来越长。
由于我们只关心 border,所以只需要截取 \(S[\max(0,|S|-|T|),|S|]\)。
故每回合用来跑 KMP 的串为 \(T + @ + S[\max(0,|S|-|T|),|S|]\)。
中间的特殊字符是用来防止相交的,例如 \(S =aba\),\(T = aaba\),若使用 \(aabaaba\),border 是 \(4\),而 \(1\) 是正确的,所以使用 \(aaba@aba\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define die(x) { cout << x << "\n";return ;}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
string ans = "";
while (n--) {
string s;
cin >> s;
string t = " " + s + "@" + ans.substr(ans.size() - min(ans.size(), s.size()));
vector<int> fail(t.size());
for (int i = 2, p = 0; i < t.size(); i++) {
while (p && t[i] != t[p + 1]) {
p = fail[p];
}
if (t[i] == t[p + 1]) {
p++;
}
fail[i] = p;
}
ans += s.substr(fail[t.size() - 1]);
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}【P2375 [NOI2014] 动物园】
题意:求出一个 \(\text{num}\) 数组,\(\text{num}[i]\) 代表字符串 \(S[1,i]\) 的子串中既是它的后缀同时又是它的前缀,并且该后缀与该前缀不重合。
\(1 \le |S| \le 10^6\)。
暴力做法是跑 KMP,对每个 \(i\) 跳 fail,找出所有的 border。跳了几次 \(\text{num[i]}\) 就是多少。
不重叠也就是只把长度小于原串一半的 border 计入答案。
倍增优化,\(jp[i][j]\) 代表字符串第 \(i\) 个位置跳了 \(2^j\) 次后的 border 长度。
时间复杂度 \(O(|S|\log |S|)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define die(x) { cout << x << "\n";return ;}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
constexpr int modp = 1e9 + 7;
void solve() {
string s;
cin >> s;
s = " " + s;
int n = s.size();
vector<int> fail(n);
vector jp(n, vector<int>(25));
for (int i = 2, p = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (p && s[i] != s[p + 1]) {
p = fail[p];
}
if (s[i] == s[p + 1]) {
p++;
}
fail[i] = p;
jp[i][0] = fail[i];
}
for (int j = 1; j < 25; j++) {
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
jp[i][j] = jp[ jp[i][j - 1] ][j - 1];
}
}
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x = i;
for (int j = 24; j >= 0; j--) {
if (jp[x][j] * 2 > i) {
x = jp[x][j];
}
}
int res = 0;
for (int j = 24; j >= 0; j--) {
if (jp[x][j]) {
res += 1LL << j;
x = jp[x][j];
}
}
ans *= (res + 1) % modp;
ans %= modp;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}但这个跳了几次的问题在预处理时就能记录。
因为每转移一次相当于跳了的次数 \(+1\),假如更新了
fail[i] = p,那么直接 num[i] = num[p] + 1
即可。
不重叠同上处理,跳到长度符合要求为止。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define die(x) { cout << x << "\n";return ;}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
constexpr int modp = 1e9 + 7;
void solve() {
string s;
cin >> s;
s = " " + s;
int n = s.size();
vector<int> fail(n), num(n);
num[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2, p = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (p && s[i] != s[p + 1]) {
p = fail[p];
}
if (s[i] == s[p + 1]) {
p++;
}
fail[i] = p;
num[i] = num[p] + 1;
}
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 2, p = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (p && s[i] != s[p + 1]) {
p = fail[p];
}
if (s[i] == s[p + 1]) {
p++;
}
while (p * 2 > i) {
p = fail[p];
}
ans *= (num[p] + 1) % modp;
ans %= modp;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}【P3435 [POI2006] OKR-Periods of Words】
题意:给定字符串 \(S\),对于字符串 \(T\),称 \(T\) 是 \(S\) 的周期当且仅当 \(T\) 是 \(S\) 的真前缀且 \(S\) 是 \(T + T\) 的前缀。
求给定 \(S\) 的所有前缀的最大周期长度之和。
\(1 \le |S| \le 10^6\)。
\(S\) 是 \(T+T\) 的前缀可以理解为把 \(S\) 的一个前缀复制一份之后能完全包含 \(S\)。
设这个前缀为 \(S[1,i]\),那么 \(S[i+1,|S|]\) 必然和 \(S[1,|S|-i]\) 相等,即把前缀拿走之后剩余的部分必须是原串的一个 border。
这个前缀又要最长,那么就是最短 border。
根据 fail 数组的性质,一直跳到空串之前即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define die(x) { cout << x << "\n";return ;}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n;
string s;
cin >> n >> s;
s = " " + s;
vector<int> fail(n + 1);
for (int i = 2, p = 0; i <= n; i++) {
while (p && s[i] != s[p + 1]) {
p = fail[p];
}
if (s[i] == s[p + 1]) {
p++;
}
fail[i] = p;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int p = i;
while (fail[p]) {
p = fail[p];
}
if (fail[i]) {
fail[i] = p;
}
ans += i - p;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}【P5829 【模板】失配树】
题意:给定一个字符串 \(S\),\(m\) 组询问。每次给定 \(p,q\),求 \(S\) 的 \(p\) 前缀和 \(q\) 前缀的最长公共 border 的长度。
\(1\le p,q\le |S| \le 10^6\),\(1\le m \le 10^5\)。
fail 树,顾名思义就是连边 \(fail[i] \to i\) 形成的树,不断往上跳父亲跳到根就能得到这个字符串所有的 border。
那题目所求相当于 fail 树上点 \(p\) 和点 \(q\) 的 \(\text{LCA}\)。
特别注意:如果求出来的 \(\text{LCA}\) 是 \(p\) 或者 \(q\),那么还要往上跳一格,因为自己不是自己的 border。
时间复杂度 \(O(m\log |S|)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define die(x) { cout << x << "\n";return ;}
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
string s;
cin >> s;
int n = s.size();
s = " " + s;
vector<int> fail(n + 1);
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
adj[0].push_back(1);
for (int i = 2, p = 0; i <= n; i++) {
while (p && s[i] != s[p + 1]) {
p = fail[p];
}
if (s[i] == s[p + 1]) {
p++;
}
fail[i] = p;
adj[fail[i]].push_back(i);
}
vector<vector<int>> fa(n + 1, vector<int>(25, 0));
vector<int> depth(n + 1);
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int fath) -> void {
fa[x][0] = fath;
depth[x] = depth[fath] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= __lg(depth[x]) + 1; i++) {
fa[x][i] = fa[fa[x][i - 1]][i - 1];
}
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y != fath) {
self(self, y, x);
}
}
};
auto LCA = [&] (int x, int y) {
if (depth[x] < depth[y]) {
swap(x, y);
}
while (depth[x] > depth[y]) {
x = fa[x][__lg(depth[x] - depth[y])];
}
if (x == y) {
return x;
}
for (int i = __lg(depth[x]); i >= 0; i--) {
if (fa[x][i] != fa[y][i]) {
x = fa[x][i];
y = fa[y][i];
}
}
return fa[x][0];
};
dfs(dfs, 0, 0);
int m;
cin >> m;
while (m--) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
int res = LCA(x, y);
if (res == x || res == y) {
res = fa[res][0];
}
cout << res << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}下午 QHJ 讲计算几何,没睡过,但雨一直下,走过去还要 20 分钟,摆!
看了看集训计划确认了每个专题第一节不点名,就呆在宿舍听了。
然后就后悔了,声音断断续续的,基本就是看 PPT。
怎么感觉都是套板子鸭,很符合我之前对计算几何的印象。
但我怎么例题都不会做鸭(
正好有一段声音几乎没了,估计是在黑板上涂涂写写,我听着也难受,就去做了两个 PPT 上的题。
感觉下午亏麻了鸭!
【2024 四川省赛】F. Isoball: 2D Version
题意:给定一个圆和一个平行坐标轴的矩形,现给定一组方向向量,该圆开始沿此方向运动,问是否存在一个时刻使得圆完全包含在给定矩形中。
当圆完全被矩形包含时,圆心到该矩形四条边的距离均 \(\ge r\)。
那么我们可以把这个矩形的四条边向彼此均移动 \(r\),得到一个缩小版矩形。
此时只需要判断圆心是否在这个缩小版矩形中。
圆心的轨迹是一条射线,题目也转化为该射线是否和矩形的某一条边有交点。
射线求交即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define die(x) { cout << x << "\n";return ;}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
template<class T>
struct Point {
T x, y;
Point(T x_ = 0, T y_ = 0) : x(x_), y(y_) {}
template<class U>
operator Point<U>() {
return Point<U>(U(x), U(y));
}
Point &operator+=(Point p) & {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
return *this;
}
Point &operator-=(Point p) & {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
return *this;
}
Point &operator*=(T v) & {
x *= v;
y *= v;
return *this;
}
Point operator-() const {
return Point(-x, -y);
}
friend Point operator+(Point a, Point b) {
return a += b;
}
friend Point operator-(Point a, Point b) {
return a -= b;
}
friend Point operator*(Point a, T b) {
return a *= b;
}
friend Point operator*(T a, Point b) {
return b *= a;
}
friend bool operator==(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y;
}
};
template<class T>
T cross(Point<T> a, Point<T> b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
template<class T>
struct Line {
Point<T> a, b;
Line(Point<T> a_ = Point<T>(), Point<T> b_ = Point<T>()) : a(a_), b(b_) {}
};
template<class T>
Point<T> lineIntersection(Line<T> l1, Line<T> l2) {
return l1.a + (l1.b - l1.a) * (cross(l2.b - l2.a, l1.a - l2.a) / cross(l2.b - l2.a, l1.a - l1.b));
}
template<class T>
bool pointOnSegment(Point<T> p, Line<T> l) {
return cross(p - l.a, l.b - l.a) == 0 && min(l.a.x, l.b.x) <= p.x && p.x <= max(l.a.x, l.b.x)
&& min(l.a.y, l.b.y) <= p.y && p.y <= max(l.a.y, l.b.y);
}
// 0 : not intersect
// 1 : strictly intersect
// 2 : overlap
// 3 : intersect at endpoint
template<class T>
tuple<int, Point<T>, Point<T>> segmentIntersection(Line<T> l1, Line<T> l2) {
if (max(l1.a.x, l1.b.x) < min(l2.a.x, l2.b.x)) {
return {0, Point<T>(), Point<T>()};
}
if (min(l1.a.x, l1.b.x) > max(l2.a.x, l2.b.x)) {
return {0, Point<T>(), Point<T>()};
}
if (max(l1.a.y, l1.b.y) < min(l2.a.y, l2.b.y)) {
return {0, Point<T>(), Point<T>()};
}
if (min(l1.a.y, l1.b.y) > max(l2.a.y, l2.b.y)) {
return {0, Point<T>(), Point<T>()};
}
if (cross(l1.b - l1.a, l2.b - l2.a) == 0) {
if (cross(l1.b - l1.a, l2.a - l1.a) != 0) {
return {0, Point<T>(), Point<T>()};
} else {
auto maxx1 = max(l1.a.x, l1.b.x);
auto minx1 = min(l1.a.x, l1.b.x);
auto maxy1 = max(l1.a.y, l1.b.y);
auto miny1 = min(l1.a.y, l1.b.y);
auto maxx2 = max(l2.a.x, l2.b.x);
auto minx2 = min(l2.a.x, l2.b.x);
auto maxy2 = max(l2.a.y, l2.b.y);
auto miny2 = min(l2.a.y, l2.b.y);
Point<T> p1(max(minx1, minx2), max(miny1, miny2));
Point<T> p2(min(maxx1, maxx2), min(maxy1, maxy2));
if (!pointOnSegment(p1, l1)) {
swap(p1.y, p2.y);
}
if (p1 == p2) {
return {3, p1, p2};
} else {
return {2, p1, p2};
}
}
}
auto cp1 = cross(l2.a - l1.a, l2.b - l1.a);
auto cp2 = cross(l2.a - l1.b, l2.b - l1.b);
auto cp3 = cross(l1.a - l2.a, l1.b - l2.a);
auto cp4 = cross(l1.a - l2.b, l1.b - l2.b);
if ((cp1 > 0 && cp2 > 0) || (cp1 < 0 && cp2 < 0) || (cp3 > 0 && cp4 > 0) || (cp3 < 0 && cp4 < 0)) {
return {0, Point<T>(), Point<T>()};
}
Point p = lineIntersection(l1, l2);
if (cp1 != 0 && cp2 != 0 && cp3 != 0 && cp4 != 0) {
return {1, p, p};
} else {
return {3, p, p};
}
}
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
double x, y, r, vx, vy;
cin >> x >> y >> r >> vx >> vy;
double lx, ly, rx, ry;
cin >> lx >> ly >> rx >> ry;
lx += r;
rx -= r;
ly += r;
ry -= r;
if (lx > rx || ly > ry) {
cout << "No\n";
return ;
}
double mx = 1e7;
Line<double> l({x, y}, {x + vx * mx, y + vy * mx});
vector<Line<double>> lines = {
{{lx, ly}, {rx, ly}},
{{rx, ly}, {rx, ry}},
{{rx, ry}, {lx, ry}},
{{lx, ry}, {lx, ly}}
};
for (auto line : lines) {
if (get<0>(segmentIntersection(l, line)) > 0) {
cout << "Yes\n";
return ;
}
}
cout << "No\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}晚饭还是点外卖,一雪前耻。点了个 ¥27 的麻辣香锅,好吃捏好吃捏,分量也足,能有 4 星半(?)
专题还是不想做,动力全无。
研究了一下 PPT,本来想搞一套自己的板子,最后还是直接扒的 jiangly 的,因为哥哥写的代码实在是太好看了鸭。不过流传的版本缺失了很多内容,我照葫芦画瓢补了点上去。
专题有几题过了挺多人了,跟下榜?
十分钟写了个签到 pick 定理,然后坐了两小时牢。
菜输了,感觉还没到能徒手干专题的水平,先放着好了。
【7.10】 Day 3
起床,洗漱。
然后发现不对。
我趣,怎么我 8 点 05 的闹钟定成 7 点 05 了,太难崩了。
不知道舍友是不是被我吵醒了,脑子越来越不好使了,完蛋。
不想睡回笼觉,溜了一遍昨天学的 z 函数和 manacher。
到教室了,感觉今天讲的内容挺重要的,就坐在了前排。
结果中间想爆一下群巨被抓包了qwq。
徐神讲课还是讲得超级棒口牙,都听懂了(吗?)
甚至细到现写代码,好贴心鸭/se/se/se
后面 lxy
讲课一如既往的听不懂:讲序列自动机,嗯,开始听,讲完了?讲最小表示法,开始听,听不懂,讲完了?到
Lyndon 分解,讲完了?问我们听没听懂,此时的我
belike:(数据删除)
中午想着要不要去图书馆借个词典,但懒了,希望下午不要伏笔回收。
又点了一次昨天那个麻辣香锅,只不过换了个口味,爽爽爽。
今天还是不想睡午觉,正好 xjj 问我第二次队内赛的 H,我想起那题之前我线段树优化建图被卡爆了,就稍微写了写。
对着题解搓了一发前后缀优化建图,直接 AC,爽!
【2024 - 暑假前集训队内赛 2 - H. 金铲铲,启动!】
和图论专题 L 很类似,看题识 2sat,对于拥有小羁绊的奕子 \(u\) 和 \(v\),有 \(u \lor v\)。
而对于拥有相同大羁绊的奕子集合 \(s\),\(\forall x,y\in s\),\(\lnot x \lor \lnot y\)。
可以线段树优化建图,每个集合中的第 \(i\) 个点向第 \([1,i-1]\) 和第 \([i+1,|s|]\) 的点连边。
但这样连的边还是太多了,需要采用前后缀优化建图。
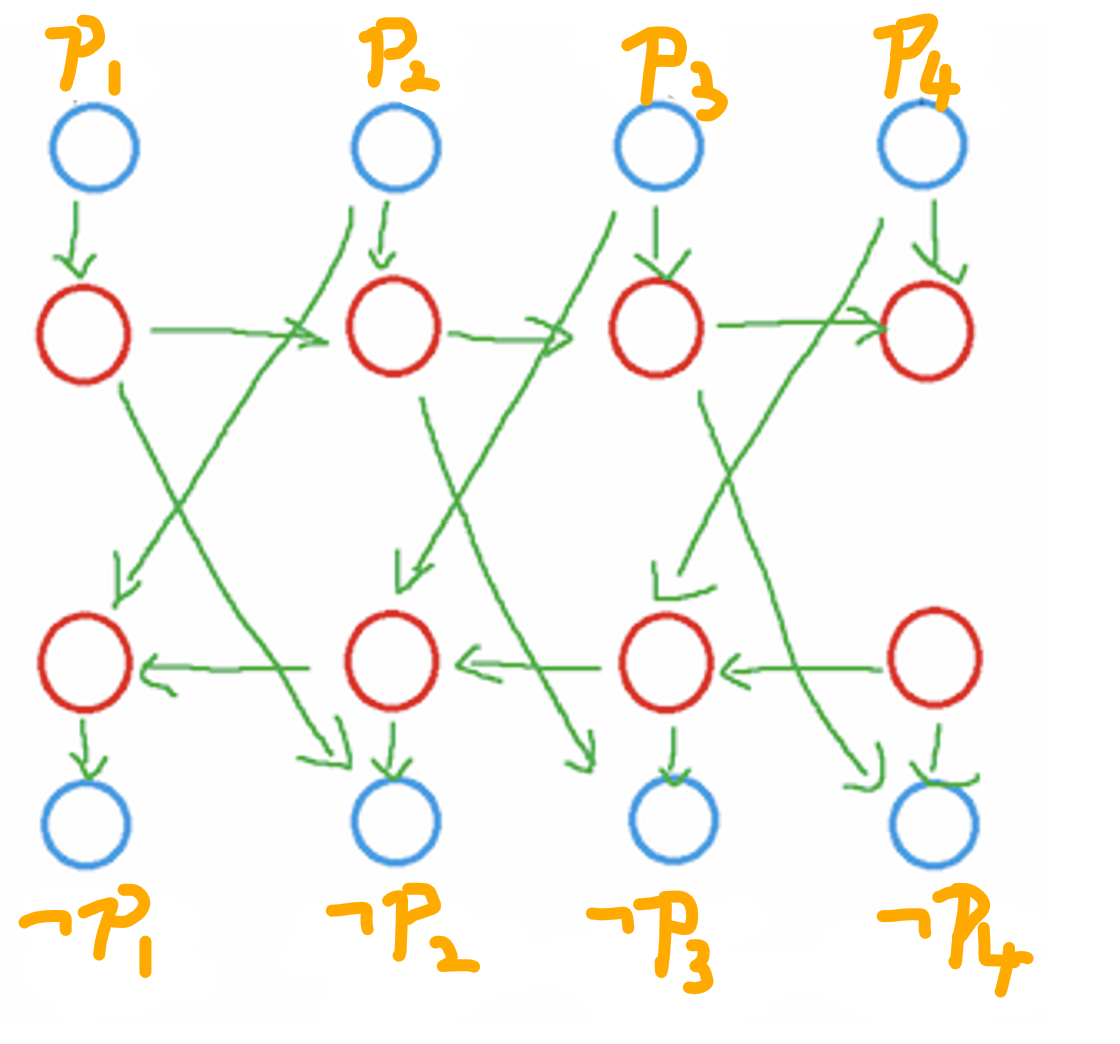
如图连边即可。第一次见到,很智慧。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define die(x) { cout << x << "\n";return ;}
#define inf INT_MAX
struct SegEdge {
int n, K, all;
vector<vector<array<int, 2>>> adj;
vector<int> id;
SegEdge() {}
SegEdge(int n) {
this->n = n;
K = 4 * n;
all = 8 * n;
adj.resize(all + 1);
id.resize(n + 1);
build(1, 1, n);
init(n);
}
void init(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
adj[id[i]].push_back({id[i] + K, 0});
adj[id[i] + K].push_back({id[i], 0});
}
}
void build(int p, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) return id[l] = p, void();
adj[p].push_back({p << 1, 0});
adj[p].push_back({p << 1 | 1, 0});
adj[(p << 1) + K].push_back({p + K, 0});
adj[(p << 1 | 1) + K].push_back({p + K, 0});
int mid = l + r >> 1;
build(p << 1, l, mid);
build(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
}
void addEdge(int p, int l, int r, int lx, int rx, int x, int w, int opt) {
if (lx <= l && r <= rx) {
if (opt == 1) adj[x + K].push_back({p, w});
else adj[p + K].push_back({x, w});
return ;
}
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (lx <= mid) addEdge(p << 1, l, mid, lx, rx, x, w, opt);
if (rx > mid) addEdge(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, lx, rx, x, w, opt);
}
void PtoP(int x, int y, int w) {
adj[id[x] + K].push_back({id[y], w});
}
void PtoS(int x, int l, int r, int w) {
addEdge(1, 1, n, l, r, id[x], w, 1);
}
void StoP(int l, int r, int x, int w) {
addEdge(1, 1, n, l, r, id[x], w, 2);
}
};
struct TwoSat {
int n;
TwoSat(int n) {
this->n = n;
}
void addbind(SegEdge &seg, int x, bool ok1, int y, bool ok2) {
seg.PtoP(x + n / 8 * (!ok1), y + n / 8 * ok2, 1);
seg.PtoP(y + n / 8 * (!ok2), x + n / 8 * ok1, 1);
}
bool work(SegEdge &seg) {
vector<int> dfn(2 * n + 1), low(2 * n + 1);
vector<int> stack_(2 * n + 1), c(2 * n + 1);
vector<bool> vis(2 * n + 1, false);
int tim = 0, top = 0, cnt = 0;
function<void(int)> tarjan = [&](int x) {
dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim;
vis[x] = true;
stack_[++top] = x;
for (auto [y, _] : seg.adj[x]) {
if (!dfn[y]) {
tarjan(y);
low[x] = min(low[x], low[y]);
} else if (vis[y]) {
low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[y]);
}
}
if (dfn[x] == low[x]) {
int now; ++cnt;
do{
now = stack_[top--];
vis[now] = false;
c[now] = cnt;
} while (x != now);
}
};
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++) {
if (!dfn[i]) tarjan(i);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n / 8; i++) {
if (c[seg.id[i]] == c[seg.id[i + n / 8]]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, m, k;
cin >> n >> m >> k;
vector<array<int, 2>> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
a[i] = {x, i};
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
vector<int> ys(n + 1), R(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
R[a[i][0]] = max(R[a[i][0]], i);
ys[a[i][1]] = i;
}
SegEdge seg(2 * n);
TwoSat ts(8 * n);
auto Add = [&] (int x, int l, int r) {
seg.PtoS(x + n, l, r, 1);
seg.StoP(l + n, r + n, x, 1);
};
int now = n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (R[a[i][0]] != i) {
int l = i + 1;
int r = R[a[i][0]];
Add(i, l, r);
}
}
while (m--) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
x = ys[x];
y = ys[y];
ts.addbind(seg, x, 1, y, 1);
}
int ans = ts.work(seg);
if (ans) {
cout << "Teamfight Tactics\n";
} else {
cout << "Crown Legends: Battlefury\n";
}
}
signed main() {
// fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define die(x) { cout << x << "\n";return ;}
#define inf INT_MAX
struct TwoSat {
int n;
vector<vector<int>> adj;
vector<int> ans;
TwoSat(int n) {
this->n = n;
adj.resize(2 * n + 1);
ans.resize(n + 1);
}
void addbind(int x, bool ok1, int y, bool ok2) {
adj[x + n * (!ok1)].push_back(y + n * ok2);
adj[y + n * (!ok2)].push_back(x + n * ok1);
}
bool work() {
vector<int> dfn(2 * n + 1), low(2 * n + 1);
vector<int> stack_(2 * n + 1), c(2 * n + 1);
vector<bool> vis(2 * n + 1, false);
vector<vector<int>> scc(2 * n + 1);
int tim = 0, top = 0, cnt = 0;
function<void(int)> tarjan = [&](int x) {
dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim;
vis[x] = true;
stack_[++top] = x;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (!dfn[y]) {
tarjan(y);
low[x] = min(low[x], low[y]);
} else if (vis[y]) {
low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[y]);
}
}
if (dfn[x] == low[x]) {
int now; ++cnt;
do{
now = stack_[top--];
vis[now] = false;
c[now] = cnt;
scc[cnt].push_back(now);
} while (x != now);
}
};
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++) {
if (!dfn[i]) tarjan(i);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (c[i] == c[i + n]) return false;
ans[i] = c[i] > c[i + n] ? 1ll : 0ll;
}
return true;
}
vector<int> getans() {
return ans;
}
};
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, m, k;
cin >> n >> m >> k;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
vector<vector<int>> b(k + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
b[a[i]].push_back(i);
}
TwoSat ts(2 * n);
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
if (b[i].empty()) {
continue;
}
for (int j = 0; j < b[i].size(); j++) {
ts.adj[b[i][j] + 2 * n].push_back(b[i][j] + 3 * n);
ts.adj[b[i][j] + n].push_back(b[i][j]);
if (j + 1 < b[i].size()) {
ts.adj[b[i][j] + 3 * n].push_back(b[i][j + 1] + 3 * n);
}
if (j - 1 >= 0) {
ts.adj[b[i][j] + n].push_back(b[i][j - 1] + n);
}
if (j + 1 < b[i].size()) {
ts.adj[b[i][j] + 3 * n].push_back(b[i][j + 1]);
}
if (j - 1 >= 0) {
ts.adj[b[i][j] + 2 * n].push_back(b[i][j - 1] + n);
}
}
}
while (m--) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
ts.addbind(x, 1, y, 1);
}
if (ts.work()) {
cout << "Teamfight Tactics\n";
} else {
cout << "Crown Legends: Battlefury\n";
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}下午队内赛,寄完了,3/10(Rank 5)
一开始随机开题,感觉 C 一眼,然后开始写,然后就不会写了,最后也没写出来。
F 题意挂了一个半小时,最后终于读懂了是 “开始和移动过程可能在同一个位置,最后不能在同一个位置,也就是一串连续的坐标,然后除了递增还可能是递减”。
E 题意至少读了 10 遍,还是搞不懂这题想求什么。我怎么感觉只有每个字符串的首字母有用,样例我也搞不懂。
挺唐的,赛时感觉很多题都能猜到是怎么做的,但写不出来。
菜。
晚饭在商业街吃了个炸鸡,一般,三星。
回到宿舍 emo 完洗完澡就 10 点了(???中间干了什么???)。
补了两题就过 12 点了,AC 自动机的例题还没看(
完蛋了完蛋了完蛋了完蛋了完蛋了完蛋了完蛋了完蛋了。
【队内赛 1E - gym104022 K. Browser Games】
题意:给定 \(n\) 个字符串 \(\{s\}\),对于每个 \(i\in[1, n]\) 回答最少用几个字符串组成字符串集 \(T\),才能使第 \(1\sim i\) 个字符串在 \(T\) 中都至少有一个前缀,且第 \(i + 1\sim n\) 个字符串的所有前缀在 \(T\) 中不存在。
\(1 \le n \le 5\cdot 10^4\),\(|s| \le 50\),字符串含 \(a\sim z\),小数点和斜杠。
考虑增加了一个字符串,那么这个字符串在增加之前造成的限制消失了,消失了多少?
我们把字符串放到 trie
树上考虑,记录每个节点最近一次的访问来自于哪个字符串(flag)以及字符串末尾标记(id)。增加字符串
\(i\) 时,可以从 id[i]
不断向上跳父亲,直到节点 flag 不为 \(i\)
为止,目前这段链就是使得答案增加的罪魁祸首。
为了统计增加了多少,我们再为 trie 树上的每个节点引入标记
cnt。意为该节点确认作为 \(T\)
中的一个答案:每次跳父亲之后,所在的满足 flag 不为
i 的节点就确认作为一个前缀,因此
cnt++;而每次答案也减少了这条链上的 cnt
个数。
时间复杂度 \(O(n|s|)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define double long double
struct Trie {
static constexpr int S = 28;
struct Node {
int fa, flag, cnt;
array<int, S> nxt;
Node() : fa{-1}, flag{-1}, cnt{0}, nxt{} {}
};
vector<Node> t;
Trie() {
t.assign(2, Node());
t[0].nxt.fill(1);
t[1].fa = 0;
}
int newNode() {
t.emplace_back();
return t.size() - 1;
}
int add(string s, int i) {
int p = 1;
for (auto c : s) {
int x;
if (c == '.') {
x = 26;
} else if (c == '/') {
x = 27;
} else {
x = c - 'a';
}
if (t[p].nxt[x] == 0) {
t[p].nxt[x] = newNode();
t[t[p].nxt[x]].fa = p;
}
p = t[p].nxt[x];
t[p].flag = i;
}
return p;
}
int next(int p, int x) {
return t[p].nxt[x];
}
int flag(int p) {
return t[p].flag;
}
int cnt(int p) {
return t[p].cnt;
}
int fa(int p) {
return t[p].fa;
}
int size() {
return t.size();
}
};
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
Trie tr;
vector<int> id(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string s;
cin >> s;
id[i] = tr.add(s, i);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int res = 0;
int j = id[i];
while (i == tr.flag(j)) {
res += tr.cnt(j);
j = tr.fa(j);
}
tr.t[j].cnt++;
ans += 1 - res;
cout << ans << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
// fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}但它 MLE 了,所以还要提前 reserve 一下(唉,卡常。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define double long double
struct Trie {
static constexpr int S = 28;
static constexpr int N = 2.5e6 + 2;
struct Node {
int fa, flag, cnt;
array<int, S> nxt;
Node() : fa{-1}, flag{-1}, cnt{0}, nxt{} {}
};
vector<Node> t;
Trie() {
t.reserve(N);
t.assign(2, Node());
t[0].nxt.fill(1);
t[1].fa = 0;
}
int newNode() {
t.emplace_back();
return t.size() - 1;
}
int add(string s, int i) {
int p = 1;
for (auto c : s) {
int x;
if (c == '.') {
x = 26;
} else if (c == '/') {
x = 27;
} else {
x = c - 'a';
}
if (t[p].nxt[x] == 0) {
t[p].nxt[x] = newNode();
t[t[p].nxt[x]].fa = p;
}
p = t[p].nxt[x];
t[p].flag = i;
}
return p;
}
int next(int p, int x) {
return t[p].nxt[x];
}
int flag(int p) {
return t[p].flag;
}
int cnt(int p) {
return t[p].cnt;
}
int fa(int p) {
return t[p].fa;
}
int size() {
return t.size();
}
};
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
Trie tr;
vector<int> id(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string s;
cin >> s;
id[i] = tr.add(s, i);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int res = 0;
int j = id[i];
while (i == tr.flag(j)) {
res += tr.cnt(j);
j = tr.fa(j);
}
tr.t[j].cnt++;
ans += 1 - res;
cout << ans << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}【队内赛 1B - gym104022 B. The Great Wall】
题意:给定长为 \(n\) 的数组,你需要将其划分为 \(k\) 段,定义每段的权值为该段元素的极差,总权值为各段的权值和。对每个 \(k=1\sim n\) 给出最大总权值。
\(1 \le n \le 10^4\),\(1 \le a_i \le 10^5\)。
妙妙题,第一步转化就十分 amazing。
一眼 dp,但每段的极差不好处理。不妨把极差转化为 \(\max(将该段一个数 \times 1,一个数 \times -1\ 后二者的和)\)。
令 \(dp[i][j][k=0\sim3]\) 表示处理了前 \(i\) 个数,分成了 \(j\) 段,且此时第 \(j\) 段的状态为 \(k\)。
\(k = 0\):既没有选 \(\times1\) 的数,也没有选 \(\times -1\) 的数。
\(k = 1\):已经选了 \(\times -1\) 的数,但没选 \(\times 1\) 的数。
\(k = 2\):已经选了 \(\times 1\) 的数,但没选 \(\times -1\) 的数。
\(k = 3\):已经选了 \(\times 1\) 的数,也选了 \(\times -1\) 的数。
这样就可以转移了,第一维可以滚动。
时间复杂度 \(O(n^2)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
vector dp(2, vector(n + 1, vector<int>(4, -inf)));
dp[0][0][3] = 0;
int t = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
t ^= 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
dp[t][j][0] = max(dp[t ^ 1][j][0],
dp[t ^ 1][j - 1][3]);
dp[t][j][1] = max({dp[t ^ 1][j][1],
dp[t ^ 1][j - 1][3] + a[i],
dp[t ^ 1][j][0] + a[i]});
dp[t][j][2] = max({dp[t ^ 1][j][2],
dp[t ^ 1][j - 1][3] - a[i],
dp[t ^ 1][j][0] - a[i]});
dp[t][j][3] = max({dp[t ^ 1][j][3],
dp[t ^ 1][j - 1][3],
dp[t ^ 1][j][2] + a[i],
dp[t ^ 1][j][1] - a[i]});
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << dp[t][i][3] << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}【队内赛 1J - gym102920 H. Needle】
题意:有三条平行 \(x\) 轴直线,直线上有缺口,三条直线上的缺口坐标分别给定为 \(\{a\},\{b\},\{c\}\),问有多少组三点共线。
\(1 \le n_a,n_b,n_c \le 5\cdot 10^4\),\(-3\cdot10^4 \le a_i,b_i,c_i \le 3\cdot 10^4\)。
结论:等效于求满足 \(a_i+c_k=2\cdot b_j\) 的三元组 \((i, j, k)\) 的数量。由中点性质易证。
移项,得 \(a_i - b_j = -c_k + b_j\)。
将 \(a_i\) 和 \(-c_k\) 存到 bitset 中,一个左移 \(b_j\) 一个右移 \(b_j\),之后 \(\&\) 起来为 \(1\) 的位置数目就是所求。
可以直接调用 bitset 中的 count() 函数,时间复杂度 \(O(\frac{n^2}{w})\)。
注意负数,需要整体加一个数全变为正数。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
constexpr int N = 6e4 + 5;
constexpr int eps = 3e4;
void solve() {
int A;
cin >> A;
bitset<N> a;
for (int i = 1; i <= A; i++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
a[x + eps] = 1;
}
int B;
cin >> B;
vector<int> b(B + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= B; i++) {
cin >> b[i];
}
int C;
cin >> C;
bitset<N> c;
for (int i = 1; i <= C; i++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
c[-x + eps] = 1;
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= B; i++) {
if (b[i] > 0) {
ans += ( (a >> b[i]) & (c << b[i]) ).count();
} else {
ans += ( (a << (-b[i]) ) & (c >> (-b[i]) ) ).count();
}
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}凌晨两点多了,AC 自动机的例题明天再说叭。
【7.11】 Day 4
被闹钟闹醒了,困困困,困困困。
上午听课,两个人讲课听起来都很舒服鸭,也不会很困。
一个是 lg,另一个是 QHJ 还是 pmh?昨天没来,不知道 QHJ 长啥样,不知道是谁。
凸包进阶那块感觉理解还差一点,计算几何我认为结合代码来学理论才能有更深的理解。
圆这部分同样,听能听懂,但代码就不知道怎么写了,后面还要自己摸索一下。
11 点不到就结束了。
中午在朝阳吃 ¥16 水煮牛肉,本来想打四星,但肉不过瘾,那就三星半。
回去没补例题,去做昨天队内赛的 C 了,一个多小时调不出来,红温了,睡了半小时。
下午队内赛 2,我怎么又寄了。5/8(Rank 9)
开完两道究极签到,然后看了眼榜,有人过 D 了,就去看了 D,然后我怎么就看了一个半小时。
怎么大家都会 D,自闭了。一开始想的是也许构造一个 \(2 \times 2\) 的就可以。然后脑子烧了,绕来绕去的。
过了一个小时才想到研究一下样例,感觉 \(2\times 3\) 可行,就是从 \((1, 1)\) 到 \((2,2)\) 决策的时候选择错误的 \((2,1)\) 而不是 \((1,2)\),但脑子又烧了。
看了下榜,怎么就到第二页了,急了。
去看了 E 和 F,E 马上能注意到满足条件的是一个矩形,但后面没想清楚就交,WA 了两发,不过马上就想清楚了。F 秒了。
直到这会稍微冷静了才会了 D,唉。
又急了,排名还是拉跨,看了下 C,但怎么只剩半小时了,乱交几发,不出意外过不了一点( * * * 晚上¥26 炙烤蟹柳寿司,好吃,四星。
然后继续和昨天队内赛 C 搏斗,搏斗完怎么九点了?????
一想到还有好多工作没做就难受。
【队内赛 1C - gym104022 D. Farm】
题意:给定一个 \(n\) 个点的图,一开始没有边。再给定 \(m\) 条边,边有边权,意为联通代价。你需要花最少的代价让图联通,同时必须满足 \(q\) 个限制条件。第 \(i\) 个条件形如从编号为 \(u_i\) 和 \(v_i\) 的边中至少选择一条。输出最小代价。
\(1 \le n \le 10^5\),\(1 \le m \le 5 \cdot 10^5\),\(0 \le q\le 16\)。
看 \(q\) 范围知二进制枚举,此时直接枚举边做最小生成树,是 \(O(2^q \cdot q\cdot m\alpha)\)。
瓶颈是枚举的边太多了,可以想象 \(q\) 既然小,那么在最后的生成树中一定有很多边是确定的,不受限制条件的约束。
考虑将所有限制条件中的边(即每一个 \(u_i\) 和每一个 \(v_i\))都建出来,然后跑最小生成树,此时新建出来的边(以下称作固定边)就是必须要选的。
那我们继续考虑一个只有固定边的新图 \(G\),此时需要枚举的边是 “两个端点在 \(G\) 中不连通的边”。用一个可持久化并查集执行每次加边,到新的二进制状态就回退,能过吗?还是不能,因为边还是太多了,如果每一个孤立点都和其它所有点连边,就是 \(O(nq)\) 的边。
但我们注意到除了孤立点以外的 \(G\)
是一个大的连通块,我们用一个 std::map
存联通任意两个连通块的最小边,这样边数就是 \(O(q^2)\) 的了。
时间复杂度 \(O(m\log m+2^q \cdot q^2)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define inf 0x7fffffff
struct DSU {
vector<int> f, siz;
vector<array<int, 3>> ver;
DSU() {}
DSU(int n) { init(n);}
void init(int n) {
f.resize(n + 2);
iota(f.begin(), f.end(), 0);
siz.assign(n + 2, 1);
}
int find(int x) {
if (x == f[x]) return x;
return find(f[x]);
}
bool same(int x, int y) {
return find(x) == find(y);
}
bool merge(int x, int y) {
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x == y) return false;
if (siz[x] < siz[y]) {
swap(x, y);
}
ver.push_back({x, y, siz[x]});
siz[x] += siz[y];
f[y] = x;
return true;
}
int size(int x) {
return siz[find(x)];
}
void roll(int v) {
while (ver.size() > v) {
auto [x, y, szx] = ver.back();
ver.pop_back();
f[y] = y;
siz[x] = szx;
}
}
};
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<array<int, 3>> a;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x, y, w;
cin >> x >> y >> w;
a.push_back({w, x, y});
}
int q;
cin >> q;
vector<array<int, 2>> choose;
vector<int> have_choosed(m);
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
x--; y--;
choose.push_back({x, y});
have_choosed[x] = true;
have_choosed[y] = true;
}
DSU dsu(n);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (have_choosed[i]) {
dsu.merge(a[i][1], a[i][2]);
}
}
vector<array<int, 3>> sorted_a = a;
sort(sorted_a.begin(), sorted_a.end());
vector<array<int, 3>> must_choose;
for (auto [w, x, y] : sorted_a) {
if (dsu.merge(x, y)) {
must_choose.push_back({w, x, y});
}
}
DSU dsu2(n);
int ori_w = 0;
for (auto [w, x, y] : must_choose) {
dsu2.merge(x, y);
ori_w += w;
}
int ori_ver = dsu2.ver.size();
map<pair<int, int>, int> minw;
vector<array<int, 3>> waiting_choose;
for (auto [w, x, y] : sorted_a) {
int xx = dsu2.find(x);
int yy = dsu2.find(y);
if (xx == yy) {
continue;
}
if (!minw.count({xx, yy})) {
minw[{xx, yy}] = minw[{yy, xx}] = w;
waiting_choose.push_back({w, x, y});
}
}
int ans = inf;
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << q); i++) {
dsu2.roll(ori_ver);
int res = ori_w;
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
for (int j = 0; j < q; j++) {
int edge = choose[j][i >> j & 1];
if (mp[edge]) {
continue;
}
mp[edge] = true;
auto [w, x, y] = a[edge];
dsu2.merge(x, y);
res += w;
}
for (auto [w, x, y] : waiting_choose) {
if (dsu2.size(1) == n) {
break;
}
if (dsu2.merge(x, y)) {
res += w;
}
}
if (dsu2.size(1) == n) {
ans = min(ans, res);
}
}
if (ans == inf) {
ans = -1;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}
C++今天的队内赛明天再补好了,明天又是字符串专题,上次字符串专题还没搞懂一点。
写了下 AC 自动机课件上的五个例题。
【P5357 【模板】AC 自动机】
题意:给定一个文本串 \(S\) 和 \(n\) 个模式串 \(T_{1\sim n}\)。求每个模式串在文本串中的出现次数。
\(1 \le n,\sum|T| \le 2\cdot 10^5\),\(1\le |S| \le 2\cdot 10^6\)。
AC 自动机上 fail 指针指向的是最长真后缀。fail 指针构成一棵树。
那么当一个节点被匹配时,其祖先也被匹配。相当于每次将根到某个单词末尾的一条链上的点 +1。
可以在树上维护 sz[x],给 \(S\) 对应的链上的点
sz[x]++。
那么单词末尾对应的节点的 sz
就是它在文本串中的出现次数。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define die(x) { cout << x << "\n";return ;}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
struct ACTree {
static constexpr int S = 26;
struct Node {
int len, fail;
array<int, S> nxt;
Node() : len{0}, fail{0}, nxt{} {}
};
vector<Node> t;
ACTree() {
t.assign(2, Node());
t[0].nxt.fill(1);
t[0].len = -1;
}
int newNode() {
t.emplace_back();
return t.size() - 1;
}
int add(string s) {
int p = 1;
for (auto c : s) {
int x = c - 'a';
if (t[p].nxt[x] == 0) {
t[p].nxt[x] = newNode();
t[t[p].nxt[x]].len = t[p].len + 1;
}
p = t[p].nxt[x];
}
return p;
}
void work() {
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < S; i++) {
if (t[x].nxt[i] == 0) {
t[x].nxt[i] = t[t[x].fail].nxt[i];
} else {
t[t[x].nxt[i]].fail = t[t[x].fail].nxt[i];
q.push(t[x].nxt[i]);
}
}
}
}
int next(int p, int x) {
return t[p].nxt[x];
}
int fail(int p) {
return t[p].fail;
}
int len(int p) {
return t[p].len;
}
int size() {
return t.size();
}
};
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
ACTree G;
vector<int> id(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string s;
cin >> s;
id[i] = G.add(s);
}
G.work();
string t;
cin >> t;
vector<int> sz(G.size());
for (int i = 0, p = 1; i < t.size(); i++) {
int x = t[i] - 'a';
p = G.next(p, x);
sz[p]++;
}
vector<vector<int>> adj(G.size());
for (int i = 1; i < G.size(); i++) {
adj[G.fail(i)].push_back(i);
}
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x) -> void {
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
self(self, y);
sz[x] += sz[y];
}
};
dfs(dfs, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << sz[id[i]] << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
// fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}【P3966 [TJOI2013] 单词】
题意:给定 \(n\) 个单词,对每个单词询问在这 \(n\) 个单词组成的文章中出现了多少次。
例如给定 a aa
aaa,则第二个单词出现了 \(3\) 遍。
\(1 \le n \le 200\),$ 单词总长度 ^6$。
看了样例才读明白题。
和 AC 自动机模板的区别就是单词之间不能跨越。
那我们直接在中间插一个特殊字符就行了,其它都一样。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
struct ACTree {
static constexpr int S = 27;
struct Node {
int len, fail;
array<int, S> nxt;
Node() : len{0}, fail{0}, nxt{} {}
};
vector<Node> t;
ACTree() {
t.assign(2, Node());
t[0].nxt.fill(1);
t[0].len = -1;
}
int newNode() {
t.emplace_back();
return t.size() - 1;
}
int add(string s) {
int p = 1;
for (auto c : s) {
int x = c - 'a';
if (t[p].nxt[x] == 0) {
t[p].nxt[x] = newNode();
t[t[p].nxt[x]].len = t[p].len + 1;
}
p = t[p].nxt[x];
}
return p;
}
void work() {
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < S; i++) {
if (t[x].nxt[i] == 0) {
t[x].nxt[i] = t[t[x].fail].nxt[i];
} else {
t[t[x].nxt[i]].fail = t[t[x].fail].nxt[i];
q.push(t[x].nxt[i]);
}
}
}
}
int next(int p, int x) {
return t[p].nxt[x];
}
int fail(int p) {
return t[p].fail;
}
int len(int p) {
return t[p].len;
}
int size() {
return t.size();
}
};
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
string t = "";
ACTree G;
vector<int> id(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string s;
cin >> s;
t += s + "@";
id[i] = G.add(s);
}
G.work();
vector<int> sz(G.size());
for (int p = 1, i = 0; i < t.size(); i++) {
int x = t[i] - 'a';
if (t[i] == '@') {
x = 26;
}
p = G.next(p, x);
sz[p]++;
}
vector<vector<int>> adj(G.size());
for (int i = 1; i < G.size(); i++) {
adj[G.fail(i)].push_back(i);
}
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x) -> void {
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
self(self, y);
sz[x] += sz[y];
}
};
dfs(dfs, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << sz[id[i]] << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}【P2414 [NOI2011] 阿狸的打字机】
题意:给定一个含 \(a\sim z,B,P\) 的字符串 \(T\),现按规则生成字符串集合 \(S\):
有一个 Cache,初始为空,开始从左到右读取 \(T\) 中字符。
若读取到 \(a\sim z\),在 Cache 中加入相应字符。
若读取到 \(P\),将 Cache 中的字符串拷贝一份到 \(S\) 中。
若读取到 \(B\),删除 Cache 中最后一次加入的字符。
给定 \(m\) 个询问,每次给定 \(x, y\),询问 \(S\) 中的第 \(x\) 个字符串在第 \(y\) 个字符串中出现了几次。
\(1 \le x, y \le 10^5\),\(1 \le m \le 10^5\),\(1 \le |T| \le 10^5\)。
暴力是对于每一个询问都建 AC 自动机并询问。
进阶一点可以对于相同的 \(y\) 记录所有的 \(x\),这样是一次建树多次询问。
这里的 “建树” 是指给字符串 \(y\) 在
fail 树上对应的链设置 sz。
还可以更聪明一点,我们思考 \(P\) 操作和 \(B\) 操作的本质:
\(P\) 操作拷贝了一份 Cache,但迫于空间限制我们肯定不能显式储存,于是只储存该字符串的 endpos。
\(B\) 操作 “退格” 相当于将当前指针移动到父亲节点的位置。
这样我们就可以像读取一般字符串一样读取 \(T\) 了!
将 \(T\) 放到 AC 自动机上跑,对于
\(a\sim z\) 就直接
sz[p]++,删除操作就 sz[p]--。
对于询问,我们知道
endpos,相当于子树求和,而上一行的两个操作相当于单点加,就有用树状数组维护
sz 的思路了。对着 fail 树进行 dfs,记录 dfn 即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(|T|+m)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
template <typename T>
struct Fenwick {
int n;
vector<T> tr;
Fenwick() {}
Fenwick(int n) { init(n + 1);}
void init(int n) {
this->n = n;
tr.assign(n + 1, (T){});
}
void add(int pos, T x) {
while (pos <= n) {
tr[pos] += x;
pos += pos & -pos;
}
}
T sum(int pos) {
T res = 0;
while (pos) {
res += tr[pos];
pos -= pos & -pos;
}
return res;
}
T query(int l, int r) {
return sum(r) - sum(l - 1);
}
};
struct ACTree {
static constexpr int S = 26;
struct Node {
int fa, fail;
array<int, S> nxt;
Node() : fa{-1}, fail{0}, nxt{} {}
};
vector<Node> t;
vector<int> endpos;
ACTree() {
t.assign(2, Node());
t[0].nxt.fill(1);
}
int newNode() {
t.emplace_back();
return t.size() - 1;
}
void add(string s) {
int p = 1;
for (auto c : s) {
if (c == 'P') {
endpos.push_back(p);
} else if (c == 'B') {
p = t[p].fa;
} else {
int x = c - 'a';
if (t[p].nxt[x] == 0) {
t[p].nxt[x] = newNode();
t[t[p].nxt[x]].fa = p;
}
p = t[p].nxt[x];
}
}
}
void work() {
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < S; i++) {
if (t[x].nxt[i] == 0) {
t[x].nxt[i] = t[t[x].fail].nxt[i];
} else {
t[t[x].nxt[i]].fail = t[t[x].fail].nxt[i];
q.push(t[x].nxt[i]);
}
}
}
}
int next(int p, int x) {
return t[p].nxt[x];
}
int fail(int p) {
return t[p].fail;
}
int fa(int p) {
return t[p].fa;
}
int size() {
return t.size();
}
};
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
string t;
cin >> t;
ACTree G;
G.add(t);
G.work();
vector<vector<int>> adj(G.size());
for (int i = 1; i < G.size(); i++) {
adj[G.fail(i)].push_back(i);
}
vector<int> sz(G.size()), dfn(G.size());
int tim = 0;
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x) -> void {
dfn[x] = ++tim;
sz[x] = 1;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
self(self, y);
sz[x] += sz[y];
}
};
dfs(dfs, 1);
int m;
cin >> m;
vector<vector<array<int, 2>>> qry(G.endpos.size());
vector<int> ans(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
x--; y--;
qry[y].push_back({x, i});
}
Fenwick<int> fen(G.size());
for (int p = 1, tot = -1, i = 0; i < t.size(); i++) {
if (t[i] == 'B') {
fen.add(dfn[p], -1);
p = G.fa(p);
} else if (t[i] != 'P') {
p = G.next(p, t[i] - 'a');
fen.add(dfn[p], 1);
} else {
tot++;
for (auto [id, qid] : qry[tot]) {
int x = G.endpos[id];
ans[qid] = fen.query(dfn[x], dfn[x] + sz[x] - 1);
}
}
}
for (auto x : ans) {
cout << x << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}【P2444 [POI2000] 病毒】
题意:给定 \(n\) 个 \(01\) 串,问是否存在一个无限长的 \(01\) 串不包含任何一个给定的 \(01\) 串作为子串。
\(1 \le n \le 2000\),\(1\le \sum|S| \le 3\cdot 10^4\)。
假定存在这么一个无限长的 \(01\) 串,记作 \(T\)。
那么把 \(T\) 放到这 \(n\) 个 \(01\) 串构成的 AC 自动机上跑,一定是不断失配,并且跳 fail 指针跳到的点不在任何 endpos 的子树中。
为此,我们把所有的 endpos 及其子树都标记为危险节点。具体的,bfs 构建 fail 指针的时候,如果 fail 指针指向的点(最长后缀)是危险节点,那么当前节点就标记为危险。
因为是无限,所以指针肯定是在一个不存在危险节点的环上绕圈。
在 next 指针上跑 dfs 找环即可,注意避开危险节点。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
struct ACTree {
static constexpr int S = 2;
struct Node {
int end, fail;
array<int, S> nxt;
Node() : end{0}, fail{0}, nxt{} {}
};
vector<Node> t;
ACTree() {
t.assign(2, Node());
t[0].nxt.fill(1);
}
int newNode() {
t.emplace_back();
return t.size() - 1;
}
void add(string s) {
int p = 1;
for (auto c : s) {
int x = c - '0';
if (t[p].nxt[x] == 0) {
t[p].nxt[x] = newNode();
}
p = t[p].nxt[x];
}
t[p].end = true;
}
void work() {
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < S; i++) {
if (t[x].nxt[i] == 0) {
t[x].nxt[i] = t[t[x].fail].nxt[i];
} else {
t[t[x].nxt[i]].fail = t[t[x].fail].nxt[i];
if (t[t[t[x].nxt[i]].fail].end) {
t[t[x].nxt[i]].end = true;
}
q.push(t[x].nxt[i]);
}
}
}
}
int next(int p, int x) {
return t[p].nxt[x];
}
int fail(int p) {
return t[p].fail;
}
int isend(int p) {
return t[p].end;
}
int size() {
return t.size();
}
};
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
ACTree G;
vector<string> s(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> s[i];
G.add(s[i]);
}
G.work();
vector<int> vis(G.size()), circle(G.size());
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x) -> int {
circle[x] = true;
for (auto y : {G.next(x, 0), G.next(x, 1)}) {
if (circle[y]) {
return true;
}
if (vis[y] || G.isend(y)) {
continue;
}
vis[y] = true;
if (self(self, y)) {
return true;
}
}
circle[x] = false;
return false;
};
if (dfs(dfs, 1)) {
cout << "TAK\n";
} else {
cout << "NIE\n";
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}还有一题,但是太难了,我先放着。
【7.12】 Day 5
醒了,下床,趴桌上继续睡。
上午按安排徐神讲后缀数组,包大爷讲后缀自动机。因为听起来就高级,我也没接触过,所以打起了十二分精神捏。
先讲后缀数组,刚开始听觉得很有道理,但怎么逐渐听不懂了。也不算逐渐,就徐神讲怎么从长度为 \(d\) 扩展到长度为 \(2d\) 的时候就懵了(
感觉再听听就懂了,就没问,结果一直懵,懵到最后我不好意思让徐神重新讲了QAQ。
我认为也许是后缀数组本身就很难不容易讲明白。
后面讲后缀自动机我状态就好多了,包大爷发音清晰思维缜密我坐第一排看着它真是大帅辣听它讲真是幸福捏。
中午朝阳¥15 可乐鸡饭,很牛啊,4 星。这个默认给你的饭很少,下次得向阿姨要多一点。
回到宿舍水了下群直接睡了。以往中午我都不怎么睡,但可能昨晚睡比较晚?
下午第三次队内赛,我怎么又白给了。4/8(Rank16)
一个小时开了 ABI,然后怎么 C 又坐牢了鸭。
不能算坐牢,这个是刚开始就有思路,但写了一坨还调不对(
wa5,wa6,wa10,tle61…
唉,没想清楚导致的。
D 红晕了,上手就搞了个 \(\text{dp[2][N]}\),我在写什么????
赛后发现 D 和 F 都是 ez,前者一个 dfs,后者直接把差值扔进优先队列。Link-D Link-F
这下遥遥落后了。
更自卑了。想似,就这样吧,说不定我的实力真的止于 div2C 了。
晚上没吃。
【队内赛 3E - CF406D. Hill Climbing】
题意:有 \(n\) 座山,第 \(i\) 座山山顶在 \((x_i,y_i)\)。如果两个人站在两座山的山顶可以互相看到,则这两座山之间有绳子连接。有 \(m\) 支队伍,每队有两个人,每个人都可以通过绳子到达直连的最右边的山顶。现给定每支队伍两个人初始所在的山的编号 \(a\) 和 \(b\),问他们在哪座山的山顶相遇。
\(1 \le n,m \le 10^5\),\(1 \le x_i \le10^7\),\(1 \le y_i \le 10^{11}\)。
题图画的很清楚,因为选的是尽可能往后连的绳子,所以两个人通过绳子攀爬的路径都是凸的。
换言之,每座山选择向右到达的山的编号(*)是唯一的,连边能构成一棵树。
那么答案就是两个人所在点的 LCA。
(*)可以在求上凸包的过程中处理出来,即栈顶编号。
时间复杂度 \(O(n\log n+m\log n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
struct Point {
int x, y;
Point(int x = 0, int y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
};
bool operator==(const Point &a, const Point &b) {
return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y;
}
Point operator+(const Point &a, const Point &b) {
return Point(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y);
}
Point operator-(const Point &a, const Point &b) {
return Point(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y);
}
int cross(const Point &a, const Point &b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
vector<int> getUpHull(vector<Point> p) {
int n = p.size();
vector<int> nxt(n);
vector<int> h;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (h.size() > 1 && cross(p[i] - p[h.back()], p[i] - p[h[h.size() - 2]]) > 0) {
h.pop_back();
}
if (h.size() > 0) {
nxt[i] = h.back();
} else {
nxt[i] = n - 1;
}
h.push_back(i);
}
return nxt;
}
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<Point> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
a[i] = {x, y};
}
vector<int> nxt = getUpHull(a);
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
adj[nxt[i - 1] + 1].push_back(i);
}
vector<vector<int>> fa(n + 1, vector<int>(25, 0));
vector<int> dep(n + 1);
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int fath) -> void {
fa[x][0] = fath;
dep[x] = dep[fath] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= __lg(dep[x]) + 1; i++) {
fa[x][i] = fa[fa[x][i - 1]][i - 1];
}
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y != fath) {
self(self, y, x);
}
}
};
auto LCA = [&] (int x, int y) {
if (dep[x] < dep[y]) {
swap(x, y);
}
while (dep[x] > dep[y]) {
x = fa[x][__lg(dep[x] - dep[y])];
}
if (x == y) {
return x;
}
for (int i = __lg(dep[x]); i >= 0; i--) {
if (fa[x][i] != fa[y][i]) {
x = fa[x][i];
y = fa[y][i];
}
}
return fa[x][0];
};
dfs(dfs, n, 0);
int m;
cin >> m;
while (m--) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
cout << LCA(x, y) << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}剩下一个 G,本来不想写的,但题解的做法让人称奇道妙。
但一个多小时了还有几处细节想不清楚,先欠着。
昨天的队内赛还没补,那就补两题。
【队内赛 2C - CF337D. Book of Evil】
题意:给定一棵 \(n\) 个节点的树,树上有 \(m\) 个关键点,点集设为 \(S\)。再给定一个整数 \(d\),求满足 \(\forall i\in S,\ \text{dis}(x,i)\le d\) 的节点 \(x\) 的个数。
\(1 \le m\le n\le 10^5\)。
对于每个点判断离它半径为 \(d\) 的范围内是否有 \(m\) 个关键点。
将关键点权值设为 \(1\),其余为 \(0\)。就变成了以某个点为中心的范围权值和。
点分树即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(n\log^2n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define inf 0x7fffffff
constexpr int mx = 5e6;
struct Node {
int sum;
Node *ch[2];
} node[mx];
int cnt = 0;
struct SegmentTree {
Node *rt;
SegmentTree() {
rt = NULL;
}
Node *New() {
return &node[cnt++];
}
void add(Node *&p, int pos, int val, int l, int r) {
if (!p) {
p = New();
}
if (l == r) {
p->sum += val;
return ;
}
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (pos <= mid) {
add(p->ch[0], pos, val, l, mid);
} else {
add(p->ch[1], pos, val, mid + 1, r);
}
p->sum = (p->ch[0] ? p->ch[0]->sum : 0) +
(p->ch[1] ? p->ch[1]->sum : 0);
}
int query(Node *p, int ql, int qr, int l, int r) {
if (!p) {
return 0;
}
if (l == ql && r == qr) {
return p->sum;
}
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (qr <= mid) {
return query(p->ch[0], ql, qr, l, mid);
}
if (ql > mid) {
return query(p->ch[1], ql, qr, mid + 1, r);
}
return query(p->ch[0], ql, mid, l, mid) +
query(p->ch[1], mid + 1, qr, mid + 1, r);
};
};
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, m, d;
cin >> n >> m >> d;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
a[x] = 1;
}
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
vector<vector<int>> st(18, vector<int>(2 * n + 1));
vector<int> dep(n + 1), id(n + 1), lg2(2 * n + 1);
int tim = 0;
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int fath) -> void {
dep[x] = dep[fath] + 1;
st[0][++tim] = x;
id[x] = tim;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y != fath) {
self(self, y, x);
st[0][++tim] = x;
}
}
};
auto Lower = [&] (int x, int y) {
return dep[x] < dep[y] ? x : y;
};
auto getST = [&] () {
for (int i = 2; i <= tim; i++) {
lg2[i] = lg2[i >> 1] + 1;
}
for (int i = 1; (1 << i) <= tim; i++) {
int w = (1 << i);
for (int j = 1; j + w - 1 <= tim; j++) {
st[i][j] = Lower(st[i - 1][j], st[i - 1][j + w / 2]);
}
}
};
auto LCA = [&] (int x, int y) {
x = id[x];
y = id[y];
if (x > y) {
swap(x, y);
}
int i = lg2[y - x + 1];
return Lower(st[i][x], st[i][y - (1 << i) + 1]);
};
auto dist = [&] (int x, int y) {
return dep[x] + dep[y] - 2 * dep[LCA(x, y)];
};
dfs(dfs, 1, 0);
getST();
int all = n, rt = -1;
vector<int> sz(n + 1), mx(n + 1), vis(n + 1);
auto getsz = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
sz[x] = 1;
mx[x] = 0;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa || vis[y]) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
sz[x] += sz[y];
mx[x] = max(mx[x], sz[y]);
}
mx[x] = max(mx[x], all - sz[x]);
if (mx[x] < mx[rt]) {
rt = x;
}
};
vector<int> dsz(n + 1), dfa(n + 1);
auto dfz = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
vis[x] = true;
dsz[x] = all;
dfa[x] = fa;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa || vis[y]) {
continue;
}
all = sz[y];
mx[rt = 0] = inf;
getsz(getsz, y, x);
getsz(getsz, rt, 0);
self(self, rt, x);
}
};
mx[rt = 0] = inf;
getsz(getsz, 1, 0);
getsz(getsz, rt, 0);
dfz(dfz, rt, 0);
vector<SegmentTree> seg1(n + 1), seg2(n + 1);
auto Add = [&] (int x, int val) -> void {
int now = x;
while (now) {
int fa = dfa[now];
seg1[now].add(seg1[now].rt, dist(now, x), val, 0, dsz[now]);
if (fa) {
seg2[now].add(seg2[now].rt, dist(fa, x), val, 0, dsz[fa]);
}
now = fa;
}
};
auto Query = [&] (int x, int k) -> int {
int res = 0;
int now = x, lst = 0;
while (now) {
int dt = dist(now, x);
if (dt > k) {
lst = now;
now = dfa[now];
continue;
}
res += seg1[now].query(seg1[now].rt, 0, k - dt, 0, dsz[now]);
if (lst) {
res -= seg2[lst].query(seg2[lst].rt, 0, k - dt, 0, dsz[now]);
}
lst = now;
now = dfa[now];
}
return res;
};
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (a[i]) Add(i, a[i]);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ans += Query(i, d) == m;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}但这题显然有更简单的结论做法。
类比树的直径的性质:距离树上任意一点最远的点一定是直径两个端点中的一个。
可以得到结论:距离树上任意一点最远的关键点一定是 “树上距离最远的两个关键点” 中的一个。
证明需要分类讨论,见 Link。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, m, d;
cin >> n >> m >> d;
vector<int> a(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
auto getdis = [&] (int rt) {
vector<int> dis(n + 1);
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
dis[x] = dis[fa] + 1;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
}
};
dis[0] = -1;
dfs(dfs, rt, 0);
return dis;
};
vector<int> dis1 = getdis(1);
int ml = 0, mr = 0;
int mxdis = -1;
for (auto x : a) {
if (dis1[x] > mxdis) {
mxdis = dis1[x];
ml = x;
}
}
vector<int> dis2 = getdis(ml);
mxdis = -1;
for (auto x : a) {
if (dis2[x] > mxdis) {
mxdis = dis2[x];
mr = x;
}
}
dis1 = getdis(mr);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (dis1[i] <= d && dis2[i] <= d) {
ans++;
}
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}上面两种方法一个写起来复杂,一个取巧,那么还有一个比较套路的换根 dp 做法。
我们钦定 \(i\) 为根,定义 \(dp_{i,0/1}\)。
\(dp_{i,0}\) 代表 \(i\) 离与它最远的关键点 \(j\) 之间的距离,即最后答案。
\(dp_{i,1}\) 代表除 \(j\) 所在的 \(i\) 的子树外,与 \(i\) 距离最远的关键点和 \(i\) 之间的距离。
第一次以 \(1\) 为根进行 dfs,同时 \(fr_i\) 记录 \(dp_{i,0}\) 从哪个节点转移而来:
vector dp(n + 1, vector<int>(2, -inf));
vector<int> from(n + 1);
auto dfs1 = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
if (a[x]) {
dp[x][0] = 0;
}
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
int t = dp[y][0] + 1;
if (t > dp[x][0]) {
dp[x][1] = dp[x][0];
dp[x][0] = t;
from[x] = y;
} else if (t > dp[x][1]) {
dp[x][1] = t;
}
}
};此时的 \(dp_{i}\) 从节点 \(1\) 辐向 \(i\) 的一侧拥有符合上述意义的答案。
考虑换根,从 \(fa\to x\),根据 \(fr_{fa}\) 是否等于 \(x\),选择 \(dp_{fa,0}\) 或 \(dp_{fa,1}\) 进行转移。
记得此时更新 \(dp_{x,0}\) 时也要同步更新 \(fr_x\)。
auto dfs2 = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
int t;
if (from[fa] != x) {
t = dp[fa][0] + 1;
} else {
t = dp[fa][1] + 1;
}
if (t > dp[x][0]) {
dp[x][1] = dp[x][0];
dp[x][0] = t;
from[x] = fa;
} else if (t > dp[x][1]) {
dp[x][1] = t;
}
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
}
};
C++不理解可以模拟一下题目的样例,以及将节点 \(4\) 也变为关键点的情况。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, m, d;
cin >> n >> m >> d;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
a[x] = 1;
}
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
vector dp(n + 1, vector<int>(2, -inf));
vector<int> from(n + 1);
auto dfs1 = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
if (a[x]) {
dp[x][0] = 0;
}
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
int t = dp[y][0] + 1;
if (t > dp[x][0]) {
dp[x][1] = dp[x][0];
dp[x][0] = t;
from[x] = y;
} else if (t > dp[x][1]) {
dp[x][1] = t;
}
}
};
dfs1(dfs1, 1, 0);
auto dfs2 = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
int t;
if (from[fa] != x) {
t = dp[fa][0] + 1;
} else {
t = dp[fa][1] + 1;
}
if (t > dp[x][0]) {
dp[x][1] = dp[x][0];
dp[x][0] = t;
from[x] = fa;
} else if (t > dp[x][1]) {
dp[x][1] = t;
}
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
}
};
for (auto y : adj[1]) {
dfs2(dfs2, y, 1);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (dp[i][0] <= d) {
ans++;
}
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}
C++还有一题但是点分树折磨了我两个小时,我要睡觉了。
骗自己罢了,不眠之夜。
【7.13】 Day 6
雨一直下。
【7.14】 Day 7
雨一直下。
晚上躺在床上突然想通了什么,伟大的一步。
晚上快 22 点多了才下床,笔记本充电器不知道去哪了,应该是在 234。骑车过去拿,但灯都黑了,无功而返,跟 xxx 借了一个。
0 点 35,vp 了昨天的 abc,6/7,G 把板子喂到嘴里了。
就 F 有点意思,写一下。
题意:给定一棵 \(n\) 个点的树,定义 \(dis(x, y)\) 为树上 \(x,y\) 间的距离。有一个 \(n\) 个点的完全图 \(G\),其中 \(w(x,y)=dis(x,y)\)。求这个完全图的一个最大权匹配,输出匹配方案。
\(2 \le n \le 2\cdot 10^5\)。
结论:令 \(c\) 为树的重心,则满足以下条件的匹配 \(S\) 为答案:
- \(\forall (x_i,y_i)\in S\),\(x_i\) 和 \(y_i\) 位于重心两侧。
证明:拆贡献,令一条边两侧的点数为 \(a\) 和 \(n-a\),则该边的贡献为 \(\min(a,n-a)\)。因为理想情况点少的这一侧的所有点都能跨过这条边寻找自己的匹配。那么答案的上界就是所有边的贡献和,即 \(\sum\min(a,n-a)\)。
对于重心 \(c\),我们令 \(e\) 为以 \(c\) 为根的某个子树中的某一条边,此时 \(e\) 的两侧中点比较少的一定是远离重心方向的这一侧。 按照我们的理论,这一侧的点只要跨越了这条边寻找匹配就成功了,此时它们匹配了重心另一侧的点,满足条件。
不难发现对于以 \(c\) 为根的每一个子树中的所有边都满足上述条件,达到了贡献最大值,证毕。
于是我们可以进行如下构造:
找到树的重心 \(c\),令 \(c\) 的若干子树为 \(T_1,T_2,\cdots\)。
令数组 \(A=\{T_1 中点的编号,T_2 中点的编号,\cdots\}\)。
若 \(n\) 为偶数,将 \(c\) 补在 \(A\) 的末尾。
\(\forall i\in[0,\frac{n}{2})\),\((A_i,A_{i+\frac{n}{2}})\) 为一个匹配。\((0-\text{index})\)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
vector<int> sz(n + 1), mx(n + 1);
int rt = -1;
auto getsz = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
sz[x] = 1;
mx[x] = 0;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
sz[x] += sz[y];
mx[x] = max(mx[x], sz[y]);
}
mx[x] = max(mx[x], n - sz[x]);
if (mx[x] < mx[rt]) {
rt = x;
}
};
getsz(getsz, 1, 0);
vector<int> a;
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
a.push_back(x);
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
}
};
for (auto x : adj[rt]) {
dfs(dfs, x, rt);
}
if (n % 2 == 0) {
a.push_back(rt);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
cout << a[i] << " " << a[i + n / 2] << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}
C++【7.15】 Day 8
10 点 30 的闹钟,10 点 28 醒了,正好提前两分钟下床等着关闹钟(
中午大伙一起去朝阳吃饭,点了个¥16 叉烧鸡,很一般,两星半或者三星。
吃完到 234 打队内赛五。开始前几分钟发现
solved 1 of 11,很乐,截个图发到了群里,然后发现大伙怎么都做过。结果比赛开始就被菜猫换掉了,虽然没换掉也是当成新题做的说。
开局直接 A 上手,写着写着怎么不会了。看来以后写题还是得养成想好再动笔的习惯(后有伏笔
第一个小时开了四道签到,唉,爽!再看榜怎么大伙签得比我快这么多鸭。我主要是被那个字符串奇数位升序偶数位降序卡手了,后面灵机一动字母换成数字,然后偶数位取反。唉,差点就没签出来。
J 也是一眼,但怎么又开始 wa3,wa4 了。干脆直接跳转到 F,这不是龙数吗,咔咔咔一顿码,样例忒弱,疯狂提交,最好的结果是 tle6,自闭了。冷静分析了一下但感觉最多就是 2log,更何况还有神秘的势能分析加持,怎么会事呢?
那干脆再跳转到 E,哎呀这不是每个点向直连的编号最小点连边吗,怎么 wa9。红晕了。
中途发现 J 原来是有个 special 的情况,判掉就好了。E 又一通交,终于发现自己连最小生成树都不会写了(
B 过了一堆,但我不是很懂。I 也过了一堆,怎么大伙都会构造。
6/11(Rank 23)收尾,蒸蒸日下了。
晚上回朝阳吃了个可乐鸡饭。
回宿舍本来想着洗个澡就回 234 补题,但碰了床就想睡,就睡到了八点多。
洗完澡回到 234,补一题就差不多 CF 了。
【队内赛 5i. 唉,构造 - gym104160 F. Half Mixed】
题意:给定正整数 \(n,m\),你需要构造一个 \(n\times m\) 的 \(01\) 矩阵,使得纯子矩阵个数 \(=\) 杂子矩阵个数。
纯子矩阵指内部只有 \(0\) 或 \(1\) 的矩阵。杂子矩阵指内部既有 \(0\) 又有 \(1\) 的矩阵。
输出构造方案或报告不存在。
\(1\le n,m\le 10^6\),\(1\le \sum n\cdot m\le 5\cdot10^6\)。
对于一个 \(1\times m\) 的矩形,其子矩阵个数为 \(A=\dfrac{m(m + 1)}{2}\)。
对于一个 \(n\times 1\) 的矩形,其子矩阵个数为 \(B=\dfrac{n(n + 1)}{2}\)。
乘法原理,对于 \(n\times m\) 的矩形,子矩阵个数为 \(C=\dfrac{n(n + 1)}{2}\cdot\dfrac{m(m + 1)}{2}\)。
那么,纯子矩阵个数 \(=\) 杂子矩阵个数 \(= \dfrac{C}{2}\)。若 \(C\) 为奇数,无法构造。
否则,\(A\) 和 \(B\) 至少有一个偶数,不妨令 \(A\) 为偶数。根据乘法原理,如果我们能够构造一个拥有 \(\dfrac{A}{2}\) 个纯子矩阵(杂子矩阵)的 \(1\times m\) 的矩阵。复制 \(n\) 份,总纯子矩阵个数就是 \(\dfrac{A}{2}\cdot B=\dfrac{C}{2}\),满足题意。
而这 \(1\times m\) 的矩阵必然由若干 \(01\) 段组成,设每段的长度为 \(d_i\),则需要构造 \(d_i\) 满足:
\(\sum d_i=m\)
\(\sum \dfrac{d_i(d_i+1)}{2}=\dfrac{A}{2}=\dfrac{m(m+1)}{4}\)
按题解的说法此时贪心从大到小枚举 \(d_i\),就一定会有合适的取值,正确性我并没有想得很透彻。
我的做法是二分 \(d_i\),设二分出的 \(d_i=mid\),此时剩下 \(left-mid\) 段,二式剩下 \(T\)。假设每段独立,即 \(01010\cdots\),产生 \(left-mid\) 的贡献。那么只要 \(\dfrac{mid(mid+1)}{2} \le T-(left-mid)\) 就往更大的方向更新。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int all = n * (n + 1) / 2 * m * (m + 1) / 2;
if (all & 1) {
cout << "No\n";
return ;
}
cout << "Yes\n";
bool rev = 0;
if ((n * (n + 1) / 2) % 2 == 0) {
swap(n, m);
rev = 1;
}
int T = m * (m + 1) / 4, left = m;
vector<int> a;
while (T) {
int l = 1, r = left, res = 0;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (mid * (mid + 1) / 2 <= T - (left - mid)) {
res = mid;
l = mid + 1;
} else {
r = mid - 1;
}
}
T -= res * (res + 1) / 2;
left -= res;
a.push_back(res);
}
vector<int> ans(m + 1);
int now = 1, ths = 0;
for (auto x : a) {
ths ^= 1;
for (int i = now; i <= now + x - 1; i++) {
ans[i] = ths;
}
now += x;
}
while (now <= m) {
ths ^= 1;
ans[now] = ths;
now++;
}
if (!rev) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
cout << ans[j] << " \n"[j == m];
}
}
} else {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << ans[j] << " \n"[i == n];
}
}
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}晚上打 CF,前三题基本都挺顺利的。
A 冷静了一分钟感觉直接用个 std::multiset
模拟就成,只要不把分离出的 \(1\)
塞回去就不会很慢。(赛后发现就我最笨了) B 注意到一段 \(0\) 可以缩成一个 \(0\),\(1\)
自然是越多越好,不用处理,最后比较 \(1\) 的个数是否 \(>\) \(0\) 的个数就行。
C 卡了 10 分钟,但很快把样例 bitset
输出了一下,就发现端倪了,每次只要 \(0\) 的位次从高位向地位移动就行。
长度就是 popcount(n) + 1。
你说得对,但是:
std::__builtin_popcount(S) 不彳亍!
std::__builtin_popcountll(S) 彳亍!
浪费了十分钟,警钟长鸣。
D 上手就写了个取两次取完所有点的,看了下榜发现 lyc 和 wbc 都瞬 wa 了,就发现不对劲。
思考了一下,三次取完所有点是不是就行了!很牛啊,写写写,唉,wa 了。
怎么会是呢,是不是要钦定若干条边 dp,看看第三次取哪些。
然后时间很快就过了,唉,好像三次不彳亍!唉,这下不牛了。
怎么大伙都过 D 了,又垫底了。
赛后发现这题有 2log,1log,甚至线性的做法,都写写看好了。
【CF1988 - D. The Omnipotent Monster Killer】
题意:给定一棵树,点有点权,意为将该点留下所需的代价。你可以分若干轮将这棵树的所有节点删空,要求每一轮次中,每条边两侧的顶点不能同时被删,每轮结束剩下的点结算代价。问将树删空的最小代价。
\(1 \le n \le 3\cdot 10^5\),\(1 \le a_i \le 10^{12}\)。
【solution - \(O(n\log^2n)/O(n\log n)\) 】
可以想象贪心必不优。同时猜测删空所需的轮数并不多,实际不超过 \(O(\log n)\) 轮。
令 \(dp_{x, t}\) 代表删空 \(x\) 的子树,且在第 \(t\) 轮删去 \(x\) 的最小代价。
得到以下转移方程: \[ dp_{x,t}=\sum_{y\in son_x}\left(\min_{t'\neq t}dp_{y, t'}\right)+w_x\times(t+1) \]
答案为 \(\min\limits_{i=1}^{\log_n} dp_{1,i}\)。
暴力枚举 \(t\) 和 \(t'\) 进行转移,时间复杂度 \(O(n\log^2 n)\)。
虽然 \(t'=t\) 不计入答案,但 \(t'<t\) 和 \(t' > t\) 计入答案。故记录前缀 \(\min\) 和后缀 \(\min\),时间复杂度 \(O(n\log n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
vector dp(n + 1, vector<int>(20, 0));
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
dp[x][i] = (i + 1) * a[x];
}
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
int mn = inf;
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++) {
if (i == j) {
continue;
}
mn = min(mn, dp[y][j]);
}
dp[x][i] += mn;
}
}
};
dfs(dfs, 1, 0);
cout << *min_element(dp[1].begin(), dp[1].end()) << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
vector dp(n + 1, vector<int>(20));
vector<int> pre(20), suf(20);
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
dp[x][i] = (i + 1) * a[x];
}
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
pre[0] = dp[y][0];
for (int i = 1; i < 20; i++) {
pre[i] = min(pre[i - 1], dp[y][i]);
}
suf[19] = dp[y][19];
for (int i = 18; i >= 0; i--) {
suf[i] = min(suf[i + 1], dp[y][i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
int t = inf;
if (i > 0) {
t = min(t, pre[i - 1]);
}
if (i < 19) {
t = min(t, suf[i + 1]);
}
dp[x][i] += t;
}
}
};
dfs(dfs, 1, 0);
cout << *min_element(dp[1].begin(), dp[1].end()) << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}线性我还不会,明日再补。
【7.16】 Day 9
10 点 35 被闹醒,下床继续睡到 11 点。
朝阳,¥15 烤肉饭两荤两素,感觉素菜和荤菜品种都不如沙河阳光餐厅。
烤肉饭就是烤肉饭的味道,本来是三星,但它那个鸡腿搞得挺好吃,三星半把。
预感到又是坐牢的一天呐米娜桑。
猜对了,继续蒸蒸日下。
先是 A 维护得一坨,再是两个半小时没做出 F,糖丸了。
赛后发现 \(n\) 怎么是 \(5000\) 鸭,下意识以为是 \(1e5\) 之类的了。虽然正解也不是 \(O(n^2)\) 的,但没准 \(O(n^2)\) 就恰好会呢?呜呜。
被 F 红晕了,H 都没仔细看。赛后发现就是 \(p_i\) 和 \(p_j\) 互相问,十五分钟秒了(
菜,直接补题吧,没什么好说的。
【队内赛 6 - F. 迫近的客星 - CF370C. Mittens】
题意:给定一个 \(n\) 个数的数组 \(\{a\}\),你需要寻找 \(\{a\}\) 的一个排列 \(\{b\}\)(指 \(\{b\}\) 和 \(\{a\}\) 仅有元素排列顺序不同) 使得满足 \(a_i \neq b_i\) 的下标数量尽可能多。
\(1 \le n \le 5000\),\(1 \le m \le 100\)。
结论:将 \(\{a\}\) 排序后右移 \(\dfrac{n}{2}\) 再复原排序得到 \(\{b\}\)。(该题只要求输出映射方案,不需要复原排序) 很智慧的构造,设 \(\{a\}\) 排序之后最长连续段长度为 \(d\),分两种情况讨论:
- 若 \(d \le \left\lfloor\dfrac{n}{2}\right\rfloor\),如下图。最长段(蓝色)可以错开,剩下的连续段长度都不超过 \(d\),因此可以用其它段(红色)补足空隙,此时上下两个数组就没有重合的地方了。
- 考虑右移 \(\dfrac{n}{2}\),如下图。最长段显然不会重合,其它段用不同颜色进行了标明,意在说明若在空隙的地方(即 \(l_2\) 右端)\(\{a\}\),\(\{b\}\) 有重合,那么其他段的长度至少要从 \(l_1\) 右端开始直到 \(l_2\) 右端,长度 \(> \dfrac{n}{2}\),与假设相悖。
 * 若 \(d >
\dfrac{n}{2}\),如下图。最长段(蓝色)已经不可避免地相交,剩下段(红色)不可能再重叠,因此最大匹配的下标数量为
\(n-d\)。
* 若 \(d >
\dfrac{n}{2}\),如下图。最长段(蓝色)已经不可避免地相交,剩下段(红色)不可能再重叠,因此最大匹配的下标数量为
\(n-d\)。
 * 考虑右移 \(\dfrac{n}{2}\),如下图。因为右移之后蓝色段
\((>\dfrac{n}{2})+\dfrac{n}{2}\to
(>n)\) 必然超出右边界,因此剩下的区域仍然要么被 \(\{a\}\) 的蓝色段覆盖,要么被 \(\{b\}\) 的蓝色段覆盖,取到最大匹配。
* 考虑右移 \(\dfrac{n}{2}\),如下图。因为右移之后蓝色段
\((>\dfrac{n}{2})+\dfrac{n}{2}\to
(>n)\) 必然超出右边界,因此剩下的区域仍然要么被 \(\{a\}\) 的蓝色段覆盖,要么被 \(\{b\}\) 的蓝色段覆盖,取到最大匹配。
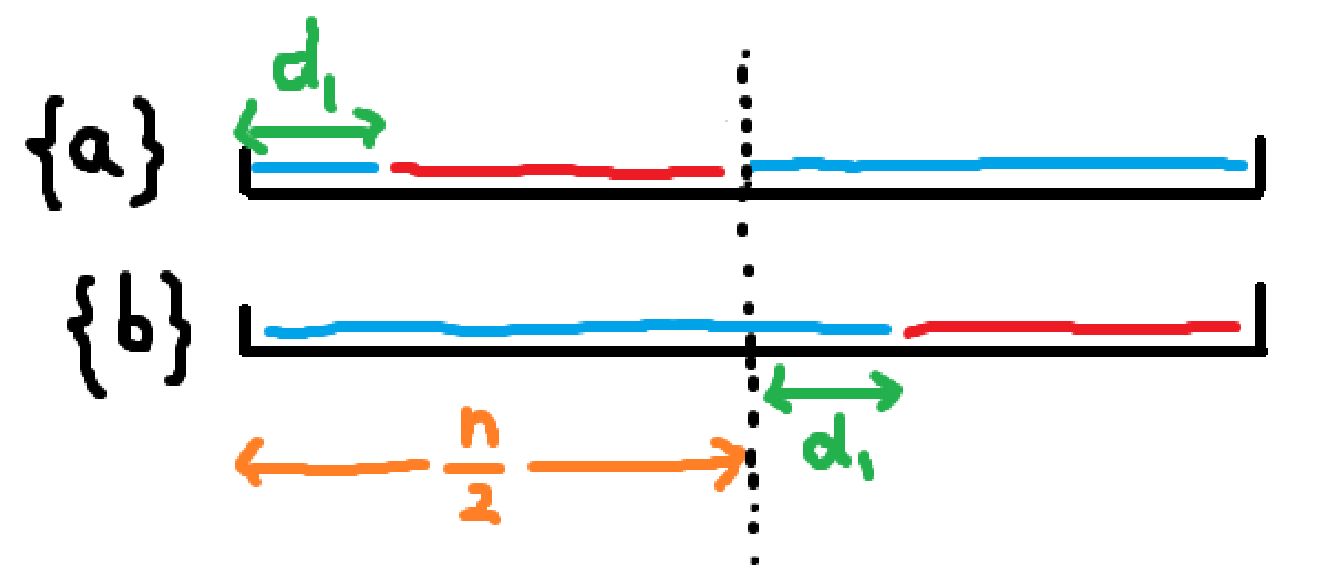
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ans += a[i] != a[(i + n / 2) % n];
}
cout << ans << "\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << a[i] << " " << a[(i + n / 2) % n] << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}【队内赛 6 - E. 辞行久远之躯 - CF1242B. 0-1 MST】
题意:给定一个包含 \(n\) 个节点的完全图,以及图中的 \(m\) 条长度为 \(1\) 的边,其它边长度均为 \(0\)。求该图最小生成树的权值。
\(1 \le n \le 10^5\),\(1 \le m\le \min(\frac{n(n-1)}{2}, 10^5)\)。
我们发现大部分的边都是 \(0\) 边,换种说法如果只保留图上的 \(0\) 边,之后只有少量的边需要我们连接。对于两个全 \(0\) 连通块,若用一条 \(1\) 边连接它们,那么这一大苟的连通块相当于拥有权值为 \(1\) 的最小生成树。
同理,若该图全 \(0\) 连通块的个数为 \(c\),那么需要用 \(c-1\) 条 \(1\) 边连接它们使整个图联通,这个图的最小生成树的权值自然就是 \(c-1\)。
现在考虑求 \(c\)。以下面的 \(K_4\) 完全图(图A)为例:
其中红色虚边为 \(0\) 边,绿色实边为 \(1\) 边。我们按照编号顺序依次遍历 \(1\sim n\),关注连通块的变化。
一开始有节点 \(1\),全 \(0\) 连通块默认为 \(1\)。现在加进来节点 \(2\),如何判断全 \(0\) 连通块个数是否增加?
要知道,\(0\) 边数量是极多的,我们不能遍历 \(0\) 边,我们能操作的只有 \(1\) 边。那么遍历与 \(2\) 相连的 \(1\) 边,发现没有(目前只考虑节点 \(1,2\) 构成的子图,所以连向右侧的 \(1\) 边暂不考虑)。那么自然全是 \(0\) 边,用并查集把 \(1,2\) 连起来,全 \(0\) 连通块个数不变。
现在加进来节点 \(3\),发现存在 \(1\) 边 \((1,3)\) 和 \((2,3)\)。我们不妨用一个标记数组
cnt 标记一下,即对于 \(1\)
边 \(x\to y(y < x)\) 有
cnt[dsu.find(y)]++。接着我们遍历先前的连通块,判断是否有连通块
\(x\) 的大小 dsu.size(x)
比 cnt[x] 大。因为两个点之间不是 \(1\) 边就是 \(0\) 边,如果 dsu.size(x)
更大,说明向这个连通块连的边有 \(0\)
边,进一步说明全 \(0\)
连通块的个数没有增加,如下图(图B)。
该图满足 dsu.size(1) = 2 > cnt[1] = 1。此时节点 \(3\) 的加入不影响全 \(0\) 连通块个数,直接用并查集并起来。
而图 A 则是 dsu.size(1) = 2 <= cnt[1] = 2。此时全
\(0\) 连通块个数 \(+1\)。
现在会了怎么判断全 \(0\) 连通块个数增加,那会不会减少呢?
这是添加节点 \(5\) 之后的另一个例子,不难看出此时全 \(0\) 连通块数量发生了 \(2\to 1\) 的变化。
那我们动态维护这个数值就有点困难了。但我们只关心最后的结果:节点
\(5\) 添加,老样子判断
dsu.size(1) = 2 > cnt[1] = 0 且
dsu.size(3) = 2 > cnt[3] = 0,就把 \(1\) 和 \(5\),\(3\)
和 \(5\)
所在的连通块并起来了。此时对于节点 \(1\sim
5\),恰有一个满足
dsu.find(i) = i。这启示我们最后的答案就是
dsu.find(i) = i 的节点的个数,不必动态维护连通块个数。
复杂度分析:对于每个节点,都有并或不并。合并显然最多 \(n\) 次;而不合并,那么该节点至少和先前的连通块存在一条 \(1\) 边,\(1\) 边一共有 \(m\) 条。因此是 \(O(n\alpha+m)\) 的。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
struct DSU {
vector<int> f, siz;
DSU() {}
DSU(int n) { init(n);}
void init(int n) {
f.resize(n + 2);
siz.resize(n + 2);
for(int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) {
f[i] = i;
siz[i] = 1;
}
}
int find(int x) {
if (x == f[x]) return x;
return f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
bool same(int x, int y) {
return find(x) == find(y);
}
bool merge(int x, int y) {
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x == y) return false;
if (siz[x] < siz[y]) {
swap(x, y);
}
siz[x] += siz[y];
f[y] = x;
return true;
}
int size(int x) {
return siz[find(x)];
}
};
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
DSU dsu(n);
vector<int> rt;
map<int, int> cnt;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cnt.clear();
for (auto x : adj[i]) {
if (x < i) {
cnt[dsu.find(x)]++;
}
}
for (auto x : rt) {
x = dsu.find(x);
if (dsu.size(x) > cnt[x]) {
dsu.merge(x, i);
}
}
if (dsu.find(i) == i) {
rt.push_back(i);
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ans += dsu.find(i) == i;
}
cout << ans - 1 << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}【队内赛 6 - G. 我们终将重逢 - CF1117D. Magic Gems】
题意:有无数个魔法宝石,每个魔法宝石可以分解成 \(m\) 个普通宝石,两种宝石都占据 \(1\) 的空间,后者不能再被分解。问有多少种分解方案,可以使最后得到的宝石恰好占据 \(n\) 个空间。两种分解方案不同当且仅当分解的魔法宝石数量不同,或者是所用宝石的编号不同。答案对 \(10^9+7\) 取模。
\(1 \le n \le 10^{18}\),\(2 \le m \le 100\)。
可以将题目概括为用若干个 \(m\) 个 \(0\) 和若干个 \(1\) 组成的长为 \(n\) 的 \(01\) 串计数。
不妨令 \(f_i\) 代表长为 \(i\) 的这样的串的数目,则转移为: \[ f_i = \begin{cases}1&, i < m \\f_{i - 1} + f_{i - m}&, \text{otherwise}\end{cases} \]
意为可以在长为 \(i-1\) 的串末尾加 \(1\) 或长为 \(i-m\) 的串末尾加 \(m\) 个 \(0\) 来达到该状态。
取其中 \(f_i\) 和 \(f_{i-m}\),列出在它们之间的转移式如下: \[ \begin{align}f_i = 1\cdot f_{i - 1}+0\cdot f_{i - 2}+ 0\cdot f_{i - 3} + \cdots&+0\cdot f_{i - m + 2} + 0\cdot f_{i - m + 1} + 1\cdot f_{i - m} \\f_{i-1} = 1\cdot f_{i - 1}+0\cdot f_{i - 2}+ 0\cdot f_{i - 3} + \cdots&+0\cdot f_{i - m + 2} + 0\cdot f_{i - m + 1} + 0\cdot f_{i - m} \\f_{i-2} = 0\cdot f_{i - 1}+1\cdot f_{i - 2}+ 0\cdot f_{i - 3} + \cdots&+0\cdot f_{i - m + 2} + 0\cdot f_{i - m + 1} + 0\cdot f_{i - m} \\f_{i-3} = 0\cdot f_{i - 1}+0\cdot f_{i - 2}+ 1\cdot f_{i - 3} + \cdots&+0\cdot f_{i - m + 2} + 0\cdot f_{i - m + 1} + 0\cdot f_{i - m} \\\vdots \\f_{i-m+2} = 0\cdot f_{i - 1}+0\cdot f_{i - 2}+ 0\cdot f_{i - 3} + \cdots&+1\cdot f_{i - m + 2} + 0\cdot f_{i - m + 1} + 0\cdot f_{i - m} \\f_{i-m+1} = 0\cdot f_{i - 1}+0\cdot f_{i - 2}+ 0\cdot f_{i - 3} + \cdots&+0\cdot f_{i - m + 2} + 1\cdot f_{i - m + 1} + 0\cdot f_{i - m} \\\end{align} \]
取系数矩阵,得到可以用矩阵快速幂加速的转移形式: \[ \begin{bmatrix}f_i \\f_{i-1} \\\vdots \\f_{i-m+2} \\f_{i+m-1}\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}1& & & & &1\\1& & & & & \\ &1& & & & \\ & &\ddots& & &\\ & & &1& & \\ & & & &1& \\\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}f_{i-1} \\f_{i-2} \\\vdots \\f_{i-m+1} \\f_{i-m}\end{bmatrix} \]
时间复杂度 \(O(m^3\log n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
struct matrix {
int n, m;
vector<vector<int>> a;
matrix(int n) : n(n), m(n), a(n, vector<int>(n, 0)) {}
matrix(int n, int m) : n(n), m(m), a(n, vector<int>(m, 0)) {}
matrix(int n, int m, int k) : n(n), m(m), a(n, vector<int>(m, k)) {}
void read() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cin >> a[i][j];
}
}
}
void print() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++, cout << "\n") {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cout << a[i][j] << " ";
}
}
}
void build() {
for (int i = 0; i < min(n, m); i++) {
a[i][i] = 1;
}
}
matrix tp() {
matrix z(m, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
z.a[j][i] = a[i][j];
}
}
return z;
}
};
constexpr int modp = 1e9 + 7;
matrix operator * (const matrix &x, const matrix &y) {
assert(x.m == y.n);
matrix z(x.n, y.m);
for (int k = 0; k < x.m; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < x.n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < y.m; j++) {
z.a[i][j] += x.a[i][k] * y.a[k][j] % modp;
z.a[i][j] %= modp;
}
}
}
return z;
}
matrix qpow(matrix a, int k) {
assert(a.n == a.m);
matrix z(a.n);
z.build();
for ( ; k; k >>= 1, a = a * a) {
if (k & 1) z = z * a;
}
return z;
}
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
if (n < m) {
cout << "1\n";
return ;
}
matrix G(m);
for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++) {
G.a[i + 1][i] = 1;
}
G.a[0][0] = 1;
G.a[0][m - 1] = 1;
matrix ans = qpow(G, n - m + 1) * matrix(m, 1, 1);
cout << ans.a[0][0] << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}【7.17】 Day 10
床起晚了,还下雨,直接赶到教室了。
上午徐神和包爷讲字符串专题。
虽然此前想象过,但事实是除了 C 这个签到之外其它题都没听懂 QAQ
甚至 C 的证明也没怎么懂,不知道会字符串的那帮人脑子是怎么转的。
慢慢来吧。
午饭外卖搞了个¥22 方便面炒鸡,肉给的很多,性价比在线,吃起来也香,四星半。
中午倒头就睡,一直在梦里的感觉真好鸭。
又到了悲闻哀见的队内赛时间。
开局 wa,难崩。
半小时开完三道签到,然后转向 C。一看就是分类讨论,这种题我一直捏不准,所以写的格外有条理。
大概写了二十来分钟,交!wa3!尼玛!果断拍!卧槽怎么十万组没拍出来!啊?
后面终于发现是最开始的特判错了!因为对拍很难拍无解我就略过了!唉,浪费了半小时左右。
然后看 B,啊?又是分类讨论?写!交!wa50!啊??????????
不知道为什么刚刚 C 拍的这么果断我这时候又犹豫了,开始手动检查逻辑,不出意外没检查出来。
磨磨唧唧了半天才拍,结果一下就拍出来了,是一个非常细的地方。
这次竟然浪费了 40 分钟,尼玛的。那只剩 25 分钟看 H 那个构造了,思前想后感觉只能知道后 \(n-k+1\) 个数和第 \(k\) 个数的大小关系,不知道前 \(1\sim k-1\) 个数。结束了,后面看了题解大呼智慧。
晚上和沙河的大伙一起去吃了 Kingburger!拼了鸡块和汉堡,我又搞了个 9.9 的 1+1,爽了。
味道不知道怎么评价,毕竟汉堡就是汉堡的味道,薯条就是薯条的味道,甜辣酱就是甜辣酱的味道。就好比在广西三品王就是三品王味,粉之都就是粉之都味一样,从小吃到大的东西,平时啥时候灵机一动就想吃,吃了上顿又不想吃下顿。
吃完和 xxx 回到基础实验大楼补题。
【队内赛 7 - H. 再多看一眼就会爆炸 - CF1720D. Strange Device】
题意:交互题。系统初始一个长为 \(n\) 的数组 \(\{a\}\),保证所有元素互不相同。给定正整数 \(k\),你每次可以询问 \(k\) 个不同的下标,系统会返回对应的 \(k\) 个数中的第 \(m\) 小的数的下标和值。最多可以询问 \(n\) 次,需要让你猜出 \(m\)。
\(1 \le k < n \le 500\),\(1 \le a_i \le 10^9\)。保证 \(1 \le m \le k\)。
据说有做法能只用下标而不用值,很牛。这里只说最简单的做法(不一定最容易想)
一种消耗 \(k+1\le n\) 次询问的方案如下:
只取前 \(k+1\) 个数,其余部分可以扔掉。
第 \(i\) 次询问序列:\([1,i-1]\land[i+1,k+1]\)。
不难发现答案只会有两个值,分别是这 \(k+1\) 个数的第 \(m\) 小数和第 \(m+1\) 小数。当去掉的数 \(a_i \le m\) 时询问到的就是后者,否则前者。
那么第 \(m + 1\) 小数被询问到的次数恰好是 \(m\)。取这上述两个值中的较大者,出现次数就是答案。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
void solve() {
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
if (k == 1) {
cout << "! 1" << endl;
return ;
}
auto query = [&] (int pos) -> array<int, 2> {
cout << "? ";
for (int i = 1; i <= k + 1; i++) {
if (i == pos) {
continue;
}
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int id, x;
cin >> id >> x;
return {id, x};
};
vector<array<int, 2>> a(k + 2);
map<int, int> mp;
for (int i = 1; i <= k + 1; i++) {
a[i] = query(i);
mp[a[i][1]]++;
}
int ans;
for (auto [_, x] : mp) {
ans = x;
}
cout << "! " << ans << endl;
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}【队内赛 7 - D. 这种感觉我从未有 - CF1720D. Cut and Stick】
题意:给定长为 \(n\) 的数组以及 \(q\) 次询问。每次询问一个区间 \([l, r]\),问把该区间最少分为几个子序列,使每个子序列(设长度为 \(len\))众数的出现次数 \(\le \left\lceil\frac{len}{2}\right\rceil\)。
\(1\le n,q,a_i \le 3\cdot 10^5\)。
设区间长度为 \(len\),众数的出现次数是 \(x\)。若 \(x\le \left\lceil\frac{len}{2}\right\rceil\),答案是 \(1\)。否则考虑分组,一种最优方案如下:
其它非众数一共有 \(len-x\) 个,将其与 \(len-x+1\) 个众数组合,因为此时长度是奇数,故组合后的序列是合法的。
剩下的众数有 \(x-(len-x+1)=2x-len-1\) 个,每个众数单独一组。
此时有了 \(2x-len\) 组,可以证明这是最优的。
证明就是此时划分成的每个子序列 “众数 \(-\) 非众数” 都达到了最大值 \(1\),为最饱和的状态。
剩下的问题就变成了典题 “求区间众数个数“,常用莫队和主席树。
同时众数因为有比较强的数量特征,随机化取众数也是十分可行的。这在数据结构专题 \(L\) 题有充分体现。
两种方法的时间复杂度分别是 \(O((n+q)\log n)\) \(\text{and}\) \(O(n+Aq\log n)\),\(A\) 为常数。
我这里糅合(懒)了一下,写了个莫队 \(+\) 随机化,\(O(q\log n+Aq\sqrt{n})\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
mt19937_64 rng(time(0));
int Rand(int l, int r) {
return rng() % (r - l + 1) + l;
}
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, q;
cin >> n >> q;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
vector<array<int, 3>> qry(q);
for (int i = 0; i < q; i++) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
qry[i] = {l, r, i};
}
int sz = n / sqrtl(1.0 * q * 2 / 3);
sort(qry.begin(), qry.end(),
[&] (array<int, 3> i, array<int, 3> j) {
if (i[0] / sz == j[0] / sz) {
if ((i[0] / sz) % 2) {
return i[1] < j[1];
} else {
return i[1] > j[1];
}
} else {
return i[0] / sz < j[0] / sz;
}
}) ;
vector<int> cnt(n + 1);
auto add = [&] (int x) {
cnt[a[x]]++;
};
auto del = [&] (int x) {
cnt[a[x]]--;
};
vector<int> ans(q);
int l = 1, r = 0;
for (auto [ql, qr, id] : qry) {
while (l > ql) {
add(--l);
}
while (l < ql) {
del(l++);
}
while (r < qr) {
add(++r);
}
while (r > qr) {
del(r--);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 25; i++) {
int pos = Rand(l, r);
if (cnt[a[pos]] > (r - l + 2) / 2) {
ans[id] = 2 * cnt[a[pos]] - (r - l + 1);
break;
}
}
if (!ans[id]) {
ans[id] = 1;
}
}
for (auto x : ans) {
cout << x << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}【7.18】 Day 11
起床了吗?如起。
午饭没吃,起床直接传送到 234 了。
下午 5h 队内赛。
前面稳扎稳打,比赛不到一半开了 6 题,自我感觉还是不错的。
然后就急转直下了,后面都在杠 F,怎么大家都会做?
赛后发现原来是我刚看 F 就得出了一个错误的结论 ”边界四个角只能选一个“,因为数据范围比较小后面我就往二分想了。这也太蠢了。
但二分的话最密也只能压缩到 \(9\sim10\) 次左右,红晕了。
最后半小时看了下榜随便开了个 K,看样例猜了个 BSGS,不出意料 wa2 了。
赛后 Vingying 讲题,思路很清晰鸭,甚至还有回放,爱了!期待下一次 vy 场OwO!
晚上跟 xxx 和 jbx 出去麦。
麦完回来又睡了,虽然很不情愿,一堆题没补,字符串也没看,但还是想打 CF 的时候能精神一点。
两个小时醒来 CF 继续唐!B 样例都没读懂代码就写完了,wa2 之后又搞到第 35 分钟才搞对。
C 一个简单 dp,也想了一个来小时。
剩半个小时,看了眼榜感觉 E 有希望,盲猜硬贪什么的。
结果把 xor 看成 or 了,完蛋。赛后发现是原,原题我还 AC 过,唐!
先从队内赛开始补,感觉 vy 选的题很有 edu 意义。CF 的题择日吧。
【队内赛 8 - C. ズッコケ問答 - gym103469E. Eulerian?】
题意:交互题。系统隐藏了一个 \(n\) 个点的无向连通图 \(G\),保证没有重边和自环。
你可以进行至多 \(60\) 次询问,每次询问 \(G\) 中一个点集,系统会返回该点集构成的导出子图的边数。
你的目标是确定 \(G\) 中是否存在一条欧拉回路。交互器不会自适应。
\(3 \le n \le 10^4\),保证 \(G\) 中边数不超过 \(10^5\)。
交互器无法自适应(即 \(G\) 不会随着询问而变化)提示我们采用随机化方法。
一个无向图存在欧拉回路的充要条件是所有顶点的度均为偶数。
我们考虑将 \(G\) 中的顶点随机分成两个集合 \(A, B\)。此时 \(G\) 中的边被分成了三部分:在 \(A\) 的导出子图中,在 \(B\) 的导出子图之中,以及横跨在 \(A, B\) 两个点集之间。
如果 \(A\) 中的顶点的度均为偶数,那么 \(A\) 中所有顶点的度数和也为偶数,又因为在 \(A\) 中的边每条贡献 \(2\) 的度数,不改变奇偶性,那么横跨在 \(A,B\) 之间的边也应该是偶数条。
故有如下询问方案:
消耗 \(1\) 次询问所有的 \(n\) 个点,得到 \(G\) 的总边数。
重复 \(29\) 次将 \(G\) 随机划分成 \(A,B\)。消耗 \(29\cdot2\) 次分别询问 \(A,B\) 导出子图中的边数,从而用总边数减去它们得到横跨边的数量。
若至少 \(1\) 次询问到了 \(A,B\) 间有奇数条横跨边,判定不存在欧拉回路;反之存在。
正确性证明:横跨边数目为奇数或偶数各占 \(\frac{1}{2}\) 概率,\(29\) 次判定仍旧失败的概率为 \(\frac{1}{2^{29}}\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
mt19937_64 rng(time(0));
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n;
cout << "? " << n << " ";
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cin >> m;
int test_case = 29;
bool ok = true;
while (test_case--) {
vector<int> A, B;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int o = rng() % 2;
if (o > 0) {
A.push_back(i);
} else {
B.push_back(i);
}
}
cout << "? " << A.size() << " ";
for (auto x : A) {
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int cnt1;
cin >> cnt1;
cout << "? " << B.size() << " ";
for (auto x : B) {
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int cnt2;
cin >> cnt2;
int mid = m - cnt1 - cnt2;
if (mid & 1) {
ok = false;
break;
}
}
if (ok) {
cout << "! YES" << endl;
} else {
cout << "! NO" << endl;
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
// cout.flush();
}
return 0;
}【队内赛 8 - K. 世界のまん中 - gym103469F. Fancy Formulas】
题意:给定一个质数 \(p\),以及 \(q\) 组询问。每次给定两个二元组 \((a,b)\) 和 \((c,d)\),保证 \(p\nmid (a+b)\)。
一次操作可以选择如下其一,你可以无限次操作。问是否能将 \((a,b)\) 转化为 \((c,d)\)。
\((a,b):=(2a\bmod p, (b+p-a)\bmod p)\)
\((a, b):=((a+p-b)\bmod p, 2b\bmod p)\)
\(2 \le p \le 10^9+7\),\(1\le q\le 10^5\)。
无论那种操作,操作后的 \((a, b)\) 均满足 \(s=(a+b)\bmod p\) 不变。
那么知道 \((a,b)\) 中的 \(a\) 或 \(b\),另一个也同时确定,\((c,d)\) 同理。
于是不妨将问题转化为:每次将一个整数 \(a\) 进行 \(a:=2a\) 或 \(a:= a-b\) 的操作,能否将 \(a\to c\)。
而 \(a:=a-b \Leftrightarrow a:=a-(s-a)\)。即 \(a:=2a-s\)。
但有 \(s\) 在仍旧不好处理,考虑给 \(a,c\) 都乘上 \(s^{-1}\),此时满足 \((a+b)\bmod p = 1\)。
问题再次转化为每次将一个整数 \(a\) 进行 \(a:=2a\) 或 \(a:=2a-1\) 的操作,能否将 \(a\to c\)。
这样就变成了单变量问题。注意到对 \(a\) 进行 \(k\) 次操作后得到的数一定在一个区间范围内连续分布,具体的,是 \([2^ka-(2^k-1), 2^ka]\)。而当 \(k > 30\) 的时候,这个区间的长度会 \(\ge p\),意味着在 \(\bmod p\) 意义下拥有 \(0\sim p-1\) 中的所有取值,就一定能找到和 \(c\bmod p\) 同余的数。
于是直接枚举 \(k\),当值域区间内第一次存在和 \(c\) 同余的数时,对应的 \(k\) 就是答案。
时间复杂度 \(O(q\log p)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
int qpow(int k, int n, int p) {
int s = 1;
for ( ; n; n >>= 1, k = k * k % p) {
if (n & 1) s = s * k % p;
}
return s;
}
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int p, q;
cin >> p >> q;
while (q--) {
int a, b, c, d;
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d;
if ((a + b) % p != (c + d) % p) {
cout << "-1\n";
continue;
}
int s = (a + b) % p;
a = a * qpow(s, p - 2, p) % p;
c = c * qpow(s, p - 2, p) % p;
if (a == c) {
cout << "0\n";
continue;
}
int cover = 0;
for (int i = 1, l = a, r = a; ; i++) {
l = l * 2 - 1;
r = r * 2;
if (l < 0) {
l = p - 1;
r = p;
}
int len = r - l + 1;
if (len >= p) {
cout << i << "\n";
break;
}
int lp = l % p;
int rp = r % p;
if (lp <= rp && lp <= c && c <= rp) {
cout << i << "\n";
break;
}
if (lp > rp && (c >= lp || c <= rp)) {
cout << i << "\n";
break;
}
}
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}【队内赛 8 - G. 名前をつけてやる - gym102471H. King】
题意:给定一个质数 \(p\)。一个长为 \(n\) 的序列 \(\{a\}\) 被称作 good,当且仅当 \(\exists q\in[1,p),\ \forall i \in[2, n], \ qa_{i-1}\equiv a_i \pmod{p}\)。
给定一个序列 \(\{b\}\),设其最长的 good 子序列长度为 \(len\)。若 \(len \ge \frac{n}{2}\) 输出 \(len\);否则输出 \(-1\)。
\(2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5\),\(2 \le p \le 10^9+7\)。
题目中 \(len \ge \frac{n}{2}\) 其实是一个随机化暗示。这意味着组成该子序列的元素在原序列中分布的十分密集。
如果 \(n\) 为奇数,那么至少存在一对相邻的数,它们的比值正好是公比(鸽笼原理)。
如果 \(n\) 为偶数,极限情况也是 \(\text{xoxoxoxo}\)(\(\text{x}\) 代表出现在最长的 good 子序列中),此时正好占到总长度的 \(\frac{1}{2}\)。
那么我们可以进行以下操作若干次以得到正确答案:
从 \(\{b\}\) 中随机选一对数 \((x, y)\),满足 \(y = x + 1\) or \(y = x + 2\)。
令公比为 \(\dfrac{b_y}{b_x}\),向 \(x\) 左侧和 \(y\) 右侧拓展得到满足该公比的最长 good 序列,设长度为 \(m\)。
若 \(2 \cdot m \ge n\),更新答案。
正确性证明:不是很会,但显然失败概率极低。实际取 \(50\) 次左右就能 AC 了。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
mt19937_64 rng(time(0));
int Rand(int l, int r) {
return rng() % (r - l + 1) + l;
}
int modp;
int qpow(int k, int n) {
int s = 1;
for ( ; n; n >>= 1, k = k * k % modp) {
if (n & 1) s = s * k % modp;
}
return s;
}
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n >> modp;
vector<int> b(n + 1), inv(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> b[i];
inv[i] = qpow(b[i], modp - 2);
}
int test_case = 50;
int ans = -1;
while (test_case--) {
int x = Rand(1, n - 1);
for (auto y : {x + 1, x + 2}) {
if (y > n) {
continue;
}
int d = b[y] * inv[x] % modp;
int res = 2;
for (int i = y + 1, lst = y; i <= n; i++) {
if (b[i] * inv[lst] % modp == d) {
res++;
lst = i;
}
}
for (int i = x - 1, lst = x; i >= 1; i--) {
if (b[lst] * inv[i] % modp == d) {
res++;
lst = i;
}
}
if (2 * res >= n) {
ans = max(ans, res);
}
}
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}【队内赛 8 - J. ワンターフォゲール - gym102992D. Degree of Spanning Tree】
题意:给你一张 \(n\) 个点 \(m\) 条边的无向图,你需要找到它的一个生成树,满足所有节点度数 \(\le \frac{n}{2}\)。
\(2 \le n \le 10^5\),\(n - 1\le m\le 2\cdot 10^5\)。
有正常做法,也有随机化做法,这里叙述后者。
我们先将所有边都连起来,尝试 dfs 找到一棵符合要求的生成树。
重复以下过程若干次:
随机一个起点,开始 dfs。
每到一个未经过的点 \(x\),将 \(x\) 的邻接边序列 shuffle 一遍。
遍历邻接边序列,在 \(x\) 不超度数的情况下能连边就连边,递归到点 \(y\)。
若遍历完所有点即找到一个连边方案。
实测 \(50\) 次就能 AC。正确性最不好证明的一集。
时间复杂度 \(O(50n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
mt19937_64 rng(time(0));
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
vector<int> vis(n + 1), deg(n + 1);
vector<array<int, 2>> ans;
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x) -> void {
vis[x] = true;
shuffle(adj[x].begin(), adj[x].end(), rng);
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (vis[y] || deg[x] >= n / 2) {
continue;
}
deg[x]++;
deg[y]++;
ans.push_back({x, y});
self(self, y);
}
};
int test_case = 100;
while (test_case--) {
vis.assign(n + 1, 0);
deg.assign(n + 1, 0);
ans.clear();
dfs(dfs, rng() % n + 1);
if (ans.size() == n - 1) {
cout << "Yes\n";
for (auto [x, y] : ans) {
cout << x << " " << y << "\n";
}
return ;
}
}
cout << "No\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}【7.19】 Day 12
定了 9 点的闹钟,但经典下床继续睡。
中午在基础实验大楼一楼售货机买了一个面包一盒纯牛奶。鉴定为贪睡导致的。
下午是 psk 场,不知道会不会整什么花活(然而并没有)。
经典从 M 倒序开题,我超,真是原。这题我怎么感觉在哪里见过啊?但没能想起来,悲。
手算了一下样例,发现样例都算不对。
跟榜过了三道签到。但 lyc 15min 过的 J 我怎么签不出来鸭?第一感觉是直接横坐标 \(+1\) 或纵坐标 \(+1\),狂wa,遂放着。
看榜 wbc 过了 D,看了下题,感觉和第三场队内赛的某个题很像,都是中间夹了个回文串,抄了个 manacher 就过了。
然后看 E,观察到一定是 \(1/3\) 一组 \(2\) 一组,就写了个二分图染色交了上去,怎么又 wa 了鸭。再次确定了一下思路,又捏了几个边界情况,感觉都没问题,就直接对拍启动了。结果拍出来是我 dfs 挂了,不是哥们?
继续看 J,我超为什么不对呢?干脆又写了个对拍。马上拍出来了,原来不一定是端点旁边啊?那我不会了。
看榜 lyc 过了 G,看题这不是逆序对模板题吗?15min 秒了。
怎么 J 和 L 过了一堆了鸭。L 还是推不出样例,J 画了几个图猜了个结论,又 wa。
红温了红温了红温了红温了红温了。直到赛后也没有过 J。
没有讲题,就去吃饭了。朝阳¥16 黑椒牛肉,还不错,三星半或者四星。
回 234 补题,但是头晕晕的,不知道什么时候就趴桌子上睡着了。醒来快 9 点半了。
感觉一天什么都没做,倒是欠的题又多了一堆。
【7.20】 Day 13
没起,起了。
没吃,吃了。(精神错乱)
下午和 B 搏斗 3h,终于在最后把 B 做出来了,排名鉴定为人口普查,唉。
【队内赛 10 - Being Meltdown - CF1516D. Cut】
题意:给定长度为 \(n\) 的序列 \(\{a\}\),\(q\) 次询问。每次询问一段区间 \([l, r]\),问至少要把这个区间分为几个子区间,才能使每个子区间的数的乘积等于这个子区间内所有数的 \(\text{Lcm}\)。
\(1 \le n,q,a_i \le 10^5\)。
区间乘积 \(=\) 区间 \(\text{Lcm}\) 即区间中的数两两互质。
那么对于每个询问只需要从左往右扫,如果加上这个数之后区间不满足两两互质,就新开另一个区间。
考虑优化这个过程,通过枚举质因数,可以预处理出 \(nxt_i\) 代表 \(i\) 后面第一个不和 \(a_i\) 互质的数的位置。
那么一段区间两两互质等价于右端点是 \([l, r]\) 中所有的 \(nxt_i-1\) 取 \(\min\)。
具体地,令 \(dp_i\) 代表以 \(i\) 为左端点时,下一个左端点的位置,即:\(dp_i = \min\limits_{j = i}^{nxt_i - 1}nxt_j\)。这个式子可以用 st 表 \(O(n\log n)\) 预处理。
那么每次询问就可以不断跳到下一个左端点的位置,以求出区间数量。
套路化地,还可以倍增加速:令 \(dp_{i, j}\) 代表 \(i\) 后面第 \(2^j\) 个左端点的位置。
时间复杂度 \(O((n+q)\log n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
vector<int> prime;
void init_phi(int n) {
vector<bool> not_prime(n + 1);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if(!not_prime[i]) {
prime.push_back(i);
}
for (auto j : prime) {
if (i * j > n) {
break;
}
not_prime[i * j] = true;
if (i % j == 0) {
break;
}
}
}
}
struct SparseTable {
int n;
vector<vector<int>> ST;
SparseTable(vector<int> &arr) {
this->n = arr.size() - 1;
ST.resize(n +1 ,vector<int>(26));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
ST[i][0] = arr[i];
}
for (int j = 1; j <= __lg(n); j++) {
for (int i = 1; i + (1LL << j) - 1 <= n; i++) {
ST[i][j] = min(ST[i][j - 1], ST[i + (1LL << (j - 1))][j - 1]);
}
}
}
int query(int l,int r) {
int len = __lg(r - l + 1);
return min(ST[l][len], ST[r - (1LL << len) + 1][len]);
}
};
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, q;
cin >> n >> q;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
int mx = *max_element(a.begin(), a.end());
vector<vector<int>> b(mx + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x = a[i];
for (auto p : prime) {
if (p * p > x) {
break;
}
if (x % p == 0) {
b[p].push_back(i);
while (x % p == 0) {
x /= p;
}
}
}
if (x != 1) {
b[x].push_back(i);
}
}
vector<int> nxt(n + 1, n + 2);
for (int i = 2; i <= mx; i++) {
if (b[i].empty()) {
continue;
}
for (int j = 0; j < b[i].size() - 1; j++) {
nxt[b[i][j]] = min(nxt[b[i][j]], b[i][j + 1]);
}
}
SparseTable st(nxt);
vector dp(n + 3, vector<int>(26));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i][0] = st.query(i, min(n, nxt[i] - 1));
}
for (int j = 1; j <= 25; j++) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[dp[i][j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
while (q--) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
int pos = l, res = 0;
for (int i = 25; i >= 0; i--) {
if (dp[pos][i] > 0 && dp[pos][i] <= r) {
res += 1 << i;
pos = dp[pos][i];
}
}
cout << res + 1 << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
init_phi(1e5);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}晚上 atc,犯病了,E 拉了坨大的,后面发现只要把四周框起来就行了。
CF 继续犯病,D 很快就想到一行里黑色格子的数量大于 \(4\) 就直接消行。但剩下的 \(n\times 4\) 不会处理,脑子里一直想的状压 dp,一行记作一个状态,结果转移直到比赛结束都没写出来。
新建一个超级源点,先用并查集把边框和源点连起来。那么从 \(1\sim Y\),依次遍历海拔高度为 \(i\) 的点,看其四周有没有海拔小于等于它的点,有就并起来,那么和源点并起来的点的个数就是被淹没的点的个数。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
struct DSU {
vector<int> f, siz;
DSU() {}
DSU(int n) { init(n);}
void init(int n) {
f.resize(n + 2);
siz.resize(n + 2);
for(int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) {
f[i] = i;
siz[i] = 1;
}
}
int find(int x) {
if (x == f[x]) return x;
return f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
bool same(int x, int y) {
return find(x) == find(y);
}
bool merge(int x, int y) {
x = find(x);
y = find(y);
if (x == y) return false;
if (siz[x] < siz[y]) {
swap(x, y);
}
siz[x] += siz[y];
f[y] = x;
return true;
}
int size(int x) {
return siz[find(x)];
}
};
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n, m, t;
cin >> n >> m >> t;
vector a(n + 2, vector<int>(m + 2));
vector<vector<array<int, 2>>> b(t + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
cin >> a[i][j];
if (a[i][j] <= t) {
b[a[i][j]].push_back({i, j});
}
}
}
int S = (n + 2) * (m + 2) + 1;
DSU dsu(S);
for (int i = 0; i < n + 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m + 2; j++) {
if (i == 0 || j == 0 || i == n + 1 || j == m + 1) {
dsu.merge(S, i * (m + 2) + j);
}
}
}
int init = dsu.size(0);
int dx[] = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int dy[] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
for (int i = 1; i <= t; i++) {
for (auto [x, y] : b[i]) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
int xx = x + dx[j];
int yy = y + dy[j];
if (a[xx][yy] <= a[x][y]) {
dsu.merge(x * (m + 2) + y, xx * (m + 2) + yy);
}
}
}
cout << n * m - (dsu.size(0) - init) << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}题意:给定一个 \(n\times n\) 的网格,第 \(i\) 行前 \(a_i\) 个格子是黑色,其余为白色。每一次操作可以选择将一行全部涂白或将一个 \(2\times 2\) 的区域全部涂白,问将所有格子涂白所需的最小操作次数。
\(1 \le n \le 2\cdot 10^5\),\(0 \le a_i \le n\)。
首先某一行如果有巨多黑色格子,直接运用第一种操作显然最佳。
第一个观察:若某行有大于 \(4\) 个黑色格子,直接整行涂白。
- 证明:大于 \(4\) 个格子,那么至少用 \(3\) 次 \(2\times 2\) 操作,最优情况将这一行连带下一行一起清理完,但如果用涂整行的操作的话仅用 \(2\) 次。
现在问题变为了将 \(n\times 4\) 的矩阵涂白的最小操作次数。
考虑一个逐行的贪心,同时引出第二个观察:若某行剩余黑格数 \(> 2\),直接整行涂白。
- 证明:当剩余黑格数 \(>2\) 时,说明该行一定没有被上一行连带消去过任何一个格子。此时用 \(2\times 2\) 消除至少需要 \(2\) 次,最优情况将下一行连带清理完,仍然不如使用 \(2\) 次整行涂白。
综上,设 flag = 0 / 1 / 2 代表该行没被上一行连带消除
\(/\) 被连带消除了 \(1\sim2\) 列的黑格 \(/\) 被连带消除了 \(3\sim 4\) 列的黑格,逐行贪心即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] > 4) {
a[i] = 0;
ans++;
}
}
vector<int> flag(n + 1);
// 1~2 cols have colored = 1
// 3~4 cols have colored = 2
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (a[i] <= 0) {
continue;
}
ans++;
if (a[i] <= 2) {
if (flag[i] == 1) {
flag[i + 1] = 2;
a[i + 1] = min(2ll, a[i + 1]);
} else {
flag[i + 1] = 1;
a[i + 1] -= 2;
}
}
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}【7.21】 Day 14
难得的周末,但是在睡梦中度过了。
我越来越喜欢睡觉了,只是有时候事情积压的太多了,只能熬夜去赶进度。
梦里什么都有,只是上一次做梦些许是半个月之前了。梦到了知更鸟,以及一些散装的小剧场。
网上有一种说法是人每次睡觉都会做梦,只是回想不起来罢了。
也许是记忆被抹杀才带来的孤独。
下午才醒,不是很想动,感觉训练对我作用不大,我的智商就摆在这里了。
越来越菜了,高中我也何尝不是这样呢?暑假一轮只剩一周,也许到最后没比赛打,没人愿意和我组队,甚至队都没进。
我努力过了吗?努力的时候不敢说自己努力了,不努力的时候也不敢说自己什么都没干。这么问也就显得乏之无味。
对不起很多人,集训队的大家,青柠工作室,以及嵌入式工作室的大家,他们都很看好我,但我就像不谙世事的孩子一样,又时不时吐露出自己悲哀的那一面。
翻了个身,之后又联想到很多心酸的事实,旁人的责备,又或者是 galgame 里的一段刀子,就像走马灯一样。
当一个人濒临崩溃的时候,它会想些什么呢?
啜泣,心绞痛,干脆继续睡了过去。
希望有羽毛和翅膀。
【7.22】 Day 15
昨晚直接在基础实验大楼睡了。11 点 30 有人推门我就醒了。
午饭又没吃,是不是只要 5h 场就没吃过午饭,好像真是。
下午队内赛,很奇怪的场,怎么我每题必 wa,真是病入膏肓了鸭。
开局 L,我用二进制考虑,结果卡壳了,遂看其它的。
开了三题怎么用了一个多小时啊,最慢的一集。感觉自己状态有问题,情绪被影响了,打字都很佛系。
再开 C,wa,稍微用力的想了下,红温之后想到负数会出问题,加了个判断过了。
L 也会了,宏观的考虑先一直乘 \(2\),看需要减多少,再分配到前面乘 \(2\) 的操作之间。
然后开始博弈,上次博弈挂完了,想雪耻。
雪耻失败了,两个小时没做出博弈,只想到 \(n\le 3\) 怎么做,\(n\) 大了脑子就转不动了。
完败,还好后面红温了也能看清 K,写了个最短路就过了。
晚上直接在 234 点了外卖,焖饼炒鸡!一般,三星半。
【队内赛 11E - gym105161K. Number Deletion Game】
题意:给定 \(n\) 堆石子,第 \(i\) 堆数量 \(a_i\)。两名玩家博弈,每轮玩家可以选择拿走最多的一堆石子中的任意个,无法操作则判输。问先手是否有必胜策略。
典题。结论是:\(a_i\) 最大值出现奇数次,先手胜;否则后手胜。
证明使用归纳法:
\(\max = 1\),显然成立。
设对 \(\max =1\sim k\) 成立,则对 \(\max= k+1\):
若 \(k+1\) 出现奇数次,则操作最后一个 \(k+1\) 的是先手。先手可以决定次大值出现偶数次,这样后手输,先手胜。
若 \(k+1\) 出现偶数次,则操作最后一个 \(k+1\) 的是后手,同理后手胜。
故结论对 \(\max=k+1\) 成立,于是对最大值为任意正整数都成立,证毕。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
int cnt = 1, j = n - 1;
while (j > 0 && a[j - 1] == a[n - 1]) {
j--;
cnt++;
}
if (cnt & 1) {
cout << "Alice\n";
} else {
cout << "Bob\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}【队内赛 11J - CF730J. Bottles】
题意:有 \(n\) 瓶水,第 \(i\) 瓶水的水量为 \(a_i\),容量为 \(b_i\)。将 \(1\) 单位水从一个瓶子转移到另一个瓶子所消耗时间为 \(1\) 秒,且可以进行无限次转移。求储存所有水所需最小瓶子数 \(k\) 以及该情况下所用最小时间 \(t\)。
\(1 \le n, a_i, b_i \le 100\)。
\(k\) 比较简单,将容量降序排序,之后按顺序取到 \(\min\limits_{k}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{k}b_i \ge \sum a_i\) 即可。
对于求最小时间 \(t\),可以转化为在这 \(n\) 个瓶中取 \(k\) 个瓶,使得剩余瓶子的水量之和最小,也就是使这 \(k\) 个瓶的水量之和最大。
这是经典的 \(01\) 背包问题,令 \(dp[i][j][s]\) 代表前 \(i\) 个瓶中选了 \(j\) 个瓶,容量之和为 \(s\) 时的最大水量,则: \[ dp[i][j][s] = \max(dp[i-1][j][s], dp[i-1][j-1][s-b_i]+a_i) \] 其中第一维可以滚动,或者倒序枚举压缩掉。
时间复杂度 \(O(n^4)\),空间复杂度 \(O(n^3)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
struct node {
int water, vol;
friend bool operator < (const node &a, const node &b) {
return a.vol > b.vol;
};
};
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<node> a(n + 1);
int sum_water = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i].water;
sum_water += a[i].water;
}
int sum_vol = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i].vol;
sum_vol += a[i].vol;
}
sort(a.begin() + 1, a.end());
int ans1 = 0;
for (int i = 1, sum = 0; i <= n; i++) {
sum += a[i].vol;
if (sum >= sum_water) {
ans1 = i;
break;
}
}
vector dp(ans1 + 1, vector<int>(sum_vol + 1, -inf));
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = ans1; j >= 1; j--) {
for (int k = sum_vol; k >= a[i].vol; k--) {
dp[j][k] = max(dp[j][k], dp[j - 1][k - a[i].vol] + a[i].water);
}
}
}
int ans2 = 0;
for (int i = sum_water; i <= sum_vol; i++) {
ans2 = max(ans2, dp[ans1][i]);
}
cout << ans1 << " " << sum_water - ans2 << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}【队内赛 11D - gym105161B. Area of the Devil】
题意:给一个半径为 \(r\) 的圆上的五段不相交的圆弧,从每个圆弧依次选择一个点然后按顺序连成一个五角星,求五角星的面积并。
\(1\le T \le 10^4\),\(1 \le r \le 10^3\)。
如下图。我们用整个圆的面积减去五个(小三角 \(+\) 弓形)的面积即可。
令 \(A_{is}\) 代表第 \(i\) 段圆弧的极角最小点,\(A_{it}\) 代表第 \(i\) 段圆弧的极角最大点。
以 \(\Delta A_{1s}B_{1}A_{5t}\) 为例,\(B_1\) 可以通过直线 \(A_{2s}A_{5t}\) 和 \(A_{1s}A_{4t}\) 求交点得到。知道了三角形三个点的坐标,利用叉积公式即可求得面积。
弓形 \(\overset{\frown}{A_{1s}A_{5t}}\) 也等价于 \(S_{\text{扇形}OA_{1s}A_{5t}} - S_{\Delta OA_{1s}A_{5t}}\)。
时间复杂度 \(O(T)\)。
值得注意的是,使用叉积公式时不需要加绝对值,因为我们求的是有向面积。
如下图(可爱的 xing4c 画出来的!),当出现优弧时,阴影部分的面积应该被加上而不是减去。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
#define pi acos(-1)
template<class T>
struct Point {
T x, y;
Point(T x_ = 0, T y_ = 0) : x(x_), y(y_) {}
Point &operator+=(Point p) & {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
return *this;
}
Point &operator-=(Point p) & {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
return *this;
}
Point &operator*=(T v) & {
x *= v;
y *= v;
return *this;
}
Point operator-() const {
return Point(-x, -y);
}
friend Point operator+(Point a, Point b) {
return a += b;
}
friend Point operator-(Point a, Point b) {
return a -= b;
}
friend Point operator*(Point a, T b) {
return a *= b;
}
friend Point operator*(T a, Point b) {
return b *= a;
}
friend bool operator==(Point a, Point b) {
return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y;
}
};
template<class T>
T cross(Point<T> a, Point<T> b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
template<class T>
struct Line {
Point<T> a, b;
Line(Point<T> a_ = Point<T>(), Point<T> b_ = Point<T>()) : a(a_), b(b_) {}
};
template<class T>
Point<T> lineIntersection(Line<T> l1, Line<T> l2) {
return l1.a + (l1.b - l1.a) *
(cross(l2.b - l2.a, l1.a - l2.a) /
cross(l2.b - l2.a, l1.a - l1.b));
}
template<class T>
double area(vector<Point<T>> a) {
int n = a.size();
double res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res += cross(a[i], a[(i + 1) % n]);
}
res /= 2;
return res;
}
/*ooooooooooooooooooooo
o templates above o
oooooooooooooooooooooo*/
void solve() {
int r;
cin >> r;
vector<Point<double>> a(5), b(5);
vector<int> ori_a(5), ori_b(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cin >> ori_a[i];
double x = r * cos((1.0 * ori_a[i] / 360) * 2 * pi);
double y = r * sin((1.0 * ori_a[i] / 360) * 2 * pi);
a[i] = {x, y};
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cin >> ori_b[i];
double x = r * cos((1.0 * ori_b[i] / 360) * 2 * pi);
double y = r * sin((1.0 * ori_b[i] / 360) * 2 * pi);
b[i] = {x, y};
}
double circle = 1.0 * r * r * pi;
double res = circle;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Line<double> l1({a[i], b[(i + 3) % 5]});
Line<double> l2({a[(i + 1) % 5], b[(i + 4) % 5]});
Point<double> p = lineIntersection(l1, l2);
res -= area(vector{p, b[(i + 4) % 5], a[i]});
res -= (circle * ((ori_a[i] - ori_b[(i + 4) % 5] + 360) % 360) / 360) -
area(vector{{0, 0}, b[(i + 4) % 5], a[i]});
}
cout << fixed << setprecision(8) << res << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
C++后缀自动机(SAM)小记
架构
不包含后缀链接时是一张有向无环图。
至多 \(2n-1\) 个点,\(3n-4\) 条边。
在线的线性算法。
Endpos
\(\text{endpos}\) 是子串在 \(S\) 中结束位置的集合,\(\text{endpos}\) 相等的子串归为一个等价类。
图上到达该节点的所有路径构成了以该等价类为结尾的所有后缀子串。
最长的子串称作 \(\text{longest(x)}\),将 \(\text{endpos}\) 等价类中的子串按长度从大到小排序得到了 \(\text{longest(x)}\) 长度连续的后缀。
原串的每个前缀都是 \(\text{longest}\)。
Link
一个状态的 \(x\) 的 \(\text{link(x)}\) 连接到最长的后缀 \(y\),满足 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 拥有属于不同等价类。
如果满足条件的后缀是空串,会直接连向起始节点。
SAM 维护的三个信息:\(\text{longest(x)}\) 的长度 \(\text{len(x)}\),后缀链接 \(\text{link(x)}\),转移 \(\text{nxt(x, c)}\)。
节点和 \(\text{link}\) 构成一棵树,称作 \(\text{parent}\) 树。
构建
每插入 \(c\) 一定会出现一个新的状态(设为 \(\text{cur}\)),且一定是 \(\text{longest(lst)}+c = \text{longest(cur)}\)。
开始时 \(\text{cur}\) 只有一个串。让指针从 \(\text{lst}\) 开始,通过 \(\text{link}\) 往起点的方向跳。对于路径上的状态 \(\text{p}\),如果没有 \(\text{nxt(p, c)}\) 的转移,那么 \(\text{nxt(p, c) = cur}\)。
因为 \(\text{link}\) 指向的都是 \(\text{longest}\) 的后缀,所以自然构成新的子串。
如果已经存在转移,设当前状态为 \(\text{p}\),\(\text{q=nxt(p,c)}\),存在两种情况:
若 \(\text{len(q)=len(p)+1}\),说明 \(\text{q}\) 中最长的字符串一定是 \(\text{longest(p)+c}\),故连 \(\text{link(cur)=q}\),退出。
否则把 \(\text{q}\) 拷贝到一个新状态 \(\text{clone}\),\(\text{clone}\) 拥有 \(\text{link(q)}\) 以及 \(q\) 所有的出边。令 \(\text{link(clone)=link(p)+1}\),再把 \(\text{q}\) 和 \(\text{cur}\) 都 \(\text{link}\) 到这个点。
继续从 \(\text{p}\) 向起点跳 \(\text{link}\),若存在指向 \(\text{q}\) 的出边,改成指向 \(\text{clone}\);否则退出。
这么做是因为 \(\text{q}\) 原来就存在,但我们不清楚 \(\text{q}\) 的最长串是不是 \(\text{longest(p)+c}\),于是将 \(\text{longest(p)+c}\) 和其在 \(\text{q}\) 中的后缀单独拿出来,形成一个新的节点 \(\text{clone}\),以满足 \(\text{link(cur)}\) 的要求。
【7.23】 Day 16
要结束了啊,希望今天队内赛能打好一点。
rating 已经排到 20 名开外了,脑子再不发力就真寄了,脑子给点力哇qwq。
队内赛12,开题最慢的一次,不是怎么大家都会勾股数?输!
注意到了当 \(a\) 是质数的时候 \(b,c\) 一定连续,交!wa!
受不了了跟榜看 b,还好是一个简单二分,要不然 1h 过不了一题(
继续看勾股数,不是所有数质因数分解都能有解,比如 \(2\) 就没有一组解,又不会了。
继续看榜,K 中位数很有意思,map 搞了一下过了。G,H 都 wa2,2h 了,急急急。
F 有一个人过了,我一看,我趣!这不跑两遍就行了吗,这么简单竟然 2h 才开出来,G 加了特判也过了。
然后终于会勾股数了,特判了一组 8 15 17,\(8\) 之后 \(2\) 的倍数都这么搞。
H 是个分类讨论,wa119,红温!拍!成了!但改了好久。你说得对但 M 怎么一直过不了鸭。
赛后在群里说,感觉做法没什么问题。结果 wbc 一眼看出我用
lower_bound 搜了一个无序的数组,尼玛!
std::lower_bound 需要保证数组有序。
std::erase(std::vector)
就算你指定了在迭代器的哪个位置,删除也是线性的!
晚上本来想在 234 打 CF 的,外卖都直接点到了 234,暴暴锅好吃捏。
但太累了,支持不住,还是回宿舍睡了。
快进到赛后,稳定汤碗。
B2 做了 90min,原来是模拟题,乐。
如果不看 B2 直接看 C 分都会高很多,掐点过样例,气得睡不着觉。
但还是睡了,因为感觉总是上午 11 点起有点那啥了,还是得调整一下。
【7.24】 Day 17
8 点下床,怎么又睡了??不过好在 9 点醒了,不算荒废了很多。
这几天要开始学字符串,学几何,写专题了。毕竟专题不做个五六道真进不了队了。
时间紧,直接把补题停了。
所以之后几天你只能在这篇文章里看到流水账了( 专题解题报告可能也会发到博客上,不过一轮结束前不能够公开。
中午朝阳,鸡扒饭,出品很稳定啊,四星。
下午队内赛 13,开局怎么这么顺,上一次 1h 过四题不知道是什么时候了。
心里正乐着结果 J 又开始了,wa3,wa5,wa9,wa11,wa27。
爆了,去看 K,类似生命游戏。直接广搜,搜完发现读错题了,我以为是 “周围有不同颜色的块就变化”。
于是看 H,裸 meet in the middle,一发过。然后 K 发现改一下就行。
J 继续红温,感觉交了得有二十多发。转向 C,写了个割边构造,wa8,没救了!
继续交 J,三十多发了,寄!
赛后听芙兰朵和小武说看我代码看乐了,然后才知道我二分图判定直接退出会导致同一个连通块搜两遍。
啊,红温了红温了红温了红温了红温了红温了红温了红温了红温了红温了。
于是和可爱的 xing4c 去汉堡王降温,爽点,爽吃。
菠萝派真的好好吃鸭,还点了个可可味的派,也好吃!
晚上宿舍睡了,然后 10 点多爬起来洗了个澡,看专题。
【7.28】后日谈
真的结束了啊?想起 7.8 的时候还在为暑假哀悼,一转眼就到尾声了。
当然,指的是一轮集训。能否进得了二轮还有待商榷,负责人把最关键的 Rating 排名藏起来了,真是趣味呢。
尝试回忆我经历了什么,第一个想到的就是群主 xcy。
他很贴心,可爱,好说话。集训的时候有一天我因为个人原因没有去,他就来宿舍找我;我听讲座他下来看我,我跟他抱怨除了第一题都没听懂,他也安慰我慢慢来。
也许很多年之后别人问我暑假集训是怎么样的,我也只能说上来这些。
毕竟学到了什么知识,谁讲课讲的特别好,谁的 PPT 又做得根屎一样,都经不住时间的冲刷。
也正是因为这样,记录才有记录的价值。就比如讲课讲得特别好的,徐神,包大✌,vingying,这些都能脱口而出。讲得烂的,啊这是能说的吗?前文已经有了,这里就不重复提了(真没有贬低的意思)。然后队内赛打得牛的,lyc,czz,rzy。尤其 lyc 鸭,经常被 2n,照这个进步速度估计明年就和银牌✌组队了啊!
此外,能想起来的就是集训队的大家。为什么这么说,因为我虽然线下唯唯诺诺,但是事水群糕手
。真的是这样,水群水的多,就能记得住集训队的大伙。大伙喜欢什么,爱看什么,经常说什么话,最后都会变成回忆的一部分。
说回集训,时间安排还是十分紧密的。这篇博客本身就能看出很多东西,就比如我不知不觉埋了各式各样的坑,几周前说的 “明天再补吧” 或许今天都没能补的上。但与其说紧吧,感觉也没那么阴沉,因为算法本身我认为就是充满乐趣的。就算我没能进队,我也会继续打 CF,明年暑假集训我还能继续陪跑。
然后不得不说的就是舍友了,jbx,xjj,还有 everflame。因为都是沙河的,所以也聊得来,队内赛打得不好,CF 打挂了都可以相互抱怨,有什么八卦也都可以图一乐。
真的结束了吗?
\[ \begin{align} &\color{Rhodamine}無くなったのか 始まったのか分からないけど\\ &\color{Cerulean}究竟是失去还是开始\\\\ &\color{Rhodamine}行くしか方法は無いんだろう?\\ &\color{Cerulean}可除了前进也没有其它办法了吧?\\\\ &\color{Rhodamine}正解がなんだ 価値なんて無いんだ\\ &\color{Cerulean}正确答案是什么 \ \ 毫无价值可言\\\\ &\color{Rhodamine}あたしは生涯 あたし以外じゃ生きられないよ\\ &\color{Cerulean}我终其一生 \ \ 都无法活成别人的模样\\\\ &\color{Rhodamine}これ以上かき乱しても明日はない\\ &\color{Cerulean}哪怕将一切颠覆搅乱仍不会迎来明天\\\\ &\color{Rhodamine}どう足掻いても明日はない\\ &\color{Cerulean}如何竭力挣扎都不会迎来明天\\\\ &\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad——\small \text{ GIRLS BAND CRY}\normalsize《空の箱\normalsize》 \end{align} \]
UPD:进队了!不知道是不是被群巨捞了QAQ