【题解】2025 UESTCPC 初赛
据说题比去年初赛要简单,但我去年抱上了 lyc 大腿,所以完全不记得去年难度怎么样了。
今年来验题,但水平有限(集训队垫底水平),只验了一些简单题。
其中 A 题是经出题人提醒做出来的,D 偷看了 Tag,H 和 L 则完全不会,等有出题人题解了我再补上来。代码都写的很唐,也不一定是最优解,不要笑话我QAQ。
主观难度分布(H、L 未做出):
签到:F,G,J,N。
Easy:B,C,I,O,P。
Easy_Mid:K,M。
Mid:D,E,Q。
Mid_Hard:\(\varnothing\)。
Hard:A。
写下这段话的时候还有三天才初赛,大胆猜测决赛线是 \(4\) 题(签到即送)。
(upd on 04.01)大一队伍 4 题,非大一队伍 5 题,外校未知。
(upd on 赛后)按榜来看 H 是 Easy/Easy_Mid,L 是 Mid_Hard/Hard。
(upd on 03.31)来点链接。
补题链接:Cdoj。
题面:Statement。
出题人题解:Solution。
查重前榜单:Scoreboard。
(upd on 赛后)来点 Statistics。
本场比赛共有 405 支队伍报名,其中正式队 278 支,打星队 127 支。
有效参赛队伍(至少通过 \(1\) 题)总计 309 支,其中正式队 212 支,打星队 97 支。
最终 3 支队伍 AK,过题数情况如下。
| 组别 | 过题数 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正式队 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 4 |
| 打星队 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 8 | 8 | 6 |
| 组别 | 过题数 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正式队 | 9 | 14 | 8 | 14 | 23 | 14 | 56 | 35 | 31 |
| 打星队 | 6 | 3 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 5 | 17 | 6 | 4 |
接收到 8978 份有效 submissions,1698 份答案正确。
(upd on 初赛日)来点赛时趣事:
08:58 哎我草怎么是我发题面,赶紧登上 dj 下了个发到群里。
09:20 卧槽了,C 怎么被暴力过了,还碾压 std。验题的时候不交暴力导致的。
09:43 大哥给 C 加了一组数据,好很多了。
10:03 哎哎,I 的精度被浮点数硬抗过去了,精度大师。
10:47 Queue 莫名其妙 5min 了,有点爆了。
10:55 Queue 越来越长了,爆爆爆,准备多搞几台服务器加 judgehost。
11:20 加了一台 8c16g 开了 8 个 judgehost,把原来的关掉了,只跑 web。
11:27 貌似有点好转(?)
11:31 好起来了。终于有时间看榜,发现 M 竟然还没人过啊,低估了。
Fun Fact:在 pool 里 M 的难度是 *1300,有点幽默。
11:41 DeepSleep 这么厉害啊,队里两个 2000+ 就是不一样。
11:52 网页 502 了????
11:55 k4c 很快就发现
/etc/php/8.2/fpm/pool.d/domjudge.conf 里
request_slowlog_timeout 的值写成了
10si,多了个 i。改完马上又好了。
12:01 L 被开出来了啊。你知道的,我一直是 DeepSleep 的粉丝。
下午就比较清闲了,大概就是时不时把 judgehost 的 internal error 给 resolved 一下。
本来想润去打洛谷的蓝桥杯模拟赛,斟酌了一下还是算了。
这期间 QQ
收到了若干人机大学生发来的弱智让人啼笑皆非的私信。
15:37 sooke 拿到了 first AK!
16:58 第一发交 clar 的代码出现了。
不知道会不会有往 clar 里交奶龙的,很期待啊!
19:08 DeepSleep 也 AK 了,仿佛看到了泥电的下一支 wf 队。
20:10 爆爆爆,O 被乱搞搞过去了。更有戏剧性的是我看出题人的题解,突然发现我验题的时候写了个错解(下面改正了),太难绷了。
在这里给大伙磕头了。
A. 炼金术士
拉姆齐定理指出,\(6\) 个点的完全图(\(K_6\))用两种颜色任意着色(每条边都必须着色),必然存在至少一个单色三角形。
这意味着我们选出的 “黑化边” 与 “白化边” 并集的边导出子图一定不含 \(K_6\)。
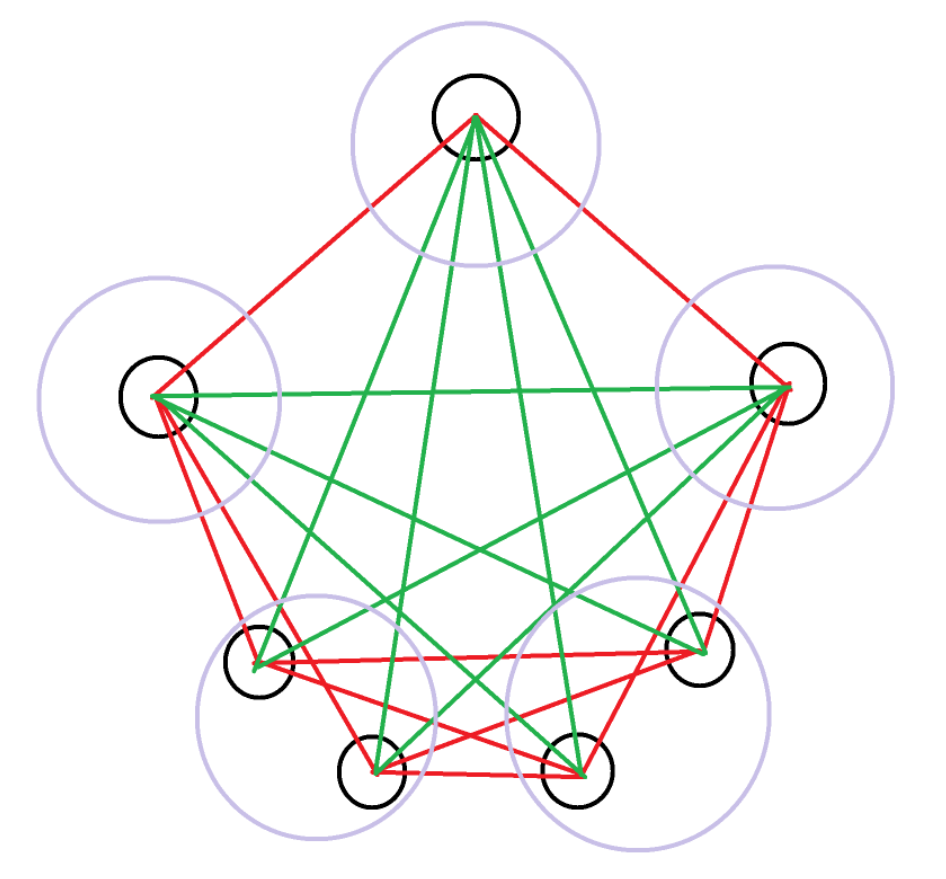
发扬人类智慧,考虑这么一种构造:将 \(n\) 个点划分成尽可能平均的 \(5\) 个集合,每个集合内部互不连边,不同集合间全部连边。
根据抽屉原理,从中任意选出 \(6\) 个点,至少有 \(2\) 个来自同一集合,没有连边,故不含 \(K_6\)。在此基础上,容易说明这样的构造具有最大连边数。
接着,我们要将这些边划分成两个集合,每个集合不含三元环,且其中一个集合能塞得下给定的长度为 \(k\) 的无环链。
再度发扬人类智慧,给上述 \(5\) 个点集编号 \(0\sim 4\),进行如下构造:
“黑化边”:点集 \(i\) 中的所有点向点集 \((i+1)\bmod 5\) 中的所有点连出的边。
“白化边”:剩下的所有边。
因为一个三元环肯定有一条边的两个端点不来自相邻的点集,故 “黑化边” 不含三元环。
而 “白化边” 要满足 “任意一条边都不来自相邻点集”,则至少需要 \(6\) 个点集,不满足。
此外,在这 \(5\) 个点集上绕圈圈,一定能构造出一条包含所有 \(n\) 个顶点的链,将给定的链随便插进一个位置即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(n^2)\)。
上图是 \(n=7\) 的图例,\(5\) 个集合的大小分别为 \(2, 2, 1, 1, 1\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
vector<int> a(k + 1);
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
vector<vector<int>> b(5);
vector<int> bel(n + 1);
{
vector<bool> vis(n + 1);
int cur = 0;
for (auto x : a) {
b[cur].push_back(x);
bel[x] = cur;
cur = (cur + 1) % 5;
vis[x] = true;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis[i]) {
b[cur].push_back(i);
bel[i] = cur;
cur = (cur + 1) % 5;
}
}
}
vector vis(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1));
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int j = (i + 1) % 5;
for (auto x : b[i]) {
for (auto y : b[j]) {
vis[x][y] = vis[y][x] = 1;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (bel[i] != bel[j] && vis[i][j] == 0) {
vis[i][j] = vis[j][i] = 2;
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
ans += (vis[i][j] > 0);
}
}
cout << ans << "\n";
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
if (vis[i][j] == 1) {
cout << '+';
} else if (vis[i][j] == 2) {
cout << '-';
} else {
cout << '0';
}
}
cout << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}B. 简单可满足性问题
假定已经将所有变量赋过了值,可以分出以下三类子句。
该子句所有变量均为 \(1\),此时子句的值为 \(1\)。
该子句所有变量均为 \(0\),此时子句的值为 \(0\)。
该子句部分变量为 \(1\),此时子句的值为 \(1\)。
注意到当我们给所有变量取反时,第一和第二类子句个数互换,第三类子句个数不变。
而 “第一 + 第三” 类子句的个数和 “第二 + 第三” 类子句的个数总有一个 \(\ge \lceil\frac{m}{2}\rceil\)。
给所有变量任意赋值,验证不满足后就全部取反,总有一个满足条件。
时间复杂度 \(O(m)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int num;
cin >> num;
int ok = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < num; j++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
ok |= y;
}
if (ok) {
res++;
}
}
int ans = 1;
if (res * 2 < m) {
ans = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << ans << " \n"[i == n - 1];
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}C. 箭串
将询问离线。暴力做就是倒序遍历每个区间,如果是
*,就覆盖;否则不操作。
用 std::set 维护当前还存活的 *
的位置。对于一个询问 \([l,r]\),二分出
std::set 中第一个 \(\ge
l\) 的位置,迭代器一直向右,修改沿途位置即可。
时间复杂度 \(O((n+m)\log n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
string s = string(n + 1, '*');
vector<array<int, 2>> op;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
op.push_back({x, y});
}
reverse(op.begin(), op.end());
vector<int> L(n + 2), R(n + 2);
set<int> t;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
L[i] = i - 1;
R[i] = i + 1;
t.insert(i);
}
auto del = [&] (int i) {
t.erase(i);
L[R[i]] = L[i];
R[L[i]] = R[i];
};
for (auto [p, l] : op) {
auto it = t.lower_bound(p);
if (it == t.end()) {
continue;
}
for (int i = *it; i <= p + l - 1; i = R[i]) {
if (i == p || i >= p + l - 3) {
s[i] = '>';
} else {
s[i] = '-';
}
del(i);
}
}
s = s.substr(1);
cout << s << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}D. 阿罗祖斯坦的桥
令 \(f[l][r],g[l][r]\) 分别表示在 \([l,r]\) 里建桥的最大数量和最小总长度,然后就是一个裸的区间 dp。
发现 \(w(l,r)=d\cdot \text{arcsin}(\frac{\text{dis}(l,r)}{d})\) 具有单调性(跨度大桥更长)和四边形不等式条件(交叉弱于包含),套一个四边形不等式优化的板子即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(n^2)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
constexpr double eps = 1e-10;
void solve() {
int n, d;
cin >> n >> d;
vector<int> a(n + 1), pre(n + 2);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
pre[i + 1] = pre[i] + a[i];
}
auto cost = [&] (int l, int r) -> double {
return 1.0 * d * asin(1.0 * (pre[r] - pre[l]) / d);
};
auto ok = [&] (int l, int r) -> bool {
return pre[r] - pre[l] <= d;
};
vector f(n + 2, vector<int>(n + 2)), m(f);
vector g(n + 2, vector<double>(n + 2));
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
m[i][i] = i;
if (i < n + 1) {
m[i][i + 1] = i;
}
}
for (int len = 2; len <= n + 1; len++) {
for (int i = 1; i + len - 1 <= n + 1; i++) {
int j = i + len - 1;
for (int k = m[i][j - 1]; k <= m[i + 1][j]; k++) {
if (f[i][k] + f[k][j] > f[i][j]) {
f[i][j] = f[i][k] + f[k][j];
g[i][j] = g[i][k] + g[k][j];
m[i][j] = k;
} else if (f[i][k] + f[k][j] == f[i][j]) {
if (g[i][k] + g[k][j] < g[i][j]) {
g[i][j] = g[i][k] + g[k][j];
m[i][j] = k;
}
}
}
if (ok(i, j)) {
f[i][j]++;
g[i][j] += cost(i, j);
}
}
}
cout << fixed << setprecision(12) << g[1][n + 1] << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}E. 猫猫城大选(困难版)
把问题 format 一下:给定一个变量 \(x\),初始为 \(0\),四种操作如下,问最终 \(x\) 的期望。
- \(x\leftarrow x+1\);
- \(x\leftarrow x-1\);
- \(\begin{cases}x\leftarrow x+1 &,x>0\\ x\leftarrow x-1&,x<0\\ p_i \text{ 概率}+1,(1-p_i)\text{ 概率}-1 &,x=0\end{cases}\)
- \(\begin{cases}x\leftarrow x-1 &,x>0\\ x\leftarrow x+1&,x<0\\ p_i \text{ 概率}+1,(1-p_i)\text{ 概率}-1 &,x=0\end{cases}\)
我们发现对于两个 \(x=0\) 的位置,其间进行的操作是确定的。
具体的,假设当前时刻操作前 \(x=0\) 且当前为第 \(3/4\) 类操作:若选择了 \(+1\),则直到下一次 \(x=0\) 之前 \(x\) 的值都是正的;若选择了 \(-1\),则直到下一次 \(x=0\) 之前 \(x\) 的值都是负的。
令 \(dp[i]\) 代表若第 \(i\) 个时刻操作前 \(x=0\),最后 \(x\) 的期望值。
从后向前转移,\(dp[i]=p[i]\cdot f(i)+(1-p[i])\cdot g(i)\)。
其中 \(f(i)/g(i)\) 代表第 \(i\) 时刻选择了 \(+1/-1\) 的情况下,之后的贡献。
以 \(f(i)\) 为例,若之后不存在 \(x=0\) 的时刻,\(f(i)=a_n-a_i+1\),其中 \(a_i\) 表示假定 \(x\) 一直 \(>0\),按顺序执行完第 \(i\) 次操作后的结果;否则设这 \(i\) 之后第一个 \(x=0\) 的时刻为 \(\text{nxt}\),有 \(f(i)=dp[\text{nxt+1}]\)。
找 \(\text{nxt}\) 的过程可以用线段树实现,时间复杂度 \(O(n\log n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
template<class T>
constexpr T power(T a, int b) {
T res = 1;
for (; b; b /= 2, a *= a)
if (b % 2) res *= a;
return res;
}
constexpr int mul(int a, int b, int p) {
int res = a * b % p;
if (res < 0) res += p;
return res;
}
template<int P>
struct MInt {
int x;
constexpr MInt() : x{} {}
constexpr MInt(int x) : x{norm(x % getMod())} {}
static int Mod;
constexpr static int getMod() { return P > 0 ? P : Mod;}
constexpr static void setMod(int Mod_) { Mod = Mod_;}
constexpr int norm(int x) const { if (x < 0) x += getMod(); if (x >= getMod()) x -= getMod(); return x;}
constexpr int val() const { return x;}
explicit constexpr operator int() const { return x;}
constexpr MInt operator-() const { MInt res; res.x = norm(getMod() - x); return res;}
constexpr MInt inv() const { assert(x != 0); return power(*this, getMod() - 2);}
constexpr MInt &operator*=(MInt rhs) & { x = mul(x, rhs.x, getMod()); return *this;}
constexpr MInt &operator+=(MInt rhs) & { x = norm(x + rhs.x); return *this;}
constexpr MInt &operator-=(MInt rhs) & { x = norm(x - rhs.x); return *this;}
constexpr MInt &operator/=(MInt rhs) & { return *this *= rhs.inv();}
friend constexpr MInt operator*(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) { MInt res = lhs; res *= rhs; return res;}
friend constexpr MInt operator+(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) { MInt res = lhs; res += rhs; return res;}
friend constexpr MInt operator-(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) { MInt res = lhs; res -= rhs; return res;}
friend constexpr MInt operator/(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) { MInt res = lhs; res /= rhs; return res;}
friend constexpr istream &operator>>(istream &is, MInt &a) { int v; is >> v; a = MInt(v); return is;}
friend constexpr ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const MInt &a) { return os << a.val();}
friend constexpr bool operator==(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) { return lhs.val() == rhs.val();}
friend constexpr bool operator!=(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) { return lhs.val() != rhs.val();}
};
template<>
int MInt<0>::Mod = 998244353;
template<int V, int P>
constexpr MInt<P> CInv = MInt<P>(V).inv();
constexpr int modp = 998244353;
using Z = MInt<modp>;
// template<int P>
// int MInt<P>::Mod = P;
// using Z = MInt<0>;
// Z::setMod(mod);
template<class Info>
struct SegmentTree {
int n;
vector<Info> tr;
SegmentTree(vector<int> &a) {
vector<Info> b(a.size());
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) {
b[i] = a[i];
}
init(b);
}
SegmentTree(vector<Info> &a) {
init(a);
}
void init(vector<Info> &a) {
n = a.size() - 1;
tr.assign((4 << __lg(n + 1)) + 5, Info());
build(1, 1, n, a);
}
#define ls (p << 1)
#define rs (p << 1 | 1)
void build(int p, int l, int r, vector<Info> &a) {
if (l == r) {
tr[p] = a[l];
return ;
}
int m = l + r >> 1;
build(ls, l, m, a);
build(rs, m + 1, r, a);
pushup(p);
}
void pushup(int p) {
tr[p] = tr[ls] + tr[rs];
}
void modify(int p, int l, int r, int pos, const Info &x) {
if (l == r) {
tr[p] = x;
return;
}
int m = l + r >> 1;
if (pos <= m) {
modify(ls, l, m, pos, x);
} else {
modify(rs, m + 1, r, pos, x);
}
pushup(p);
}
void modify(int pos, const Info &x) {
modify(1, 1, n, pos, x);
}
Info query(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr) {
if (l > qr || r < ql) {
return Info();
}
if (ql <= l && qr >= r) {
return tr[p];
}
int m = l + r >> 1;
return query(ls, l, m, ql, qr) + query(rs, m + 1, r, ql, qr);
}
Info query(int ql, int qr) {
return query(1, 1, n, ql, qr);
}
template<class F>
int findFirst(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, F &&pred) {
if (l > qr || r < ql) {
return -1;
}
if (ql <= l && qr >= r && !pred(tr[p])) {
return -1;
}
if (l == r) {
return l;
}
int m = l + r >> 1;
int res = findFirst(ls, l, m, ql, qr, pred);
if (res == -1) {
res = findFirst(rs, m + 1, r, ql, qr, pred);
}
return res;
}
template<class F>
int findFirst(int ql, int qr, F &&pred) {
if (ql > qr) {
return -1LL;
}
return findFirst(1, 1, n, ql, qr, pred);
}
template<class F>
int findLast(int p, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, F &&pred) {
if (l > qr || r < ql) {
return -1;
}
if (ql <= l && qr >= r && !pred(tr[p])) {
return -1;
}
if (l == r) {
return l;
}
int m = l + r >> 1;
int res = findLast(rs, m + 1, r, ql, qr, pred);
if (res == -1) {
res = findLast(ls, l, m, ql, qr, pred);
}
return res;
}
template<class F>
int findLast(int ql, int qr, F &&pred) {
if (ql > qr) {
return -1LL;
}
return findLast(1, 1, n, ql, qr, pred);
}
#undef ls
#undef rs
};
struct Info {
int mx = -inf;
int mn = inf;
Info() {}
Info(int x) {
mx = x;
mn = x;
}
};
Info operator+(const Info &a, const Info &b) {
Info c;
c.mx = max(a.mx, b.mx);
c.mn = min(a.mn, b.mn);
return c;
};
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> op(n + 1);
vector<Z> p(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> op[i] >> p[i];
}
vector<int> pa(n + 1), pb(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
pa[i] = pa[i - 1];
pb[i] = pb[i - 1];
if (op[i] == 1) {
pa[i]++;
pb[i]++;
} else if (op[i] == 2) {
pa[i]--;
pb[i]--;
} else if (op[i] == 3) {
pa[i]++;
pb[i]--;
} else {
pa[i]--;
pb[i]++;
}
}
SegmentTree<Info> sa(pa), sb(pb);
vector<Z> dp(n + 2);
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
auto getP = [&] () -> Z {
int pos = sa.findFirst(i + 1, n, [&] (auto A) {
return A.mn <= pa[i - 1] - 2 * (op[i] == 4);
});
if (pos == -1) {
return pa[n] - pa[i] + 1;
}
return dp[pos + 1];
};
auto getN = [&] () -> Z {
int pos = sb.findFirst(i + 1, n, [&] (auto A) {
return A.mx >= pb[i - 1] + 2 * (op[i] == 4);
});
if (pos == -1) {
return pb[n] - pb[i] - 1;
}
return dp[pos + 1];
};
dp[i] = p[i] * getP() + (1 - p[i]) * getN();
}
cout << dp[1] << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}F. 我知道你姓啥!
竖着看,相当于 \(m\) 个长为 \(n\) 的字符串。我们的目标是使这 \(m\) 个字符串互不相同。
一次添加操作相当于给每个字符串末尾添上 \(0\) 或 \(1\)。对于两个相同的字符串,在其末尾一个添 \(0\),一个添 \(1\),就能让它们不同。
用 std::map 统计出原来的 \(m\)
个字符串中出现次数最多的串,设其出现次数为 \(c\)。一次操作能让 \(c\leftarrow
\lceil\frac{c}{2}\rceil\),暴力模拟即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(nm\log m)\)。
Fun Fact:赛前出题人打算把 std::unordered_map
卡掉,但因为是签到,所以后来觉得没有必要就没卡。
Bonus:可以用 Trie 做到 \(O(nm)\)。
Fun Fact2:你可能会因为看到我 F 和 P 的题解和出题人题解一模一样,然后联想到我是出题人。这是错的,出题人只是不想写题解了就让我发一份上去。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<string> s(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> s[i];
}
map<string, int> mp;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
string t;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
t += s[i][j];
}
mp[t]++;
}
int mx = 0;
for (auto [_, x] : mp) {
mx = max(mx, x);
}
int ans = 0;
while (mx != 1) {
mx = (mx + 1) / 2;
ans++;
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}G. 猜数游戏
可以找到 \(\ge l\) 的最小的满足 \(x\bmod p=a\) 的位置 \(i\),判断 \(i\) 是否 \(\le r\)。
令 \(i=kp+a\ge l\),得 \(k\ge \lceil\frac{l-a}{p} \rceil\),故 \(i=\lceil\frac{l-a}{p}\rceil p+a\)。
时间复杂度 \(O(1)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int a, p, l, r;
cin >> a >> p >> l >> r;
int x = (l - a + p - 1) / p * p + a;
if (x <= r) {
cout << "Yes " << x << "\n";
} else {
cout << "No\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}H. 独立事件
(upd on 03.31)
当 \(P(A)=0/1\) 时,答案是 trivial 的。否则,存在以下推导: \[ \begin{align} &P(A)P(B_I)=P(A\cap B_I)\\ \rightarrow\ &P(B_I\mid A)=P(B_I\mid \overline{A}) \\ \rightarrow\ &\frac{P(AB_I)}{P(A)}=\frac{P(\overline{A}B_I)}{P(\overline{A})} \end{align} \]
记 \(f[i]\) 表示在事件 \(A\) 对应的集合中选出元素总和为 \(i\) 的方案数。
记 \(g[i]\) 表示在事件 \(\overline{A}\) 对应的集合中选出元素总和为 \(i\) 的方案数。
那么答案是: \[ \sum_{i=0}^{1000}\sum_{j=0}^{1000}f[i]\cdot g[j]\cdot [\frac{i}{P(A)}=\frac{j}{P(\overline{A})}] \]
其中,\(P(A)=\dfrac{\sum\limits_{i=1}^{k}a_i}{1000}\),\(P(\overline{A})=1-P(A)\)。\(f[i]\) 和 \(g[i]\) 可以分别用 \(01\) 背包求出。
时间复杂度 \(O(nw+w^2)\),\(w\) 为值域。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
template<class T>
constexpr T power(T a, int b) {
T res = 1;
for (; b; b /= 2, a *= a)
if (b % 2) res *= a;
return res;
}
constexpr int mul(int a, int b, int p) {
int res = a * b % p;
if (res < 0) res += p;
return res;
}
template<int P>
struct MInt {
int x;
constexpr MInt() : x{} {}
constexpr MInt(int x) : x{norm(x % getMod())} {}
static int Mod;
constexpr static int getMod() { return P > 0 ? P : Mod;}
constexpr static void setMod(int Mod_) { Mod = Mod_;}
constexpr int norm(int x) const { if (x < 0) x += getMod(); if (x >= getMod()) x -= getMod(); return x;}
constexpr int val() const { return x;}
explicit constexpr operator int() const { return x;}
constexpr MInt operator-() const { MInt res; res.x = norm(getMod() - x); return res;}
constexpr MInt inv() const { assert(x != 0); return power(*this, getMod() - 2);}
constexpr MInt &operator*=(MInt rhs) & { x = mul(x, rhs.x, getMod()); return *this;}
constexpr MInt &operator+=(MInt rhs) & { x = norm(x + rhs.x); return *this;}
constexpr MInt &operator-=(MInt rhs) & { x = norm(x - rhs.x); return *this;}
constexpr MInt &operator/=(MInt rhs) & { return *this *= rhs.inv();}
friend constexpr MInt operator*(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) { MInt res = lhs; res *= rhs; return res;}
friend constexpr MInt operator+(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) { MInt res = lhs; res += rhs; return res;}
friend constexpr MInt operator-(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) { MInt res = lhs; res -= rhs; return res;}
friend constexpr MInt operator/(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) { MInt res = lhs; res /= rhs; return res;}
friend constexpr istream &operator>>(istream &is, MInt &a) { int v; is >> v; a = MInt(v); return is;}
friend constexpr ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const MInt &a) { return os << a.val();}
friend constexpr bool operator==(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) { return lhs.val() == rhs.val();}
friend constexpr bool operator!=(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) { return lhs.val() != rhs.val();}
};
template<>
int MInt<0>::Mod = 998244353;
template<int V, int P>
constexpr MInt<P> CInv = MInt<P>(V).inv();
constexpr int modp = 998244353;
using Z = MInt<modp>;
// template<int P>
// int MInt<P>::Mod = P;
// using Z = MInt<0>;
// Z::setMod(mod);
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
int S = 0, T = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i <= k) {
S += a[i];
} else {
T += a[i];
}
}
vector<Z> f(S + 1), g(T + 1);
f[0] = 1;
g[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
for (int j = S; j >= a[i]; j--) {
f[j] += f[j - a[i]];
}
}
for (int i = k + 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = T; j >= a[i]; j--) {
g[j] += g[j - a[i]];
}
}
Z ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= S; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= T; j++) {
if (i * T == j * S) {
ans += f[i] * g[j];
}
}
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
fre(test);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}I. 圆与直线交点
因为不能出现浮点数,所以整个计算过程要保留分数形式。
python 的 fraction 是简单的,能帮你自动约分,四则运算也很方便。C++ 要么手写分数类,要么另谋出路。
使用外心坐标公式求出三角形的外心坐标 \((X,Y)\)。
任取三点之一,坐标公式计算其与外心的距离,得到半径的平方 \(R^2\)。
由点到直线的距离公式,有: \[ d=\frac{|(X-P_x)V_y-(Y-P_y)V_x|}{\sqrt{V_x^2+V_y^2}} \]
移项,两边平方,得到相切的充要条件 \([(X-P_x)V_y-(Y-P_y)V_x]^2=R^2(V_x^2+V_y^2)\)。
相交和相离改等号为不等号即可。
时间复杂度 \(O(1)\)。
from fractions import *
def solve():
x1, y1 = map(int, input().split())
x2, y2 = map(int, input().split())
x3, y3 = map(int, input().split())
Px, Py = map(int, input().split())
Vx, Vy = map(int, input().split())
A1 = (x2 - x1) * 2
B1 = (y2 - y1) * 2
C1 = x2 * x2 + y2 * y2 - x1 * x1 - y1 * y1
A2 = (x3 - x2) * 2
B2 = (y3 - y2) * 2
C2 = x3 * x3 + y3 * y3 - x2 * x2 - y2 * y2
X = Fraction(C1 * B2 - C2 * B1, A1 * B2 - A2 * B1)
Y = Fraction(A1 * C2 - A2 * C1, A1 * B2 - A2 * B1)
dx = Fraction(x1, 1) - X
dy = Fraction(y1, 1) - Y
R2 = dx * dx + dy * dy
V_sq = Vx * Vx + Vy * Vy
goal = R2 * V_sq
t1 = (X - Fraction(Px, 1)) * Fraction(Vy, 1)
t2 = (Y - Fraction(Py, 1)) * Fraction(Vx, 1)
Z = t1 - t2
Z = Z * Z;
O = Z - goal
if O == Fraction(0):
print("Or")
elif O > Fraction(0):
print("No")
else:
print("Yes")
def main():
T = int(input())
for _ in range(T):
solve()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()J. 创建用户
按照题意模拟即可。
C++ 使用 getline 读入一整行。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
string tmp;
getline(cin, tmp);
int n = stoll(tmp);
map<string, int> mp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
string s;
getline(cin, s);
string t;
int lst = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < s.size(); j++) {
if (s[j] == ' ') {
if (lst == -1) {
t += s.substr(0, j);
} else {
t += s[lst + 1];
}
lst = j;
}
}
t += s[lst + 1];
int tot = ++mp[t] - 1;
if (tot > 0) {
t += to_string(tot);
}
cout << t << "\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}K. 哲学之门
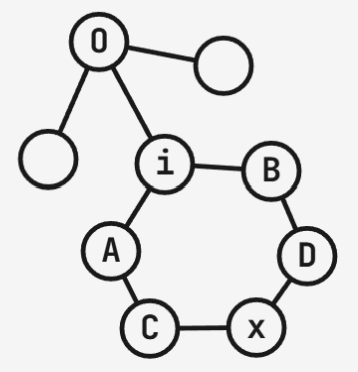
想好怎么枚举是重要的。
我的做法是枚举三度点 \(i\),遍历 \(i\) 的邻接点,让每个邻居都尝试作为 \(O\),这样 \(A,B\) 就是另外两个邻居。
再枚举 \(A\) 的邻居 \(C\),\(B\) 的邻居 \(D\)。将 \(C\) 的邻居放进一个容器里,然后枚举 \(D\) 的邻居,若和 \(C\) 共有就是 \(x\)。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
int ans = 0;
vector<int> vis(n + 1);
auto get = [&] (int i, int A, int B, int O) {
if (adj[O].size() < 3) {
return ;
}
for (auto x : adj[O]) {
if (x == A || x == B) {
return ;
}
}
vector<int> b {O, A, B};
for (auto x : adj[O]) {
vis[x] = true;
b.push_back(x);
}
vis[O] = true;
vis[A] = true;
vis[B] = true;
set<vector<int>> res;
for (auto C : adj[A]) {
if (vis[C]) {
continue;
}
vis[C] = true;
set<int> s;
for (auto x : adj[C]) {
s.insert(x);
}
for (auto D : adj[B]) {
if (vis[D]) {
continue;
}
vis[D] = true;
for (auto x : adj[D]) {
if (vis[x]) {
continue;
}
if (s.count(x)) {
ans++;
}
}
vis[D] = false;
}
vis[C] = false;
}
for (auto x : b) {
vis[x] = false;
}
};
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (adj[i].size() < 3) {
continue;
}
get(i, adj[i][0], adj[i][1], adj[i][2]);
get(i, adj[i][1], adj[i][2], adj[i][0]);
get(i, adj[i][0], adj[i][2], adj[i][1]);
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}M. 前兜车一转后兜车一转
选定的前缀和后缀可以是不交、恰交、相交,每种情况都讨论一下。
恰交是简单的。
不交的话预处理出 \(suf[i]\) 代表翻转 \(i\sim n\) 中的任一后缀的最大收益。接着枚举前缀,另一段的最大贡献就能查表了。
相交的话是类似的。枚举 \(i\) 代表翻转前缀 \(1\sim i\),此时要选定一个 \(j\in [1,i]\) 然后翻转后缀 \(j\sim n\) 并让贡献最大。推一下式子,这等价于找到让 \(|a_j-a_n|-|a_j-a_{j-1}|\) 最大的 \(j\),一样可以预处理出一个前缀和。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
auto f = [&] (int i, int j) {
return abs(a[i] - a[j]);
};
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
res += f(i, i + 1);
}
int ans = res;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
ans = max(ans, res - f(i, i + 1) + f(1, n));
}
vector<int> suf(n + 2);
for (int i = n; i > 1; i--) {
suf[i] = max(suf[i + 1], -f(i, i - 1) + f(n, i - 1));
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 2; i++) {
ans = max(ans, res - f(i, i + 1) + f(1, i + 1) + suf[i + 2]);
}
vector<int> pre(n + 1, 0);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
pre[i] = max(pre[i - 1], -f(i - 1, i) + f(i, n));
}
for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) {
ans = max(ans, res - f(i, i + 1) + f(1, i + 1) + pre[i]);
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}N. 幸运之环 II
用 dfs 找出这棵基环树的环。
找到环上最小的点 \(x\),再看一下 \(x\) 沿环上两个方向的邻居,哪个邻居小就往哪个方向输出。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
adj[y].push_back(x);
}
vector<int> cir;
{
vector<int> vis(n + 1), f(n + 1), ins(n + 1);
auto dfs = [&] (auto self, int x, int fa) -> void {
vis[x] = true;
ins[x] = true;
f[x] = fa;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (y == fa) {
continue;
}
if (ins[y] && cir.empty()) {
for (int i = x; i != y; i = f[i]) {
cir.push_back(i);
}
cir.push_back(y);
}
if (vis[y]) {
continue;
}
self(self, y, x);
}
ins[x] = false;
};
dfs(dfs, 1, 0);
}
int len = cir.size();
cout << len << " ";
cir.insert(cir.end(), cir.begin(), cir.end());
int p = -1, mn = inf;
for (int i = 1; i < cir.size() - 1; i++) {
if (cir[i] < mn) {
mn = cir[i];
p = i;
}
}
cout << cir[p] << " ";
if (cir[p - 1] < cir[p + 1]) {
int t = p, tot = 1;
while (tot < len) {
t--;
if (t < 0) {
t = cir.size() - 1;
}
cout << cir[t] << " ";
tot++;
}
} else {
int t = p, tot = 1;
while (tot < len) {
t++;
if (t == cir.size()) {
t = 0;
}
cout << cir[t] << " ";
tot++;
}
}
cout << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}O. 不走回头路
在一个强连通分量内,所有的点都可以互相到达。即同一个 SCC 内的景点可以任意安排游览顺序。
缩点,得到一个 DAG。若要能遍历所有的点,这个 DAG 必然是一条链。
在 DAG 上 dp(令 \(f[x]\) 代表以 \(x\) 结尾的链的长度的最大值),判断是否存在一个点 \(f[x]=cnt\) 即可(\(cnt\) 是缩点后的图的顶点数)。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
FunFact:一个误区是只判断缩点后的图 “恰有一个入度为 \(0\) 的点” 和 “恰有一个出度为 \(0\)” 的点,这是错误的,反例是 \(1\to 2\to 3,\ 1\to 4\to3\)。赛时的数据有这个缺陷(包括其它一些没缩点乱搞度数的做法也过了),磕头 \(+1\)。补题链接里的数据是更新过的。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<vector<int>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
adj[x].push_back(y);
}
vector<int> dfn(n + 1), low(n + 1), stk(n + 1), c(n + 1);
vector<bool> vis(n + 1);
vector<vector<int>> scc(n + 1);
int tim = 0, top = 0, cnt = 0;
function<void(int)> tarjan = [&](int x) {
dfn[x] = low[x] = ++tim;
vis[x] = true;
stk[++top] = x;
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (!dfn[y]) {
tarjan(y);
low[x] = min(low[x], low[y]);
} else if (vis[y]) {
low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[y]);
}
}
if (dfn[x] == low[x]) {
int now; ++cnt;
do {
now = stk[top--];
vis[now] = false;
c[now] = cnt;
scc[cnt].push_back(now);
} while(x != now);
}
};
vector<set<int>> Adj(n + 1);
auto shrinkPoint = [&]() {
for (int x = 1; x <= n; x++) {
for (auto y : adj[x]) {
if (c[x] == c[y]) continue;
Adj[c[x]].insert(c[y]);
}
}
};
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!dfn[i]) {
tarjan(i);
}
}
shrinkPoint();
vector<int> rd(cnt + 1);
for (int x = 1; x <= cnt; x++) {
for (auto y : Adj[x]) {
rd[y]++;
}
}
queue<int> q;
vector<int> f(cnt + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
if (rd[i] == 0) {
q.push(i);
f[i] = 1;
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
for (auto y : Adj[x]) {
f[y] = max(f[y], f[x] + 1);
if (--rd[y] == 0) {
q.push(y);
}
}
}
if (*max_element(f.begin(), f.end()) == cnt) {
cout << "Yes\n";
} else {
cout << "No\n";
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}P. 相同字符
预处理 \(pre[i]\) 代表从前向后在 \(a\) 中匹配上 \(b\) 中的字符的个数,即 \(a[0..i]\) 能匹配上 \(b[0..(pre[i]-1)]\)。
预处理 \(suf[i]\) 代表从后向前在 \(a\) 中匹配上 \(b\) 中的字符的个数,即 \(a[i..n-1]\) 能匹配上 \(b[(m-suf[i])..m-1]\)。
上述的匹配不区分大小写。
若 \(a\) 中无大写字母,判断 \(\max(suf[0],pre[n-1])=m\) 是否成立即可。
否则枚举 \(b\) 中每一个与大写字母相同的位置 \(i\),判断 \(pre[i-1] \ge i\) 和 \(suf[i+1]\ge m-i-1\) 是否成立。
时间复杂度 \(O(n)\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
string a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
int n = a.size();
int m = b.size();
int pos = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (isupper(a[i])) {
pos = i;
a[i] = tolower(a[i]);
}
}
vector<int> pre(n), suf(n);
pre[0] = (a[0] == b[0]);
suf[n - 1] = (a.back() == b.back());
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
pre[i] = pre[i - 1];
if (pre[i] < m) {
pre[i] += (b[pre[i]] == a[i]);
}
}
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
suf[i] = suf[i + 1];
if (suf[i] < m) {
suf[i] += (b[m - suf[i] - 1] == a[i]);
}
}
if (pos == -1) {
if (max(suf[0], pre[n - 1]) == m) {
cout << "Yes\n";
return ;
}
} else {
int L = (pos == 0 ? 0 : pre[pos - 1]);
int R = (pos == n - 1 ? 0 : suf[pos + 1]);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (b[i] == a[pos]) {
if (L >= i && R >= m - i - 1) {
cout << "Yes\n";
return;
}
}
}
}
cout << "No\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}Q. 校车
数据范围识状压。将给定的 \(w\) 个路口称作关键点。
令 \(dp[S][i]\) 代表从起点出发经过了状态 \(S\) 中的点,最终到达关键点 \(i\) 所需的路程。
初态:\(dp[\{i\}][i]=\text{dis}(1,p_i)\)。
转移:\(dp[S\cup \{j\}][j]=\min(dp[S\cup \{j\}][j],dp[S][i]+\text{dis}(p_i,p_j))\),其中 \(i\in S,j\not\in S\)。
那么经过 \(S\) 中的点再返回起点的最短距离 \(f[S]=\min\limits_{i\in S}(dp[S][i]+\text{dis}(1,p_i))\)。
二分答案,设二分出的答案是 \(mid\),问题转化为判断是否能用不超过 \(k\) 条 \(f[S]\le mid\) 的路径覆盖所有 \(w\) 个关键点。
设 \(g[S]\) 表示覆盖 \(S\) 中的点需要的最小路径条数,判定就是 \(g[\{1,2,\ldots,w\}]\le k\)。
初态:\(g[\varnothing]=0\)。
转移:\(g[S\cup T]=\min(g[S\cup T],g[S]+1)\),其中 \(f[T]\le mid\)。
注意:转移的时候不需要对每一个 \(S\) 都枚举所有的 \(T\),那样是 \(O(4^w)\)。只需要 \(O(3^w)\) 枚举所有所有状态的子状态就行。
时间复杂度 \(O(wm\log m+w^22^w+20\cdot 3^{w})\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fre(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin); freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define ck(x) { cout << "check " << x << "\n"; cout.flush();}
#define int long long
#define double long double
#define inf 0x3fffffffffffffff
//-------------- templates above --------------
void solve() {
int n, m, w, k;
cin >> n >> m >> w >> k;
vector<vector<array<int, 2>>> adj(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x, y, w;
cin >> x >> y >> w;
adj[x].push_back({y, w});
adj[y].push_back({x, w});
}
vector<int> p(w);
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) {
cin >> p[i];
}
vector<int> dis(n + 1);
vector d(w, vector<int>(w));
{
auto dijkstra = [&] (int S) {
vector<int> dis(n + 1, inf);
vector<bool> vis(n + 1, false);
#define P pair<int, int>
priority_queue<P, vector<P>, greater<P>> Q;
Q.push({0, S});
dis[S] = 0;
while (!Q.empty()) {
auto [dist, x] = Q.top();
Q.pop();
if (vis[x]) {
continue;
}
vis[x] = true;
for (auto [y, w] : adj[x]) {
if (dis[y] > dist + w) {
dis[y] = dist + w;
Q.push({dis[y], y});
}
}
}
return dis;
};
dis = dijkstra(1);
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) {
auto A = dijkstra(p[i]);
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
d[i][j] = A[p[j]];
}
}
}
vector dp(1 << w, vector<int>(w, inf));
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) {
dp[1 << i][i] = dis[p[i]];
}
for (int S = 0; S < (1 << w); S++) {
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) {
if ((S >> i & 1) == 0 || dp[S][i] == inf) {
continue;
}
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
if ((S >> j & 1) == 0) {
int nS = S | (1 << j);
if (d[i][j] < 1e10) {
dp[nS][j] = min(dp[nS][j], dp[S][i] + d[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
}
vector<int> f(1 << w, inf);
int mx = 0;
for (int S = 0; S < (1 << w); S++) {
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++) {
if ((S >> i & 1) && dp[S][i] != inf) {
f[S] = min(f[S], dp[S][i] + dis[p[i]]);
}
}
if (f[S] < 1e10) {
mx = max(mx, f[S]);
}
}
auto check = [&] (int mid) {
vector<int> g(1 << w, inf);
g[0] = 0;
for (int S = 0; S < (1 << w); S++) {
for (int T = S; ; T = (T - 1) & S) {
if (f[S ^ T] <= mid) {
g[S] = min(g[S], g[T] + 1);
}
if (T == 0) {
break;
}
}
}
return g[(1 << w) - 1] <= k;
};
int l = 1, r = mx, ans = -1;
while (l <= r) {
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (check(mid)) {
ans = mid;
r = mid - 1;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
cout << ans << "\n";
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T = 1;
while (T--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}